![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
161 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
poison definition
|
- a substance that causes dose-related adverse health effects at relatively small doses
|
|
|
toxicant = ?
|
poison
|
|
|
toxin definition
|
- poison of biological origin
|
|
|
toxicity
|
characterization of the potency and toxic effecs associated with a poison
|
|
|
toxicosis
|
disease/syndrome caused by a poison
|
|
|
how are carcinogens evaluated differently than poisons?
|
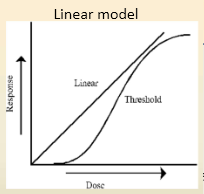
- with carcinogens we assume there is no safe level of exposure
- with every exposure there will be potential for mutagenic change - there is no NOAEL - evaluated under the linear model |
|
|
what kind of response graph do vitamins and trace elements usually have?
|
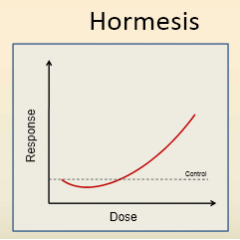
- hormesis
- low dose response is opposite of high dose response |
|
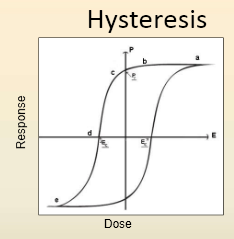
name an example that would cause a shift to the right
name an example that would cause a shift to the left |
- right: Inappropriate response
- Usually seen with some type of adaptive process - ex: increase in enzyme for the metabolism of a toxicant - left: inability of the animal to deal with the toxicant - ex: liver damage prevents conjugation of subsequent toxicant |
|
|
mixture effects of chemical reactions
2 |
- precipitation
- chemical reactions forming new compounds |
|
|
mixture effects on PK ixns
|
- changes in rates of absorption
- enzyme induction/suppression |
|
|
mixture effects on PD ixns
|
- cumulative responses
- synergism - antagonism |
|
|
what is the DOS of treatment stand for?
|
- Decontaminate
- Oppose - Support |
|
|
venom
|
a poisonous secretion produced in specialized glands and delivered via a specialized parenteral delivery system
|
|
|
venin
|
single component of a venom
|
|
|
envenomation
|
act of venom delivery
|
|
|
3 types of venomous reptiles in North America
|
- pit vipers (rattlesnakes, copperheads, cotton mouth, water moccasins)
- coral snakes - gila monsters |
|
|
pit viper family
what attribute makes them good envenomators? |
Crotalinae
- front fangs - rapid envenomation |
|
|
can venom delivery be controlled?
% breakdown based on severity |
- yes, can be controlled
- 25% are "dry" - 35% mild - 20% moderate - 10-15% severe |
|
|
viper venom contains how many different venins?
how many different venom protein families? |
- 50-100 venins
- 10-20 venom protein families |
|
|
major venin classes
name 6 |
- hyaluronidase
- myotoxins - hemorrhagic toxins - cardiotoxins - metalloproteinases - neurotoxins |
|
|
effect of hyaluronidase venin
|
- spreading factor
- breaks down connective tissue |
|
|
effect of mytoxin venin
|
- muscle necrosis
|
|
|
effect of hemorrhagic toxin venin
name 3 |
- hypercoagulation
- hypocoagulation - fibrinolysis |
|
|
effect of cardio toxins
name 2 |
- myocardial depression
- unresponsive hypotension |
|
|
effect of metalloproteinases venin
|
- general tissue necrosis
|
|
|
effect of neurotoxin viper venin
|
- transmitter release stimulation
- transmitter release inhibition - transmitter blocking |
|
|
venom local manifestations
2 one of these can cause a major problem, name it |
- tissue swelling
- pain - severe swelling can obstruct airways/perfusion |
|
|
systemic venom manifestation
3 |
- hypotension
- neurotoxic effects - coagulopathy |
|
|
clinical pathology of venom bite
4 |
- elevated creatinine
- altered blood clotting parameters - hematuria, rhabdomyolysis - echinocytosis |
|
|
are do severe local venom manifestations mean severe systemic effects or vice versa?
|
- no
- bite could have little local effects but be severe systemically |
|
|
treatment of pit viper bite
drug name ROA what is dose dependent on? |
- Crotalid Fab antivenom: CroFab
- IV admin w/in 6 hours of bite - dose dependent on venom load, not patient weight |
|
|
what is the risk of trt with antivenom?
|
- anaphylaxis
|
|
|
Elapid snakes are more commonly known as what?
