![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
84 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
list blood loss volumes for the 4 classes of shock
|
I: <750
II: 750-1500 III: 1500-2000 IV: >2000ml |
|
|
scoring for the motor part of GCS
|
I: no movement
II: extensor posturing III: flexor posturing IV: withdraws to pain V: localizes to pain VI: perposeful movement |
|
|
Canadian CT head rule
|
GCS <15 2h after injury
suspected open or depressed skull fracture any sign of basal skull fracture vomiting >= 2 episodes age >65 preimpact amnesia >30 min dangerous mechanism (ped vs mvc, ejection, fall >3ft) |
|
|
Canadian CT neck rule
|
1. None of :
age >65 parasthesias mechanism (>3ft/5stair, axial load, >100km/h, roll over/ejection, ATV) 2. plus one of the following: ambulatory at any time, delayed onset of pain, simple rearend MVC 3. then check neck rotation |
|
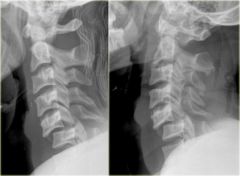
type of fracture and mechanism
|
Jefferson Fracture (burst of C1) from an axial load
note the overhanging edges of C1 on C2 |
|
name and mechanism
|
Bilateral facet dislocation
flexion injury see greater than 50% anterior dislocation of vertebrae Unstable injuruy |
|
|
types of odontoid fractures
|
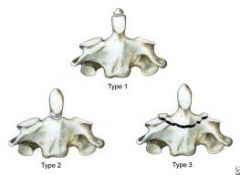
I: stable
II: unstable III: unstable |
|
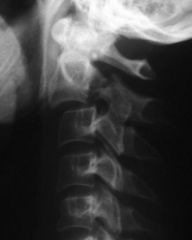
name and mechanism
|
Hangman fracture
C2 bilateral pars interarticularis fractures caused by hyperextension |
|
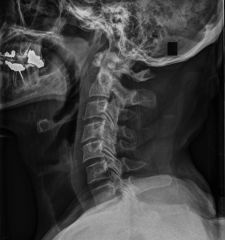
name and mechanism
|
Extension or Flexion teardrop fracture
Unstable |
|
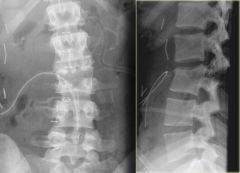
name and mechanism
|
flexion-distraction (Chance fracture)
Horizontal fracture though middle and posterior columns most commonly from flexion in MVC wearing lap belt |
|
|
Anterior Cord Syndrome
|
Mechanism: Flexion of cervical v. or direct anterior cord injury
Findings: paralysis, loss of pain and temp, preserved proprioception and vibration |
|
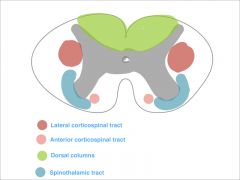
name and function of each tract
|
green- dorsal column: proprioception, vibration,
red- lateral corticospinal tract: motor function blue- spinothalamic tract: pain, temperature, touch |
|
|
Central Cord Syndrome
|
Mechanism: typically elderly hyperextension injury
Findings: Motor impairement in upper>lower limbs, and also variable touch, temperature, bladder dysfunction |
|
|
Brown-SeQuard Syndrome
|
Hemisection of cord
Findings: Ipsilateral loss of motor, vibration, sensation and contralateral loss of pain and temp |
|
|
Chest tube output requiring thoracotomy
|
>1500ml immediately or >200ml/h x 2 hr
|
|
|
Beck's Triad
|
1. Muffled heart sounds
2. JVD 3. Hypotension |
|
|
ED thoracotomy indications
|
1. Arrest within 15min of presentation after penetrating chest trauma
2. SBP <50 after fluids with pen chest trauma 3. |
|
|
P/E for posterior hip dislocation
|
shortened, internally rotated, and adducted
|
|
|
Young and Burgess Pelvic fractures
|
1. Lateral compression: fracture rami and/or iliac wings
2. Ant/Post compression: opens pubic symphysis and if opens SI joints called "open book" 3. Vertical Shear: fall from height causes shear of SI joint |
|
|
Penile fracture
|
fracture of corpus cavernosum
Tx: surgical evacuation and repair tunica albugin |
|
|
Neck zones
|
I: clavicles to cricoid
II: cricoid to angle of mandible III: angle of mandible to base of skull |
|
|
Penetrating neck trauma: hard and soft signs
|
Hard: expanding hematoma, pulsatile bleeding, air bubbling from wound, hematemesis, bruit, stridor, decreased/absent radial pulse
|
|
|
compartments of the lower leg
|
Anterior
Superficial Posterior Deep Posterior Lateral |
|
|
Findings of compartment syndrome
|
Pressure (tense compartment)
Pallor Pulselesness (late) Pain out of proportion Pain with passive stretch parasthesias |
|
|
Normal compartment pressures:
|
Normal 0-10mm Hg
>20 mm Hg is abnormal |
|
|
Urine findings of rhabdomyolysis
|
blood on dip and minimal/no RBCs on analysis
|
|
|
Parkland Formula
|
4ml x %BSA x Wt in kg = fluids over 24hrs
(only count 2nd and 3rd degree) give half in first 8hrs |
|
|
degrees of burns
|
1st: epidermis, red, no blisters
2nd superficial: partial dermis, blistering, red, painful, blanching 2nd deep: partial dermis, blistering, non-blanching, red to pail white, painful 3rd: full dermis, charred, black or white, non painful, leathery, impaired touch sensation 4th: into subcutaneous, bone, muscle |
|
|
Acid burns
|
Coagulative necrosis: causes an eschar barrier so burns less deep
|
|
|
Alkali burns
|
Liquefactive necrosis: no barrier formed and burns can be deeper than acids
|
|
|
Elbow imaging lines?
