![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Homeostasis
|
maintainence of a relatively stable internal environment by means of self-regulating mechanisms
|
|
|
Negative feedback
|
when a change in a controlled variable triggers a response that opposes the change, driving the variable in the opposite direction of the initial change
|
|
|
Internal environment/homeostasis
|
concentration of nutrient molecules
concentration of O2 and CO2 concentration of waste products pH concentration of H2O, salt, and other electrolytes temp volume and pressure |
|
|
Body systems and homeostasis
|
circulatory digestive
respiratory urinary skeletal muscular integumentary nervous endocrine reproductive immune |
|
|
Cell membrane function
|
physical isolation
regulation of exchange w/environment sensitvity (rxn to envrionment) structural support |
|
|
Fluid mosaic model
|
a fluid lipid bilayer embedded with proteins
|
|
|
Phospholipid
|
phosphate
glycerol fatty acids |
|
|
Cholesterol
|
needed to keep the membrane from being too tight
too much can stiffen membrane |
|
|
Phospholipid properties
|
forms the basic stx of the membrane
its hydrophobic interior serves a barrier to water soluble substances gives fluidity to membrane |
|
|
Types of membrane proteins
|
channels (for H2O soluble substances)
carriers (For specific substances) receptors (specific) membrane bound enzymes cell adhesions |
|
|
Impermeable substances
|
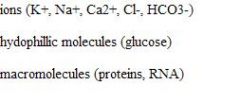
.
|
|
|
Membrane transport
|

.
|
|
|
Diffusion
|
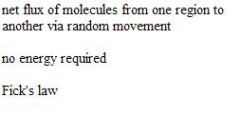
.
|
|
|
Fick's Law
|
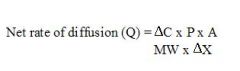
.
|
|
|
Osmosis
|

.
|
|
|
Osmolarity
|
# of particles
|
|
|
Tonicity
|
direction in which H2O moves
|
|
|
Permeable substances
|
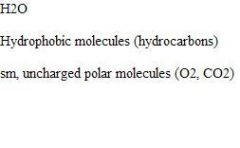
.
|
|
|
Membrane carbohydrates
|

.
|
|
|
Chemical gradient
|
he difference in concentration across the membrane
|
|
|
Electrical gradient
|
the difference in charge between 2 adjacent areas
|
|
|
isotonic
|
a solution in which the concentration of electrolyte is equal to that in cells (ex RBC in .9% salt solution)
|
|
|
hypotonic
|
a solution in which the concentration of electrolyte is below that in cells (H2O enters-lysing), hyperosmotic
|
|
|
hypertonic
|
a solution in which the concentration of electrolyte is higher to that in cells (H2O out-shrinking), hypoosmotic
|
|
|
Donnan effect
|

.
|
|
|
Channels
|

.
|
|
|
Ligand gated channels
|

.
|
|
|
External ligands
|

.
|
|
|
Internal ligands
|

.
|
|
|
Mechanically gated
|
sound waves open up ion channels on the hair cells of the inner ear to create nerve impulses that the brain interprets as sound
|
|
|
Excitable cells
|
neurons and muscle cells
|
|
|
Voltage gated
|
channels in excitable cells the open or close with changes in charge across the plasma membrane
|
|
|
Na+ channels
|

.
|
|
|
K+ channels
|

.
|
|
|
Ca+2 channel
|

.
|
|
|
Carriers
|

.
|
|
|
Facillitated diffusion
|

.
|
|
|
Uniport carrier
|
transports one thing across membrane
|
|
|
symport carrier
|
transports 2 things, in the same direction, across membrane
|
|
|
antiport carrier
|
transports 2 things, in opposite directions, across the membrane
|
|
|
Na+/K+ ATPase
|

.
|
|
|
active transport
|

.
|
|
|
internal conc"
|
.0001mM
|
|
|
Ca+2 external environment
|
10 mM
|
|
|
H+/K+ ATPase (proton pump)
|

.
|
|
|
Ca+2
ATPase |

.
|
|
|
ABC transporters
|

.
|
|
|
ABC transporter examples
|

.
|
|
|
Indirect active transport
|
uses the energy already stored in the gradient of a directly pumped ion
|
|
|
KATP
channel |
involved in glucose regulation and sulfonylurea therapy (active transporter)
|
|
|
Na+/Glucose transporter
|

.
|
|
|
Resting membrane potential
|

.
|
|
|
Membrane potential ions
|

.
|
|
|
ions
|
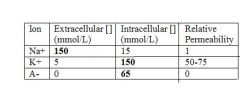
.
|
|
|
Equilibrium potential (E)
|
when the conc. gradient is exactly counterbalanced by the electrical grad.(no net movement of ion)
|
|
|
Nernst equation
|

.
|
|
|
Ca+2 external environment
|
10 mM
|
|
|
Ca+2
internal conc |
.0001mM
|
|
|
antiport carrier
|
transports 2 things, in opposite directions, across the membrane
|
|
|
symport carrier
|
transports 2 things, in the same direction, across membrane
|
|
|
uniport carrier
|
transports one thing across membrane
|