more or less agressive than pit vipers? are the fangs fixed or hinged? |
- coral snakes
- less aggressive than vipers - fixed fangs, snakes |
|
|
most important effect of highly potent coral snake venom
general |
- neurotoxin
|
|
|
MOA of coral snake neurotoxin
|
- blocks postsynaptic acetylcholine receptors
|
|
|
onset of symptoms after elapic snake bite?
name 4 symptoms |
- onset is variable, can be up to 18 hours
- respiratory depression - CNS abnormalities - loss of muscular function - respiratory muscle paralysis |
|
|
trt of elapic snake bite
antivenom? what supportive care suggested? |
- no commercially available antivenom
- compression bandage, immobilization of limb - reduces lymph drainage, delays onset of effects |
|
|
location of venom glands in Gila monster
|
- submandibular venom glands
|
|
|
Gila monster
- rate of envenomation? - CS of bite |
- slow envenomation, requires long contact time
- swelling and severe pain - may induce hypotension, nausea, vomiting |
|
|
Gila monster bite treatments
|
- trt the pain
- trt hypotension - check for retained teeth - clean/cover wounds |
|
|
name the 2 toads discussed
|
- colorado river toad
- cane toad |
|
|
what gland produces toxin on the skin of toads?
|
- parotid gland
|
|
|
- what type of toxins are present in toad secretion?
- 2 cardiac glycosides - 2 hallucinogens - 3 others |
- bufagenins and bufotoxins
- bufotenine and indolealkylamine - dopamine, EPI, serotonin |
|
|
local signs of toad toxins
|
- mouth and throat
- hypersalivation, vomiting, inflamed mucous membranes |
|
|
systemic effect of toad toxins
|
- cardiac arrhythmias
- ataxia - seizure |
|
|
trt of toad toxins
7 things to do |
- flush oral mucous membranes with water
- activated charcoal - digibind - trt cardiac arrhythmias - control seizures - enhance elimination (IV fluids, furosemide) - supportive |
|
|
black widow nesting sites
|
- basements, garages, wood piles
|
|
|
color for black widows
color of hourglass, is it always brightly colored? |
- range from black to brown/grey
- red/orange hourglass - not always brightly colored |
|
|
black widow bite
size? pain? skin reaction? |
- small wound
- initally not painful - slight swelling and redness at bite site |
|
|
black widow toxins are what kind?
what CS could we see? duration of CS? |
- neurotoxins
- sweating, cramping, muscle contractions, cardiac arrhythmias, altered breathing - most symptoms disappear by 2-3 days |
|
|
trt of black widow bite
|
- antivenin: Lyovac
- slow IV injection - analgesics |
|
|
brown recluse spiders
do the have nests? |
- no nests
- actively roams at night in search of prey |
|
|
brown recluse bite local symptoms
4 |
- initial bite not painful
- develops into a necrotic lesion with erythema, scabbing - affected tissue may slough - very slow healing |
|
|
brown recluse systemic effects (these are rare)
|
- hemolytic anemia
- but negative with a negative direct antiglobulin (Coombs) test |
|
|
trt for brown recluse bite
|
- open would management
- symptomatic trt - antibiotics |
|
|
fire ant
home? aggressive? |
- build soil mounds
- active foragers - aggressive |
|
|
mode of attack for fire ants
|
- bite and sting
|
|
|
species most affected by fire ants?
|
- ground nesting birds
- turtles - frogs |
|
|
what to fire ants use to cue others to sting and bite?
|
- pheromone cues
|
|
|
is there immediate reaction to fire ant bites/stings?
|
- yes, immediate reaction
|
|
|
trt of fire ant bites
|
- symptomatic trt
- antihistamines, topical corticosteroids |
|
|
bee and wasp
what types of toxins are present? |
- vasoactive amines
- phospholipase |
|
|
effect of massive bee and wasp bites
|
- CV collapse
- coagulopathy (due to phospholipase) |
|
|
what toxin is produced by blister beetles?
how is this transferred b/w beetles? |
- cantharidin
- produced by males, but transferred to females during copulation |
|
|
please choose the parameter of toxicity that is most reliable as a guide to determining the level of oral exposure that is safe for an individual animal
oral LD50, IV NOAEL, IV LD50, Oral LOAEL, Oral NOAEL |
- oral NOAEL
|
|
|
which one of the following types of toxicants is most likely to follow a linear dose-response model
trace metal (Cu), mutagenic carcinogen (aflatoxin), tumor-promoting carcinogen (phorbol ester), metabolizing enzyme inducer (pentobarbital), toxicant with persistent long term effects (lead) |
- mutagenic carcinogen
|
|
|
what domestic animal species is most susceptible to blister beetle toxicosis?