Radiocapitellar line |
Anterior humeral line: should pass thought middle 1/3 of capittellum
Line from radius intersects middle 1/3 of capitellum |
|
|
Monteggia fracture
|
Ulnar shaft fracture with radial head dislocation
|
|
|
Galeazzi fracture
|
radial shaft fracture with disruption of DRUJ
*unstable and requires ORIF |
|
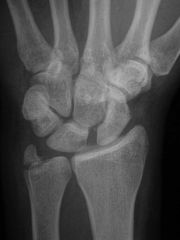
injury and x ray finding
|
scapholunate dissociation
Terry Thomas sign (widening of scaphoid-lunate space) |
|
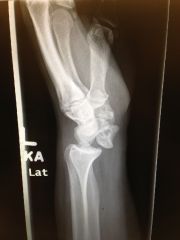
injury and xray finding?
|
Lunate dislocation
spilled tea cup sign |
|
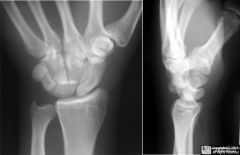
Injury and x ray findings?
|
Perilunate dislocation
Lunate properly aligned with radius but capitate not aligned with lunate |
|
|
Ulnar collateral ligament injury. Findings?
|
From valgus stress to 1st phalanx
Tender over proximal 1st phalanx laxity of 1st phalanx to valgus stress |
|
|
acceptable volar angulation of metacarpal neck fractures
|
5th: <40 degrees
4th: <30 degrees 2nd and 3rd: <10 degrees (2nd and 3rd are less mobile) |
|
|
Flexor digitorum profundus avulsion injury findings and treatment?
|
unable to flex DIP with PIP and MCP held in extension.
Requires splinting and ortho referral for surgery |
|
|
Extensor tendon rupture findings and treatment
|
unable to extend DIP
6 weeks of splint in extension |
|
|
Neer Classification
|
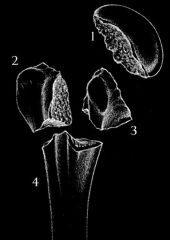
Proximal humerus fractures
4 parts: greater tubercle, humeral head, lesser tubercle, shaft count part: separation by 1cm or angulation of >45 degrees |
|
|
Ottawa Knee rules
|
X ray if any of the following:
1. Unable to bear weight x 4 steps 2. Tender only over patella 3. tender over fibular head 4. age >55 5. Inability to flex to 90 degrees |
|
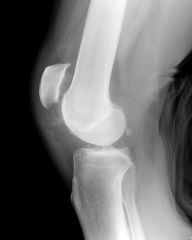
Inury?
|
high riding patella indicates patellar tendon rupture.
See suprapatellar gap and low riding patella with quadriceps rupture |
|
|
Lachman's test?
|
Tests ACL
anterior forse with knee in 30 degrees flexion more sensitive than anterior drawer |
|
|
injury to knee from rapid deceleration and pivoting (ie. soccer)
|
ACL
|
|
|
Ottawa Ankle rules
|
X ray if malleolar pain and any of:
1. Pain at base of 5th MT 2. Pain over navicular 3. Inability to wt br 4 steps at injury and in ED 4. Pain to posterior 6cm or tip of either malleoli |
|
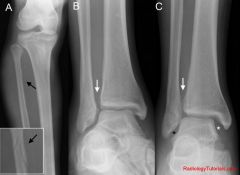
Maissoneuve fracture? and Tx?
|
Eversion injury
Medial malleolus # or deltoid disruption with disruption of syndesmosis and proximal fibula # ORIF |
|
|
Normal Bohler's angle?
|
<20 degrees
if less consider calcaneus fracture |
|
|
Lisfranc injury
|
Disruption of ligament between 1st cuneiform and 2nd metatarsal.
Look for gap between 1st and 2nd or 2nd and 3rd metatarsal or X ray. Requires ORIF. |
|
|
Most common pathogen in osteomyelitis?
|
Staph aureus
|
|
|
Microscopic findings of gout? crystals made of? Treatment?
|
Needle shaped negatively birefringent crystals.
Uric Acid Treat with NSAIDs +/- colchicine |
|
|
Pseudogout findings on microscopy? Crystals made of?
|
rhomboid shaped positively birefringent crystals.
