![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Synthesis of an alkene by DEHALOGENATION of alkyl halide
|
E2 using bulky bases
(DBU, t-BuOK, DBN, LDA) polar protic solvents favor |
|
|
Synthesis of an alkene by removing TOSYLATES
|
E2
eliminate the beta H, and it has to be in anti-periplanar |
|
|
1) Synthesis of an alkene by DEHYDRATION OF AN ALCOHOL
|
using H2SO4 or TsOH acids
II° and III° alcohols go E1 (every time there is a carbocation intermediate there is the possibility of rearrangement) I° and methyl alcohols go E2 CAN REARRANGE IN E1 |
|
|
Strong, non-nucleophilic bases
|
DBU, t-BuOK, DBN, LDA
E2 |
|
|
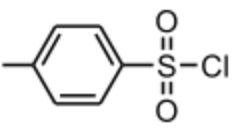
Tosyl chloride
TsCl reaction goes via E1 mechanism for II° and III° alcohols, and E2 for I° and methyl alcohols. AND every time there is a carbocation intermediate (E1 mech.) there is the possibility of rearrangement. |
|
|
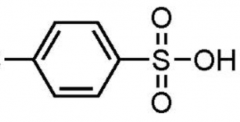
Tosyl alcohol
TsOH reaction goes via E1 mechanism for II° and III° alcohols, and E2 for I° and methyl alcohols. AND every time there is a carbocation intermediate (E1 mech.) there is the possibility of rearrangement. |
|
|
2) Synthesis of an alkene by DEHYDRATION OF AN ALCOHOL
|
using POCl3 in pyridine via E2
|
|
|
POCl3
|
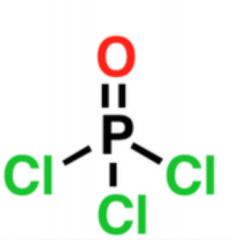
Used for the dehydration of alcohols by creating a good leaving group. Used with pyridine. E2 mechanism
|
|
|
4 ways to create an alkene
|
1) dehalogenation of alkyl halide
2) removing tosylates 3) dehydration of alcohol with H2SO4 or TsOH acids 4) dehydration of alcohol with POCl3 in pyridine |
|
|
Synthesis of alkyne
|
From geminal and vicinal dihalides: Using at least 2 equivalents of a strong base (NaNH2,
t-BuOK, LDA). Make sure there are enough beta-hydrogens to eliminate. |
|
|
Hydrohalogenation
|
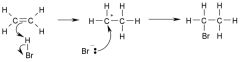
Using HX (X= Cl, Br, I)
SN1 mechanism where the most stable carbocation is formed and then attacked by the halogen. Vinyl halides (E or Z) are the product of the addition if 1 equivalent of HX is used. Geminal dihalides is the product if 2 equivalents of HX are used. (Check mechanism) |
|
|
pyridine
|
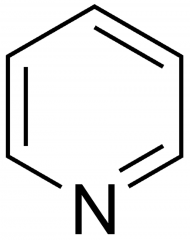
used with POCl3 in the dehydration of alcohols
|