|
- horses
|
|
|
what type of feed to blister beetles tend to congregate on?
|
- alfalfa hay
|
|
|
- cantharidin causes blisters mainly on what two surfaces?
|
- contact dependent
- GIT during ingestion - urinary during excreted |
|
|
CS related to cantharidin toxicosis in horses?
similar to what? 2 groups of CS |
- similiar to colic
- restlessness, depression, sweating - mucous membrane congestion, tachycardia |
|
|
what can we test for cantharidin exposure?
2 |
- stomach content
- urine |
|
|
what amount of cantharidin is considered clinically relevent?
|
- any detectable concentration
|
|
|
how long does it take for cantharidin to be excreted, why is this important?
|
- renal clearance in 3-4 days
- negative test result after this period is not-diagnostic |
|
|
what can you trt with to help cantharidin toxicosis?
3 |
- enhance elimination
- correct dehydration - trt colic: pain |
|
|
how can we differentiate cantharidin poisoning from colic
|
- will have frequent and diarrhea
|
|
|
synchronous diaphragmatic flutter and muscle fasciculations in a horse are a sign of what type of poisoning?
what would we find on clin path results? |
- cantharidin
- hypocalcemia - hypomagnesemia |
|
|
fire flies contain what toxin
this toxin is related to what? common reptile affected? |
- fireflies contain lucibufagins
- related to cardiac glycosides - bearded dragons |
|
|
what is the most hazardous scorpion in north america?
|
- arizona bark scorpion
|
|
|
scorpion toxin is what kind?
|
- polypeptide neurotoxin
|
|
|
most important effect of AZ bark scorpion toxin
3 others |
- hyperaeshesia (pain with any stimulus)
- agitation - tachycardia - hypertension |
|
|
trt of scorpion toxin
is antivenom available? 2 things |
- available in Mexico, experimental in US
- control pain - maintain open airway |
|
|
poisoning with metal usually only occurs only after what?
what metal might be an exception? |
- high and persistent exposure
- lead |
|
|
name 4 essential biological functions that metals are needed for
|
- electron transfer
- redox rxns - electrochemistry and signaling - structure |
|
|
toxicity mechanisms for metals
4, and give an example |
- oxidative damage: Zince
- altered electrophysiology and osmotic states: Na - competition with "normal" elements for absorption: Mo, Cu - incorporation into proteins in place of normal constituents: Pb/ Ca |
|
|
name the 6 most important veterinary metals
|
- lead
- copper - zinc - sodium - iron - arsenic (metalloid) |
|
|
primary target for lead poisoning
|
- nervous system
|
|
|
effects of lead
2 |
- mildly irritant to GI mucosa
- anemia due to interference with RBC maturation |
|
|
is there any safe exposure level of lead in humans?
|
- no
|
|
|
common sources of lead poisoning
4 |
- lead carbonate from old paint
- lead acid batteries - industrial/mining pollution - lead shot, fishing weights, toys |
|
|
what % of pit viper bites are associated with envenomations leading to severe poisoning
- 10-15 - 20 -25 - 35 - 50 |
10-15 %
|
|
|
what is the effect/function of hyaluronidase in pit viper venom
fibrinolysis, tissue necoris, neurotransmitter blocking, venom spreading, myocardial depression |
- spreading factor
|
|
|
a dog was bitten by a coral snake. how long should it be monitored for neurotoxic effects
- 4 hrs 12 hrs 18 hrs 36 hrs 72 hrs |
18 hours
|
|
|
what sample should be submitted for detecing cantharidin exposure in a horse?
whole blood, serum, urine, liver, kidney |
- urine
|
|
|
what 3 factors will increase the absorption of lead?
|
- more surface area (GIT mucosal area)
- acidic environment (low pH leads to ionization) - more time (lead particles may be trapped in reticulum |
|
|
tissue half lifes of lead
blood liver/kidney brain bone |
- few days
- weeks - months - 1000 days, but essentially a lifetime |
|
|
CNS effects of lead
name 3 |
- NT disruption
- endothelial damage/ pinpoint hemorrhage - moderate brain swelling, necrosis of gyri tips |
|
|
effect of lead on RBCs
2 |
- elevated numbers of nucleated RBCs
- variable degrees of anemia |
|
|
2 other effects of lead
|
- GIT irritation, more pronounced in monogastrics
- reduced production and fertility |
|
|
what is the most common CS seen with lead poisoning?
