![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
the central dogma of molecular biology states what? |
-information flows in one direction: DNA ---> RNA ---> protein -transcription: flow of info. from DNA to RNA -Translation: flow of info. from RNA to protein. |
|
|
what is translation? |
-actual syntethsis of protein under the directin of mRNA. -during this process the nucleotide sequence of an mRNA is translated into the amino cid sequence of a proteins. -protein synethssis requires a technical machinery of high complexitiy |
|
|
What are the four primary components of translation? |
1.) mrNA 2.) tRNA 3.) rRNA & ribosome 4.) aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases -diff. factors are involved in translation events |
|
|
what is mRNA: (messenger RNA)? |
-carries the code for protein from DNA -Codon: an ordered series of 3-nucleotide long unit in the protein coding region of the mRNA or DNA (template for translation the INFO) |
|
|
look at the image and what is happening? |
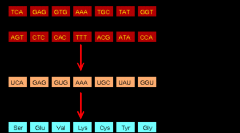
mRNA |
|
|
what is open reading frame (ORF)? Start codon? stop codon? These things are happening during what? |
-open reading frame (ORF): protein coding region of mRNA located w/in the mRNA. -Start codon: defines the reading frame, 1st amino acid -stop codon: ddefines the end of the ORF, termination -happens during mRNA |
|
|
image mRNA stop, start and ORF |

|
|
|
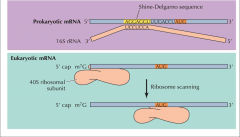
image eukary mRNA |

|
|
|
image prokar mRNA |

|
|
|
what is tRNA? |
-transports amino acids to ribosomes during translation -provide the physical interface btw the amino acids being added to the growing polypeptide chain and the codons in the mRNA (physical interface btw amino acid & codon) |
|
|
image of tRNA struct |

|
|
|
What is rRNA? |
- decodes mRNA into amino acids to interact w/tRNAs during translation by providing peptidyle transferase activity -catalyze protein syntehsis by facilatating the binding of tRNA & their amino acids to mRNA |
|
|
what is a ribosome? |
-RNA + proteins = functional ribosome -composed of 2 subunits: large subunit and small subunit -Large: contains peptidyl transferase center for the formation of peptide bonds -small: decoding center for charged tRNA's read or decode the codon units of the mRNA (coordinate recognition & catalyze bond formation) |
|
|
Ribosomes are named by what? |
velocity of their sedimentation called S: the larger the S value, the faster the sedimentation velocity and the larger the molecule |
|
|
what is S=Svedberg? |
unit of measure sedimentation velocity and named after the inventor of the ultracentrifuge, Theodor Svedberg |
|
|
rRna is not only the structure of components but also what? |
directly responsible for the key functions of the ribosome |
|
|
What is aminoacyl-tRNA syntheses? |
aka "charging" the tRNA w/the amino acid. -(coupling amino acid to tRNA's) by ammoniacal-trna synthethesis -occurs in 2 steps |
|
|
-once the tRNa is charged, a ribosome can what? |
transfer the amino acid the TRNA onto a growing peptide, according to genetic code. |
|
|
each aminoacyl-tRNA syntheses only attached to what? |
a single amino acid to a tRNA in two enzymatic steps |
|
|
the aminoacyl-tRNA syntheses charge occurs into 2 steps which are? |
1.) adenylation w/ ATP w/release of AMP 2.) transfer adenylylated to tRNA |
|
|
look at image |

