![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Definition of congruent. |
Describes relationship between two shapes with exactly same length of sides, size of angles, with sides and angles arranged exactly same way. |

|
|
|
Three types of congruence... |
Translation, rotation, reflection. |
Tr... Ro... Ref... |
|
|
Definition of rotation. |
A transformation in which a shape is rotated through an angle about a centre of rotation. |
|
|
|
Definition of translation. |

A transformation in which a shape is slid from one position to another - without turning. |
|
|
|
Translation eg |
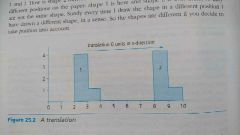
|
|
|
|
Rotation eg. |
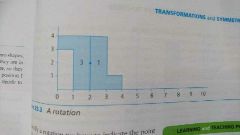
|
|
|
|
Reflection eg. |
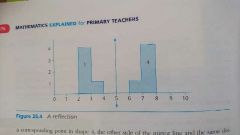
|
|
|
|
Fourth type of transformation... |
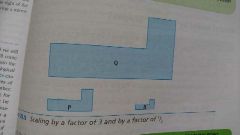
Scaling. Scaling a shape up or down by a scale factor. |
Sc... |
|
|
Relationship between transformations, scaling and ratio. |
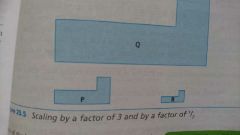
Shapes can be scaled (which is type of transformation) by ratio. Eg ratio of any length of P to corresponding length in Q is 1:3. |
|
|
|
Scaling up achieved by scale factor greater than... Scaling down achieved by scale factor less than... |
1 (Scaling by factor of 1 leaves a shape unchanged.) |
|
|
|
In general, scaling by n and 1/n are inverse transformations. |
... |
|
|
|
Definition of similar shapes. (NB 'similar' has a precise mathematical meaning.) |
When two shapes have been transformed and their lengths have changed they are no longer congruent (Congruence is transformation by: translation, rotation, reflection/combinations of). Instead they have been transformed by scaling and are similar shapes. (The lengths of the lines have changed but corresponding lines are in the same ratio - and corresponding angles are still equal.) |
|
|
|
Definition of reflection as a transformation. |

A transformation in which a shape is reflected in a mirror line and changed in its mirror image. |
|
|

Difference between: 1) Reflective symmetry/line symmetry/line of symmetry in a shape. 2) Rotational symmetry. 3) Reflection in a line as a translation.
1) Reflective symmetry/line symmetry means reflection. It's where you can draw a mirror line in a shape so it looks the same as without the mirror.
|

2) Rotational symmetry - when a shape is mapped exactly onto itself by a rotation. 3) Reflection in a line of symmetry - shapes can be reflected in a line called the mirror line because the image you want is just what you'd see if you stuck a mirror along the paper. |
|
|
|
Simple explanation of reflective symmetry... |
Sometimes when a shape is reflected in a particular mirror line it matches itself exactly. It divides the shape into two identical halves that are mirror images of each other. |
|
|
|
Repeat: Reflective symmetry and line symmetry are the same thing. The mirror line is called the line of symmetry. |
Repeat. |
|
|
|
Practical example of congruence... |
The pages in a book when they fit exactly over one another. |
|
|
|
Definition of congruence. |
A transformation of a shape that changes it into a congruent shape is called a congruence. |
|
|
|
Practical examples of transformation: 1) topological 2) perspective |
1) London Underground map. All lengths and angles have changed curved lines can become straight, but the map still retains significant features of the original network to enable a route to be determined. 2) By drawing a building that is a rectangle with a parallelogram to show perspective. |
|

