![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Occasions when the dets are placed before 1 1/4 miles |
Signal post telephone Signal box Tunnel Junction Approaching train |
|
|
How to carry out emergency protection? |
Place tcocs on all affected lines Walk 1 1/4 miles Place 3 dets on running line (20m apart) Stand 30m away from dets |
|
|
When must conductors carry out emergency protection? |
The signaller can’t provide signal protection You can not get hold of the signaller The driver is incapacitated |
|
|
What equipment is used for emergency protection? |
Red flag 2 x track circuit operating clips (tcocs) 10 x Dets PPE (Boots & Hi-Vis) |
|
|
How can you tell a distance signal and a stop signal apart? |
Distance signal can not display red, however a stop signal can. |
|
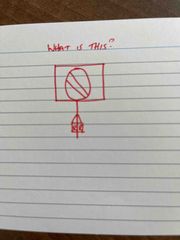
Front (Term) |
Banner repeater signal |
|

Front (Term) |
Semaphore Signal |
|
|
What is station limits? |
Station limits is the section of the line stretching from the first stop signal (home signal) to the last stop signal (section signal) that are controlled by the same signal box |
|
|
Describe ABS - The Block Section |
The block section is a section of the line stretching from the last stop signal controlled by one signal box to the first signal controlled by the next signal box. |
|
|
How to Self Dispatch? |
Confirm stops with driver (if you have relieved someone) 2 minutes before departure time - operate the TRTS if required. Ensure your DKS is switched on Assist passengers whilst maintaining vigilance down the train corridor and PTI 30 Seconds before departure- check you have a proceed aspect and the time If the PTI is clear and it’s safe to do so - close the passenger doors Check the BIL lights have gone out Re-check the time, signal, PTI Board the train and close local door Crack window open (185) and if possible check PTI and time When it is safe to do so, give the driver the ready to start signal (2 on the buzzer) Remain at the control panel - observe the platform until the train has cleared the platform. Deactivate the DKS. |
|
|
How to cross the 3rd and 4th rail? |
Consider live at all times (750 volts DC) Use an authorised crossing Look for a gap in the conductor rail or where protective boards are fitted Step over both the conductor rail and rail head in one movement Step ballast to ballast Ensure no bags or anything you are carrying comes into contact with the conductor rail |
|
|
How to protect the lines on a 3rd and 4th rail? |
Consider live at all times Apply TCOCs to the rail furthest from the conductor rail first Apply dets to the rail furthest from the conductor rail |
|
|
3 Points of a train safety check |
The train doors are properly closed (the BIL lights have gone out) Nobody is trapped in the doors, for example clothing. It is safe to start the train |
|
|
Buzzer codes |
1 = Stop 2 = Ready to Start 3 = Set back 4 = Draw forward 9 = Police assistance required 1-2 = Close doors (Power-operated) 2-2 = Do not open doors (Speak to Guard) 3-1 = Lock central door locking 3-2-1 = Testing doors (not repeated) 3-3 = Guard required by driver, or guard or driver to attend the phone 3-3-1 = Release central door locking |
|
|
What is in a kit bag? (Personal equipment) |
Torch Watch Fully charged mobile & charger Revenue equipment Personal float & publications Red & green flag Hi-Vis Safety boots Documents & report forms ID card Spit kit Schedule card Whistle Relevant keys Up to date notice |
|
|
What notice cases are in the booking on point? |
Late notice case New notice case General notice case Health & safety notice case Commercial SPAD Permanent Performance Unions |
|
|
Definition of Temporary block warning? |
TBW means 2 or more consecutive signals displaying danger and driver to pass at danger with the authorisation from hand signaller at the first signal. |
|
|
Difference between Temporary block warning and Emergency special working? |
The difference between TBW and ESW is that the driver speaks directly to the signaller (ESW) instead of the hand signaller (TBW) |
|
|
Dispatch with a dispatcher * = with a green flag & RA |
Dispatcher = confirms there is a driver Conductor = confirms stops with driver if needed Dispatcher = operates TRTS no more than 2 minutes before departure Dispatcher = 30 seconds before departure - checks time, signal, PTI Dispatcher = gives “station suites complete” tip Conductor = checks time, signal, PTI before acknowledging the tip with a hand signal, then closes doors Dispatcher = observes the BILs lights have gone off Dispatcher = rechecks the signal, time, PTI before giving “train safety check complete” tip Conductor = checks BILs lights, time, signal, PTI before acknowledging with hand signal . *raising green flag* Conductor = boards the train, cracks window open, final check of PTI and Signal before giving 2 on the buzzer. *if using green flag then no buzzer* Dispatcher = observes the train departing and the PTI. *gives RA to driver then does the obs* Conductor = observes the platform until train is clear of platform Conductor = deactivates DKS |
|
|
Hazards of operating train / coming into a station? |
The curvature of the platform making it difficult to see full length of the train or signal. Curvature of platform causing gaps between the platform edge and the train. Overcrowding - can make it difficult to see that the doors are fully closed and not obstructed. Customers running for train. Customers getting their clothes trapped in a closed door. Difference in lighting levels that may impact on visibility. Environment issues such as mist, fog, floods, snow or ice. Vegetation, platform structures or furniture obscuring signals, OFF indicators or view of the train. Being distracted by customers, mobile phone or the intercom. Vulnerable customers. Your train being too long for the platform. |