|
neurological
|
|
|
what presentation of lead poisoning is seen most commonly in dogs?
|
- GIT effects
- vomiting - diarrhea |
|
|
diagnosis of blood toxicosis needs what sample?
live animal dead animal |
- live
- whole blood - Pb binds to RBC membranes - dead - liver/kidney |
|
|
what method is used by EPA to determine impact of lead in wildlife?
|
- aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (ALAD) suppression
|
|
|
what are the 4 trt methods for lead poisoning
|
- remove the source
- counter brain edema with corticosteriods and diuretics - supportive trt: fluids, electrolytes, anti-seizures - sulfate salts to reduce absorption ---sodium sulfate, magnesium sulfate |
|
|
chelating agents for trt of lead poisoning
cattle small animals |
- Ca- EDTA for cattle
- Succimer (DMSA) for small animals |
|
|
what species are most at risk for copper poisoning
2 |
- sheep and goats
|
|
|
what appearence do kidneys have with copper poisoning?
|
- gun-metal black kidneys
|
|
|
what is the most common source of copper poisoning?
|
- excessive copper in the feed
- copper in cattle feed can be too much for sheep |
|
|
name 3 other sources of copper causing poisoning
|
orchard sprays
algaecides industrial pollution |
|
|
how is copper [ ] regulated in the body? name 3
which are sheep deficient in? |
- modulated uptake
- storage in the liver - excretion in the bile - sheep are deficient in excretion from the liver, and copper accumulates |
|
|
what effect does copper have on RBCs
2 |
- oxidative damage to RBCs
- hemolysis |
|
|
what initiates release of high liver copper to the blood?
|
stress
|
|
|
clinical presentation of copper poisoning usually occurs after what 2 occurences?
|
- chronic exposure
- acute stress |
|
|
name 4 clin path signs of copper poisoning
|
- methemoglobinemia
- anemia - hemoglobinuria - signs of liver and renal failure (elevated liver enzymes, creatinine, BUN) |
|
|
necropsy lesions for copper poisoning
4 |
- icterus
- brown colored blood - hepatosis - gun metal kidneys |
|
|
what is the relationship of Mo to Cu when ingested
|
- Mo will decrease Cu absorption and vice versa
|
|
|
what copper [ ] should not be exceeded in sheep feed?
what about cattle feed? |
- 20 ppm for sheep
- 50 ppm for cattle |
|
|
besides Mo, what other minerals will reduce uptake of copper?
3 |
- Fe
- Zn - S |
|
|
trt of copper poisoning
3 |
- remove source
- limit stress - chelation |
|
|
what should the Cu:Mo ratio be in order to prevent copper poisoning?
|
- maintain ratio at 6:1 to 10:1
|
|
|
what effect can excessive molybdenum cause?
name the mineral and effect |
- copper deficiency
|
|
|
what effects does molybdenum poisoning have?
5 |
- poor growth and production
- lightening of coat color - diarrhea - immune deficiency - glucose intolerance (type 2 diabetes?) |
|
|
what effect does zinc poisoning have in dogs?
what about other species? |
- hemolytic anemia in dogs
- pancreatitis in other species |
|
|
what are some common sources of zinc that cause problems?
|
- post 1982 pennies
- galvanized metal - zinc oxide ointments - shampoos - dietary formulation errors |
|
|
what is the MOA of zinc poisoning in dogs?
what other effect does this zinc have? |
- oxidative damage
- GIT irritation |
|
|
what effect does zinc poisoning have in other species besides dogs?
|
- zince accumulates in the pancreas
- it has cytotoxic effects causing pacreatitis |
|
|
what type of tubes are used for diagnosing Zinc poisoning, why?
|
- collect serum in tubes with royal blue tops
- rubber tops of normal tubes contain Zn |
|
|
name the 4 methods for trt of zinc poisoning
|
- give antacids to increase gastric pH: reduces Zn dissolution
- remove source: endoscopy, surgery - chelation: Ca- EDTA, Succimer - supportive: fluids, diuretics, etc |
|
|
which element has the most significant effect on the toxic potential of copper?
|
MO
|
|
|
Which chelating agent is most appropriate for treating copper poisoning in sheep?