Calcium pyrophosphate |
|
|
Synovial fluid findings in septic joint?
|
WBC> 50 000
>90% neutrophils gram stain + in only about 50% |
|
|
causes of septic joint?
|
Staph aureus most common.
Consider N. Gonnorrhea in sexually active |
|
|
tests for carpal tunnel
|
Phalen's test: symptoms with hyperflexion of wrists for 90 seconds
Tinnel's sign: median nerve parasthesias with tapping tunnel |
|
|
De Quervan's Tenosynovitis pathology, testing, Tx?
|
Synovitis of abductor pollicis longus and the extensor pollicis brevis.
Finklesteins test: pain at radial styloid with passive ulnar deviation wrist with hand in fist and thumb inside RICE, NSAIDS, +/- steroid injection |
|
|
Flexor Tenosynovitis findings?
|
Flexed posture of digit
Pain with passive extension diffuse swelling pain with palpation of flexor sheath |
|
|
Supracondylar humeral # classification
|
Gartland classification
I: anterior cortex broken but no angulation/displacement II: anterior cortex broken, angulate posteriorly with posterior cortex intact III: completely displaced (no cortex intact) |
|
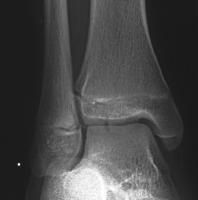
fracture and treatment
|
Tillaux fracture:
A pediatric Salter-Haris type 3 to the anterior lateral aspect of the tibia. Requires ORIF |
|
|
Dequervain's tenosynovitis
|
inflammation of extensor tendons of thumb
pain with flexion (finklesteins test) Tx: steroid injection |
|
|
Flexor Tenosynovitis signs?
|
swelling of finger
pain with passive extension pain with proximal palpation flexor tendon (palm/wrist) hand held in flexion |
|
|
Spinal stenosis
|
caused by narrowing of lumbar canal
pain with sitting wknss, parasthesias Tx: PT +/- surgery |
|
|
Central Cord syndrome
|
upper limbr>lower limb wknss
|
|
|
Anterior cord syndrome?
|
Impaired pain and temp
intact vibration, and proprioception |
|
|
Brown Sequered syndrome
|
penetrating partial transection of cord
contralateral sensory deficits and ipsilateral motor deficits |
|
|
Tilleau fracture?
|
Salter-Harris III of the medial aspect of distal tibia
|
|
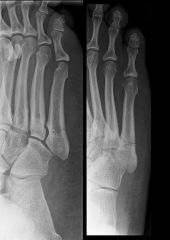
|
jones fracture
Stress fracture of base of 5th cast vs surgery |
|
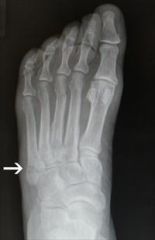
|
Dancer's fracture
avulsion of base of the 5th during inversion injury Tx: cast |
|
|
Gout
|
Uric Acid
negatively birefringent crystals needle like crystals Tx: NSAIDs |
|
|
Pseudogout
|
Calcium pyrophosphate
positively birefringent rhomboid crystals Tx: NSAIDS |
|
|
polymyositis
|
proximal muscle pain and weakness
if there is a rash- dermatomyositis elevated CK |
|
|
Polymyalgia Rheumatica
|
Fever, pain in neck, shoulders, hips
associated with temporal arteritis elevated ESR, CRP Tx: steroids |
|
|
SLE diagnostic test and symptoms
|
ANA
malar rash, polyarthralgia, multiple organ dysfunction |
|
|
Sjorgren's syndrome
|
dry eyes and dry mouth
progressive destruction of salivary/lacrimary glands |
|
|
NEXUS rule?
|
N- neuro findings (parasthesias, wknss)
S- spinal tenderness A- altered LOC I- intoxication D- distracting injury |
|
|
Unstable C-spine fractures and pneumonic?
|
Jefferson Bit off a hangman's ***
Jefferson Bilateral facet dislocation Odontoid fractures (type 2 and 3) Atlanto-occipital dislocation Hangmans Teardrop |
|
|
Jefferson
|
C1 burst fracture
|
|
|
Bilateral facet dislocation and mechanism
|
has a cervical spondylolisthesis
Mechanism: hyperflexion |
|
|
Hangmans fracture
|
hyper-extension injury
bilateral pedicle fractures of C2 |
|
|
Teardrop fracture?
|
hyperflexion or extension
anterior inferior corner broken off |
|
|
Chance Fracture
|
from lap belt injury
Flexion-distraction injury to lumbar vertebrae transverse fracture through body and splaying of spinous processes |
|
|
Central cord injuries?
|
elderly
extension injury arms>legs affected |
|
|
Anterior cord injury?
|
flexion injury
motor function impaired pain/temp impaired gross touch, and proprioception ok |
|
|
Brown-Sequard
|
Motor and proprioception impaired ipsilateral
Pain/temp impaired contralateral |