|
|
Hazards you may encounter when walking on the operational railway? |
Reduced visibility due to weather conditions. Slips/trip hazards e.g troughing, debris. Limited sighting conditions e.g infrastructure, curvature of line. Recused visibility due to lighting e.g low sunlight, darkness. Trains working in the opposite direction than normal e.g shunting. |
|
|
3 points of the electric of the over head line equipment |
Should be considered live at all times. 25,000 volts AC Minimum distance of 2.75m (9 feet) |
|
|
How to report rail dangerous goods emergency? |
Contact ECO (electric control operator) State “this is a rail dangerous good emergency” Give the United Nations number |
|
|
What to do in a situation involving rail dangerous goods? |
You must keep well clear Keep wind behind you as you face any affected welcomes or packages Avoid low lying places where gas may gather Keep unauthorised people well clear Try to put out a fire without putting yourself or anyone else at risk. Keep naked lights and lamps well clear Not to smoke, use matches or pocket lighters. Not to use mobile near any vehicles carrying flammable loads. |
|
|
Rules of walking on the operational railway |
Use an authorised walking route if one is provided. If you have to cross the line, you must not step on rails, sleepers, between moveable part or points. Use mobile phone in a position of safety and stand still until finished using mobile. Do not wear anything that makes you less able to see or hear approaching trains. Do not allow yourself to be distracted by anyone or anything. Keep a good lookout for approaching trains. Make sure you look up at least every 5 seconds so that you can reach a position of safety and be in it no less than 10 seconds before an approaching train arrives. |
|
|
How to stop a train in an emergency? |
During daylight = must display red flag or if you haven’t got one then raise both arms above your head. During darkness = must show red light to the driver or wave any light violently. |
|
|
Definition of on or near the line. Definition of not on or near the line. |
Within 3 metres of the nearest running line and there is no permanent fence or structure between you and the line. On the line itself. Not considered on or near the line if you are; on a station platform or on a level crossing. |
|
|
4 things you must know before going on or near the line. |
Max line speed Normal direction of travel Any locations of limited clearance The location of any area you must not go whilst trains are running |
|
|
When on the operational line and train approaches - what must you do? |
Stand in a position of safety or if already in a position of safety, stay there. If driver sounds the warning horn, raise one arm above your head to show that you have heard the warning. You must stay in a position of safety until the train has passed clear or you are certain you will not be put into danger by that train or any other trains. |
|
|
Phases for good and bad communication? |
Use line blocked Phonetic alphabet Use over for response back Use out for no response back Brief - to the point Clear Ask to repeat back. Do not use over and out Do not use slang Do not talk too fast Do not overload with information or underload. |
|
|
Who do you contact to obtain an isolation of the over head line equipment? |
Electric control operator (ECO) Controlling signaller |
|
|
If trains are put in danger - what do you do? |
Advise controlling signaller Stop trains Carry out emergency protection if necessary |
|
|
List the dangers to trains |
A Door not properly locked / closed An unsecured load A vehicle on fire A hot axle box A headlamp not lit A tail lamp not lit or missing |
|
|
Definition of lineside |
You are considered “lineside” if you are between the railway boundary fence and the area called “on or near the line” |
|
|
Information to give on an emergency call? |
State this is an emergency Confirm you are talking to ECO or signaller Give your name, job title, company, headcode Reason for call Anyone in danger Emergency services required? The line/lines concerned The number of nearest structure ID plate if possible Ask them to repeat to see if the message and information is understood. - Ring signaller to relay message to stop on coming trains. |
|
|
List of over head line equipment |
Catenary wire Dropper Contact wire Headspan wire Crosspan wire Structure bond Insulators Structure Structure ID Plate Along track conductor |
|
|
Position of safety |
If the line speed is less than 100MPH, a position of safety is 1.25m (4 feet) from the nearest line to which a train can approach. If the line speed is more than 100MPH then a position of safety is 2m (6 feet, 6 inches). |
|
|
What is a WON and what does it consist of? |
A weekly operating notice. Consist of 3 sections - safety notices - signalling and permanent way alterations - general instructions and notices 3 stars = denotes the last printed appearance of the item. Block line = denotes the first printed appearance of this item. |
|
|
Operational railway? |
Cess Four foot Six foot Four foot Ten foot Four foot Six foot Four foot Cess |
|
|
How to book on? |
Use booking on phone to ring train crew Enter payroll number Confirm the last 3 digits of payroll Press 1 to book on or 2 to book off If there is an alteration or train crew/control which to speak to you, then you will be transferred. |
|
|
PPE for going on the operational railway |
HI-VIS Safety footwear Anything additional they ask |
|
|
When do you protect the rear? |
When I’m either temporary block warning or emergency special working |