Ca- EDTA, Dimercaperol (BAL), Succimer (DMSA), Ammonium tetrathiomollybdate, Penicillamine |
penicillamine
|
|
|
What is the half life of lead in the skeletal system of cattle
1-3 days, 10-14 days, 60-90 days, 120-280 days, >1000 days |
>1000 days
|
|
|
what sample should be submitted for detecting acute lead poisoning in a live animal?
serum, kidney, whole blood, hair, plasma |
- whole blood for live animal
- kidney, liver for dead animal |
|
|
sodium toxicity is usually the result of what?
|
- water deprivation
|
|
|
name two lesion found with sodium toxicity, or water deprivation
|
- brain edema
- eosinophillic meningoencephalitis |
|
|
name 3 scenarios where sodium toxicity can occur
|
- water deprivation with moderately high salt intake
- ingestion of large doses of salt - sudden ingestion of large water volumes |
|
|
what species is sodium toxicity most common in
|
pigs
|
|
|
common CS for sodium toxicosis in pigs
|
- restlessness, circling, ataxia, muscle tremors, head pressing
|
|
|
how would you treat a case of sodium toxicosis?
4 things |
- SLOW oral rehydration
- SLOW IV rehydration with furosemide - rehydration by enema - mannitol diuresis to reduce brain edema |
|
|
what are the 2 most common causes of iron poisoning?
|
- dose miscalculation for piglets
- accidental ingestion by pets |
|
|
MOA for iron poisoning
|
- elemental iron is corrosive to the GI mucosa
- cause rapid fluid loss and shock - ulceration and perforation |
|
|
iron is usually bound to what protein in the blood?
excess iron leads to what? What 2 tissues are most susceptible? |
- transferrin
- unbound iron leads to free-radical mediated oxidative tissue damage: liver, myocardium |
|
|
CS of iron poisoning after ingestion
Early 1-6 hrs After latent period 6-24 hrs After 2 or more wks |
early: vomiting, diarrhea
after latent: heart and liver failure, acidosis, lethargy, seizures, coma after 2 weeks: GI scarring, strictures |
|
|
name some necropsy lesions found after iron poisoning
5 |
- gastroenteritis, gastric ulceration
- yellow-brown discoloration around injection site - swollen liver, discolored - icterus - kidneys dark in color |
|
|
confirming the diagnosis of iron poisoning can be done by what 3 methods
|
- HISTORY is usually very important
- radiographs - serum iron or total iron binding capacity |
|
|
what are some ways to treat iron poisoning?
|
- emesis/ gastric lavage
- laxatives - GI protectorants (sulcralfate) - iron chelation |
|
|
inorganic arsenic affects what tissue most commonly
|
- GIT
|
|
|
organic arsenic affects what tissue most commonly?
|
- many tissues affected
|
|
|
common sources for inorganic arsenic include
|
- herbicides
- insecticide baits - paint pigments |
|
|
lesions of inorganic arsenic poisoning
name 4 GIT lesions due to irritation and contact necrosis |
- tissue sloughing
- ulceration - hemorrhage - increased fluid secretion |
|
|
4 CS of inorganic arsenic poisoning
|
- vomiting
- diarrhea - dehydration - shock |
|
|
inorganic arsinic confirmatory test
live animal dead animal other sample? |
- live: urine, GI content
- dead: liver/ kidney - hair can be useful in chronic exposure |
|
|
treatment of inorganic arsenic poisoning
2 general ways |
- chelation: BAL (demercaprol) most effective
--- also DMSA (succimer) - supportive care: fluids/electrolytes, bicarb, blood |
|
|
which arsenic is more easily absorbed from the GIT?
|
- organic arsenic
|
|
|
does organic arsenic cause oxidative damage?
|
no
|
|
|
use of organic arsenic in feed
3 reasons |
- growth promotion
- coccidiostats - bacteriostats |
|
|
how is arsenic used in dogs?
|
- trt of HW
|
|
|
what is the effect of organic arsenic on the CNS
|
- causes axonal demyelinating neuropathy
- most severe in sciatic and optic nerves |
|
|
CS of organic arsenic poisoning in pigs
|
- ataxia, goose stepping
- blindness |
|
|
what is the general consideration for use of arsenicals in feed?
|
- arsenicals should be reduced after 2 wks of trt
|
|
|
how can you detect high circulating excess iron levels by looking at urine?
|
trt with deferoxamine and look for red color
|
|
|
what is the best sample for detecting aresenic
pancreas hair muscle muscle liver kidney |
hair
|
|
|
what nerves are most susceptible to organic arsenic poisoning?
|
sciatic
usually longest nerves |

