![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why do plants need a transport system?
|
-need regular supply of water and nutrients and remove waste.
-plants: multicellular ,small sa:v - epithelial cells direct diffusion plants cells further away from supply slow diffusion. |
|
|
What is the vascular tissue/bundle?
|
transport tissue in plant contains xylem and phloem
|
|
|
What is transported in the xylem, and in which direction does it go?
|
Xylem : transports
-water, soluble minerals -travel upwards |
|
|
What is transported in phloem and, on which direction?
|
Phloem: Transports
-dissolved substances (sugar) -up or down |
|
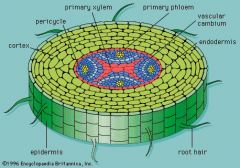
Explain the structure of the Dicotyledonous root
|
-Central core X =primary Xylem
-primary Phloem in between the arms of the X-shaped xylem -In between the xylem and phloem is a layer : Vascular cambium. -Around the vascular bundle is the endodermis -Inside endodermis is the pericyle. -Cortex between endodermis and epidermis. -root hairs on epidermis. |
|
|
Define pericycle
|
-Layer of cells
-lies inside endodermis -consists of meristem cells -division of meristem cells give rise to lateral roots. |
|
|
Define endodermis
|
-A ring of cells forming the inner layer of cortex
-surrounding area containing xylem and phloem. |
|
|
Define cambium
|
-layer of meristem cells
-divide to produce new xylem and phloem. |

