![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define thermodynamics. |
Conversion of heat to energy. Only concerned with final destination, not pathways. |
|
|
What is the 1st Law of Thermodynamics? |
Universal energy is constant. |
|
|
What is the 2nd Law of Thermodynamics? |
Energy transformation increases universal disorder (entropy, ΔS). |
|
|
What is the equation for Gibbs Free Energy? |
ΔG=ΔH-TΔS |
|
|
What is the equation for enthalpy? |
ΔH-ΔE-PΔV |
|
|
What does a positive ΔG mean? Negative? |
If (+) then non-spontaneous, unfavorable, endergonic, exothermic reaction. |
|
|
What happens in Gibbs Free Energy is in equilibrium? |
ΔG=ΔG^0'+RTln(K) where Keq=[products]/[reactants]
Reactants and products turnover at the same rate but concentration is constant.
Equilibrium tends towards to lowest energy state. |
|
|
Define kinetics. |
Study of the reaction rate after Ea has been reached. |
|
|
Define catalysts. |
Increase the reaction rate by reducing Ea without changing ΔG
Stabilizes the transition state (TS).
Not consumed or changing in the reaction. |
|
|
Name a common type of catalyst. |
Enzymes. |
|
|
What are proteases? |
Protein-cleaving enzymes with a serine reside in the active site whose -OH acts as a nucleophile to attract polypeptide residues. |
|
|
Name and define the four types of enzyme activity. |
• Covalent modification: proteins may have different groups covalently attached that regulate their activity• Proteolytic cleavage: many enzymes are synthesized in inactive forms (zymogens) activated by cleavage by a protease• Associations: some enzymes have catalytic activity in one polypeptide subunit regulated by association with a separate regulatory subunit (constitutive activity)• Allosteric regulation: binding of small molecules to certain sites on an enzyme that aren't the active site (usually noncovalent and reversibly bound) |
|
|
Define negative feedback. |
An end-product doesn't shut off an enzyme earlier in the pathway. |
|
|
Define positive feedback. |
Enzyme is stimulated by its substrate or a molecule that synthesizes the substrate. |
|
|
Define enzyme kinetics. |
Study of the rate of product formation from substrates in the presence of enzymes |
|
|
What is the reaction rate? |
Reaction rate (V) is the amount of product formed per unit time and is directly proportional to substrate. |
|
|
Define saturated enzymes. |
Substrate levels are so high the reaction doesn't increase when more is added. |
|
|
Define cooperativity and explain the graph. |
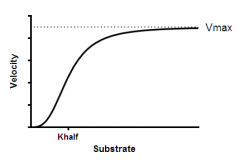
Substrate binding to a macromolecule promotes substrate binding. Tense state (bottom, substrate affinity is low), relaxed state (slope, substrate impacts rate) & saturated (Vmax, top)
|
|
|
Define competitive and noncompetitive inhibitors. |
Competitive: inhibitor binds at the active site, competes with substrate. Adding substrate overcomes inhibition (Vmax doesn't change, Km increases)
Noncompetitive: inhibitor binds at allosteric site, doesn't compete with substrate. (Lowers Vmax, Km doesn't change)
|
|
|
Explain oxidation and reduction. |
Oxidization: "bind to oxygen" when oxygen is added and hydrogen or electrons are removed
Reduction: "remove oxygen" when hydrogen or electrons are added and oxygen is removed |
|
|
Define catabolism and anabolism. |
Catabolism: breakdown of molecules.
Anabolism: formation of molecules. |
|
|
Explain oxidative catabolism. |
Extracts energy from glucose includes glycolysis, PDC, Krebs cycle, and electron transport. |
|
|
What is glycolysis and what is the yield? |
Glucose is split into two pyruvic acids aerobically in the cytoplasm. Glycerol phosphate shuttles NADH to inner mitochondria matrix.
Yields: -2 ATP, 4 ATP, 2 NADH (3 ATP in eukaryotes, 5 in prokaryotes)
|
|
|
What does the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) do and what does this yield? |
Functions in mitochondrial matrix to convert pyruvate to acetyl CoA and generate 2 NADH (5 ATP). |
|
|
What happens in the Krebs cycle and what does it yield? |
Takes the 2C acetyl from acetyl CoA, combines with oxaloacetate and releases 2 CO2.
Yields: 6 NADH (15 ATP), 2 FADH2 (3 ATP) and 2 GTP (2 ATP) |
|
|
What is electron transport and where does it occur? |
NADH and FADH2 are oxidized in the inner mitochondrial matrix, ends with the reduction of oxygen and the creation of a proton gradient.
|
|
|
What is cellular respiration and how much ATP is produced? |
Oxidation of carbohydrates, reduction of electron carriers, and generation of ATP.
30 ATP in eukaryotes, 32 in prokaryotes |
|
|
Define fermentation. |
In anaerobic conditions, regenerates NAD+ by using pyruvate to accept high energy electrons (i.e. ethanol and lactate) to allow glycolysis to continue
|
|
|
What is the appearance of structural and catalyst proteins? |
Structural are fibrous (i.e. collagen) and catalyst are spherical (i.e. enzymes) |
|
|
DDefine cofactors. |
Needed for enzyme's function but don't interact |
|
|
Define prosthetic group. |
Nonprotein molecule covalently bound to an enzyme at the active site (i.e. vitamins) |
|
|
How do unfavorable reactions occur? |
By coupling them to favorable reaction. |

