![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What's a transition metal? |
An element which forms one or more stable ions which have incomplete d sub-shell |
|
|
What is a coordination number? |
The number of near neighbouring atoms that are bonded to the central ion. |
|
|
What is a ligand? |
A ligand is an atom, ion or molecule that donates a pair of electrons to the central ion |
|
|
What's a monodentate ligand? |
Which the ion or molecule uses one lone pair of e- to form a dative bond |
|
|
What's a bidentate ligand? |
A complex molecule or ion that can form two dative bonds with the central metal ion |
|
|
Special properties |
•Coloured ions •Complexes ions •Good catalysts •Variable oxidation states |
|
|
Colours of ions? |
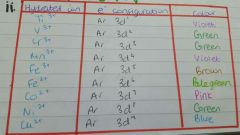
|
|
|
Transition metals as catalysts |
A transition metal can act as a catalyst because it's energetically available for d-orbitals can accept electrons from a reactant molecule. Transition metals are good catalysts. Reactants are absorbed temporarily on to the catalyst surface. When the reactions is complete, products diffuse away leaving catalyst surface available.
Variable oxidation state of transition metal ions allows them to bind to reactants to give reaction intermediates. |
|
|
EDTA |
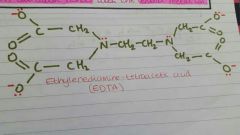
|
|
|
Copper (ll) Cu2+ |
Metal aqua ion: [Cu(H2O)6]2+ blue solution
With OH- or NH3: [Cu(H2O)4(OH)2] blue precipitate
With excess OH- : [Cu(H2O)4(OH)2] blue precipitate (insoluble)
With excess NH3: [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+ deep blue solution |
|
|
Iron (ll) Fe2+ |
Metal aqua ion: [Fe(H2O)6]2+ Green solution
With OH- or NH3: [Fe(H2O)4(OH)2] Green precipitate
With excess OH-: [Fe(H2O)4(OH)2] Green precipitate (insoluble)
With excess NH3: [Fe(H2O)4(OH)2] Green precipitate (insoluble) |
|
|
Iron (lll) Fe3+ |
Metal aqua ion: [Fe(H2O)6]3+ Pale yellow/pink solution
With OH- or NH3:[Fe(H2O)3(OH)3] Brown precipitate
With excess OH-:[Fe(H2O)3(OH)3] Brown precipitate (insoluble)
With excess NH3:[Fe(H2O)3(OH)3] Brown precipitate (insoluble) |
|
|
Manganese (ll) Mn2+ |
Metal aqua ion: [Mn(H2O)6]2+ Pale pink solution
With OH- or NH3:[Mn(H2O)4(OH)2] Brown precipitate
With excess OH-:[Mn(H2O)4(OH)2] Brown precipitate (insoluble)
With excess NH3:[Mn(H2O)4(OH)2] Brown precipitate (insoluble) |
|
|
Nickel (ll) Ni2+ |
Metal aqua ion: [Ni(H2O)6]2+ Green solution
With OH- or NH3:[Ni(H2O)4(OH)2] Green precipitate
With excess OH-: [Ni(H2O)4(OH)2] Green precipitate (insoluble)
With excess NH3: [Ni(NH3)6]2+ Blue solution |
|
|
Chromium (lll) Cr3+ |
Metal aqua ion: [Cr(H2O)6]3+ Violet solution
With OH- or NH3:[Cr(H2O)3(OH)3] Green precipitate
With excess OH-: [Cr(OH)6]3- Green solution
With excess NH3: [Cr(NH3)6]3+ Purple solution |
|
|
Copper reduced by zinc |
Cu2+ + Zn ➡ Cu + Zn2+ |
|
|
Why is an ion coloured? |
• The ligand causes the 3d subshell to split to two different levels • Electron repulsion from the ligand causes energy of the 3d electrons to increase. • The electrons in the lower energy levels absorb light energy and jump to a higher level. • The electrons emit the energy and return to its ground state. |
|
|
Cis-platin |
A platinum compound which is a powerful anticancer drug. Prevents cancer cells from dividing. |
|
|
Catalytic converts |
Use a fine coating of a platinum catalyst supported on a heat-resisting ceramic material to give a large surface area. |
|
|
Photochromic lenses |
Lenses response specifically to UV in sunlight. Molecules in the lenses, associated with silver halides, change shape according to the UV intensity. In artificial lighting, lenses remain transparent |
|
|
Catalyst development |
•Catalyst help a reaction to take place at lower temperatures and pressures which saves energy and reduces costs. •Has a higher atom economy which reduces the amount of raw materials used, decreasing waste products. |
|
|
Evaluation of catalytic converters |
Advantages: •Reducing air pollution and smog by unburnt fuel •Removing nitrogen oxides and carbon dioxide Disadvantages: •Reduces fuel economy •Catalyst can be poisoned by lead petrol •May take time to warm up releasing pollutants |
|
|
Polychromic sunglasses |
Sunglasses gave a thin reflective coating, often chromium. Sunglasses adjust to light conditions; becoming darker I'm bright sunlight and reducing glare |
|
|
Zinc (ll) Zn2+ |
Metal aqua ion: [Zn(H2O)6]2+ Colourless solution With OH- or NH3: [Zn(H2O)4(OH)2] White precipitate With excess OH-: [Zn(OH)4]2- Colourless solution With excess NH3: [Zn(NH3)4]2+ Colourless solution |
|
|
Chromium oxidation states |
(Cr2O7)2- Orange Oxidation state +6
(CrO4)2- Yellow Oxidation state +6
Cr3+ Green Oxidation state +3
Cr2+ Blue Oxidation state +2
|
|
|
Vanadium(v) oxide catalyst |

|
|
|
Vanadium ions |
V2+ Lavender Oxidation state +2 V3+ Green Oxidation state +3 VO2+ Blue Oxidation state +4 VO2+ VO3- Yellow Colourless Oxidation state +5 |
|
|
Vanadium half equations |

|

