![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
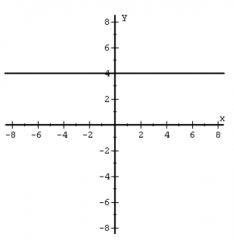
|
Constant Function f(x) = a |
|
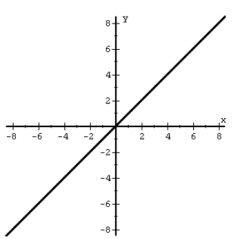
|
Linear Function f(x) = x |
|
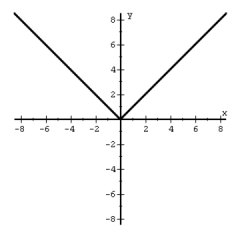
|
Absolute Value Function, f(x) = |x| |
|
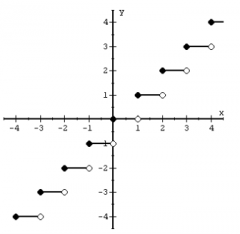
|
Integer Function (Step function) f(x) = int(x) |
|
|
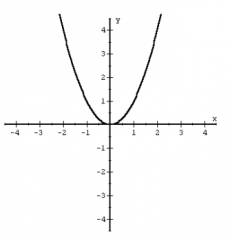
Quadratic Function (Parabola) f(x) = x^2 |
|
|
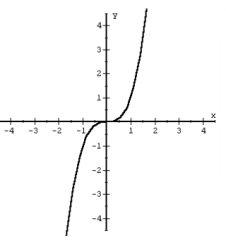
Cubic Function f(x) = x^3 |
|
|
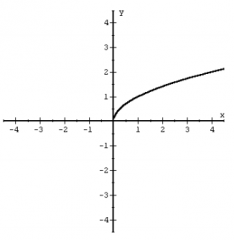
Square Root Function f(x) = sqrt(x) |
|
|
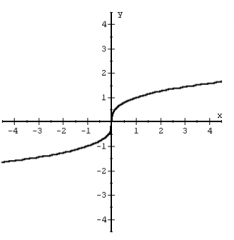
Cube Root Function f(x) = cbrt(x) |
|
|
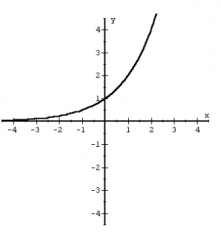
Exponential Function f(x) = e^x |
|
|
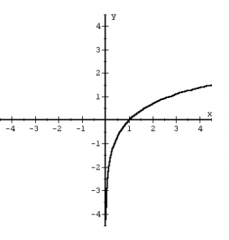
Logarithmic Function f(x) = ln(x) |
|
|
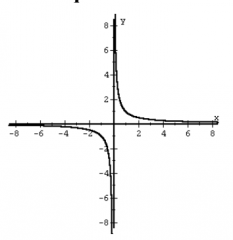
Reciprocal Function (simplest Rational) f(x) = 1/x |
|
|
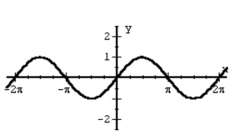
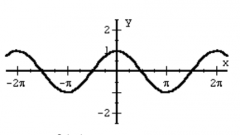
Sine Function f(x) = sin(x) |
|
|
Cosine Function f(x) = cos(x) |
|
|
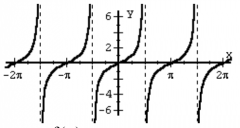
Tangent Function f(x) = tan(x) |
|
|
Three terms for the point/number where a function crosses the x-axis. |
Root, Zero, x-intercept. |
|
|
Standard Equation of a Circle |
(x-h)^2 + (y-k)^2 = r^2 |
|
|
point slope form of a line |
y - y1 = m (x - x1) |
|
|
Domain Restrictions ( what are they? when do they happen?) |
number that can't be inputted in a function happen when #/0 or sqrt(-#) |
|
|
Odd Functions (What does its graph look like? How can we check algebraically?) |
Origin Symmetry Check: plug -x and -y in , should get same function. |
|
|
Even Functions (What does its graph look like? How can we check algebraic |
Y-axis symmetry Check: plug -x for x, should get same function. |
|
|
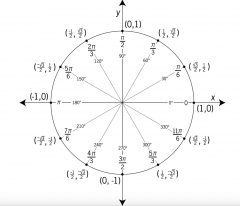
Draw the first quadrant of the unit circle. |
|
|
|
sin (0) |
0 |
|
|
cos(0) |
1 |
|
|
sin(pi/3) |
sqrt(3)/2 |
|
|
cos(pi/6) |
sqrt(3)/2 |
|
|
sin(pi/4) |
sqrt(2)/2 |
|
|
cos(pi/3) |
1/2 |
|
|
What is a reference angle? |
Terminal side of an angle with respect to the horizontal axis. |
|
|
sin (a +- b) = |
sin(a)cos(b) +- sin(b)cos(a) |
|
|
cos(a+-b) = |
cos(a)cos(b) -+ sin(a)sin(b) *** opposite sign *** |
|
|
tan(a+-b)= |
( tan(a) +- tan(b)) / ( 1-+ tan(a)tan(b) ) *** same sign on top, opposite on bottom *** |
|
|
Trig Pythagorean Identities |
sin^2 + cos^2 = 1 1 + tan^2 = sec^2 1 + cos^2 = csc^2 |
|
|
How do you find the amplitude of a sin/cos function written in standard form? What does this number tell you about the graph? |
Standard Forms: y = a sin(bx+c) y = a cos(bx+c) Amplitude (height of a wave) = |a| |
|
|
How do you find the period of a sin/cos function written in standard form? What does this number tell you about the graph? |
Standard Forms: y = a sin(bx+c) y = a cos(bx+c) Amplitude (length of a wave) = 2pi/b |
|
|
arcsin(sqrt(2)/2) = |
pi/4, 3pi/4, 9pi/4, 11pi/4, ... etc |
|
|
arccos(0) = |
pi/2, 3pi/2, 5pi/2, etc.... |
|
|
arctan(1) = |
pi/4, 5pi/4, 9pi/4, etc.... |
|
|
Law of Sines |
sin(a)/ A = sin(b)/ B = sin(C)/C |
|
|
Law of Cosines |
c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2abcos(c) |
|
|
How do you write and what is the meaning of.... the limit of f(x) as x approaches a. |
What happens to the y-values of this function when x gets close to the value a? |