|
|
|
list the translation players and their function? |
1.) mRNa: template for translation (information) 2.) ribosome: coordiante recognition & catalzye bond formation 3.) tRNA;s: physical interface btw amino acid and codon 4.)Aminoacyl-tRNA syntheases: couple amino acid to tRNA's |
|
|
RNA translation can be divided into four steps which are? |
1.) initiation 2.) elongation 3.) termination 4.) ribosome recycling |
|
|
what happeins in the 1st step of translation INITIATIon? |
(form initiation complex = ribosome bind to specific initiation start site (initiator tRNA + initiation codon = bound to ribosome) |
|
|
what happens in the 2nd step of translations elongation? |
-amino acids join to the growing polypeptide -the same steps are related over & over again until the termination codon is reached in the message. |
|
|
what happens in the 3rd step of translation termination? |
termination codon gives the signal for the protein synthesis, in which the ready-made protein is released from the ribosome. |
|
|
what happens in the 4th step of translation ribosome recycling? |
-critical last step in translation after the release of polypeptide chain |
|
|
The translation process are mediated by what? |
-an ordered series of interdependent factor binding & releases event -this ensures that one step occurs before the previous steps is completed (goes step by step) |
|
|
what are 3 events that must occurred in initiation of translation to be successful? |
1.) ribosome must be recruited into the mRNA 2.) charged tRNA must be placed into the P site of the ribsome 3.) ribosome must be correctly positioned over the start codon(the correct positioning of the ribosome over th start codon is critical ) |
|
|
initiation events vary in what? |
prokaryoteic and eukarytoic mRNA's |
|
|
what happens in prokaryotic cells in translation initiation process? |
1. )SHine sequence RBS base pairs w/ 3' end 16S 2.) precedes the AUG initiation AUG = methinione 3.) 3 translation initiation factors IF1, IF2, IF3 involve in initiation 4.) 2 initiaation complexes form in initiation events 30S initiation complex & 70S initiation complex 5.) initiator TRNA is charged, initiate codon and enter P site. |
|
|
what happens in eukaryotic cells in translation initiation process? |
1.) mRNA's is bound to 40S subunit by the 7methylG cap 2.)ribosome scans along until it finds an AUG 3.) at least 8 translation initiation factors (elF1A, elF2, elF5b, elF3) 4.) 3 initiation complexes are formed in initiation 5.) 43 S pre-initiation complex, 48S pre-initiation complex and 80 S initiation complex |
|
|
initiation always begins w/ what? |
amino acid methionine |
|
|
images iniation of eukary and prokary |
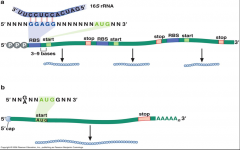
-prokaryotic = polycistornic -eukary = monocistronic |
|
|
name the 3 binding sites of the ribosomes? |
1.) A site 2.) P Site 3.) E site APE |
|
|
what is A site? |
binding site for aminoacylated tRNA |
|
|
what is P site? |
binding site for peptidyletRNA ( forms the peptide bond) |
|
|
what is the E site? |
exit site (binding site for the tRNA that is released after growing polypeptide chain has been transferred to the aminoacyl-tRNA. |
|
|
image of the 3 binding sites of ribosome |
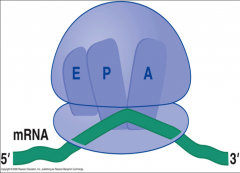
|
|
|
what happens during translation-initiation? |
- a charged tRNA placed into the P site of the ribosome and correctly positioned over the start codon -large subunit joins to small subunit at the very end of initiation
|
|
|
image of translation -initation |

|
|
|
image of translations -initation for eukaryotic = 48S pre-initiation complex |

|
|
|
list the initiation factors for prokaryoes? |
IF1 IF2 IF3 |
|
|
list the initiation factors for eukaryotes? |
-elF1A, -elF2, elF5b -eIF3 -elF1, elf4a,elF4E,elf4g,elf4b |
|
|
what are the funcitions for IF1 & elf1A? |
blocks ribosme A site
|
|
|
what is the function of IF2, elf2 & elF5b? |
faciliatte initiator tRNA binding site to the P-site of 40 S subunit |
|
|
function of IF3? |
prevents ribosomal subunit association |
|
|
function of elf1, elf4a, elf4E, elf4g and elf4b? |
prepare mRNa template for ribsome binding |
|
|
once the ribosome is assembled w/ the charged initiator tRNA in the P site, polypeptide synthesis happens and translation shifts to what? |
elongation |
|
|
what 3 key events for the correct addition of each amino acid in elongation? |
1.) correct aminoacyl-tRNA loaded into A site 2.) peptide bond is formed 3.) peptidyl-tRNA in the A site is translocated to the Psite so that the ribosome is ready for another cycle of codon recongntion & peptide bond formation |
|
|
what happens in elongation ? |
-highly conserved btw the prokar and eukary cells -3 elongation factors : EF-Tu, EF-G, EF-Ts -incoming aminoacyl-tRNA, peptide bond formatin & translocation -RNA translation shift into termination stage |
|
|
image of translation - elongation |

|
|
|
image of translation - elongation 2 |

|
|
|
what happens in RNA translation in the termination stage? |
3 key events in termination -mRNA conintues on past the stop codon. Remaining portion is not translated: it is 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) -release factors are diff. in pro & eukar |
|
|
what are the 3 key events in termination stage? |
1.) all protein coding-regions end in one of the 3 stop codons 2.) stop codons are recognized by proteins called "release factors" that cause ribosome, mRNA & new polypeptide to separate. New polypetide = completed 3.) Ribsome recycling after polypeptide releases |
|
|
terminato factors for both prokaryotes and eukaryotes |

|
|
|
steps of termination image |

|
|
|
what happens in ribosome recycling? |
It's mediated by ribosome recycling factor(RRF), EF-G,IF3 in prokaryotes and is not understood in eukaryotes |
|
|
image of ribosome recycling |
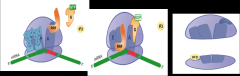
|
|
|
translation overview image |

|

