![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
101 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
How does energy enter the ecosystem? |
By light |
|
|
|
What does photosynthesis generate? |
Oxygen and organic molecules |
|
|
|
How do cells generate ATP? |
They use chemical energy stored in organic molecules |
|
|
|
How do catabolic pathways yield energy? |
By oxidizing organic fuels. |
|
|
|
How do catabolic pathways work? |
They release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules. |
|
|
|
What does breaking down complex molecules do? |
Release electrons |
|
|
|
Is the breakdown of organic molecules is exergonic or endergonic? |
Exergonic |
|
|
|
What kind of energy is released in the breakdown of organic molecules? |
Potential energy |
|
|
|
What is fermentation? |
A partial degradation of sugars that occurs without Oxygen |
Wine, cheese, beer, bread |
|
|
What are the 3 types of catabolic pathways to produce ATP? |
Fermentation Aerobic respiration Anaerobic respiration |
|
|
|
Aerobic and anaerobic respiration are both considered what? |
Cellular respiration |
Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel. |
|
|
What is involved in aerobic respiration? |
Consumes organic molecules and Oxygen, yielding ATP. |
|
|
|
What is anaerobic respiration? |
Similar to aerobic respiration, but consumes compounds other than oxygen. |
|
|
|
Organic compounds + oxygen —> |
Carbon dioxide + water + energy |
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 —> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + energy (ATP and heat) |
|
|
How is energy released in reactions? |
The transfer of electrons releases energy stored in organic molecules. |
|
|
|
What is released energy used for? |
Synthesize ATP |
|
|
|
What are redox reactions? |
Chemical reactions that transfer electrons between reactants |
|
|
|
What is LEO says GER? |
Losing Electrons: Oxidation Gaining Electrons: Reduction |
|
|
|
What is Oxidation? |
A substance loses electrons and is oxidized |
|
|
|
What is reduction? |
A substance gains electrons, or is reduced (the amount of positive charge is reduced) |
|
|
|
In a redox reaction, what is the reducing agent? |
The electron donor |
|
|
|
What is the oxidizing agent in a redox reaction? |
The electron receptor |
|
|
|
Why do some redox reactions not transfer electrons? |
They change the electron sharing in covalent bonds. |
|
|
|
What is Xe- |
The electron donor Become oxidized Is the reducing agent (reduces Y) |
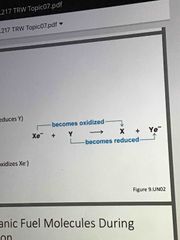
|
|
|
What is Y? |
Accepts electron Becomes Reduced Is the oxidizing agent (oxidizes Xe-) |
|
|
|
What are sources of high energy electrons? |
Organic molecules with an abundance of H |
|
|
|
How is energy released during CR? |
As the electrons associated with H ions are transferred to O, a lower energy state |
|
|
|
What happens during CR (redox) |
Fuel (glucose) is oxidized Oxygen is reduced |
|
|
|
During the Stepwise Energy Harvest, electrons are transferred first from what, to where? |
Electrons are transferred from organic compounds to NAD+, a coenzyme. |
|
|
|
As an electron acceptor, what does NAD+ function as? |
It functions as an oxidizing agent during CR |
|
|
|
What does each NADH represent? And what IS NADH |
Represents stored energy that is tapped to synthesize ATP NADH is the reduced form of NAD |
|
|
|
Where does NADH send electrons? |
The ETC |
|
|
|
How does the ETC pass electrons? |
IN a series of steps |
|
|
|
What function does Oxygen play in the ETC? |
Plus electrons down the chain in an energy-yielding tumble |
|
|
|
What are the 3 steps of CR? |
Glycolysis CAC Oxidative Phosphorylation |
|
|
|
What is glycolysis in CR? |
Breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate |
|
|
|
What is the Citric Acid Cycle in CR? |
Completes the breakdown of glucose |
|
|
|
What is Oxidative Phosphorylation in terms of ATP production? |
Powered by redox reactions of the electron transport chain 90% of ATP production |
|
|
|
What is Substrate level Phosphorylation in terms of ATP production? |
Enzyme transfers phosphate group from substrate to ADP Less ATP produced via glycolysis and the CAC |
|
|
|
How much ATP is produced for each glucose molecule? |
Up to 32 ATP molecules |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of Glycolysis? |
Oxidizing glucose to pyruvate |
|
|
|
What is Glycolysis? |
Sugar Splitting |
|
|
|
What does glycolysis do to one molecule of Glucose? |
Splits one glucose into 2 pyruvate |
|
|
|
Where does glycolysis occur? |
In the cytosol |
|
|
|
Is Oxygen needed for glycolysis? |
Nope, doesn’t matter. |
|
|
|
What types of cells support glycolysis? |
Eukaryotic and Prokarytic |
|
|
|
What are the 2 major phases o Glycolysis? |
NRG investment phase NRG payoff phase |
|
|
|
What is the NRG investment phase? |
Cell expends energy (2ATP) |
|
|
|
What is NRG payoff phase? |
Cell produces ATP is substrate level phosphorylation. |
|
|
|
What is the Net Production from one glucose? |
2 Pyruvate 2 ATP 2 H2O 2 NADH and 2 H+ |
|
|
|
What happens at the end of Glycolysis? |
All of the C originally in glucose is found in the 2 molecules of pyruvate. NO C is released as CO2 in glycolysis |
|
|
|
What happens to pyruvate in the presence of Oxygen? |
It enters a mitochondrian |
|
|
|
In Pyruvate Oxidation, what is completed? |
Oxidation of glucose |
|
|
|
What must happen before the CAC can begin? |
Pyruvate needs to be converted to Acetyl Coenzyme A (Acetyl CoA) |
|
|
|
What does pyruvate do in terms of Glycolysis and the CAC? |
It links them |
|
|
|
What is a function of Pyruvate Oxydation? |
Converts Pyruvate to Acetyl CoA |
|
|
|
How is Pyruvate oxidation carried out? (3) |
1. Oxidation of pyruvate and release of CO2 2. Reduction of NAD+ to NADH 3. Combination of the remaining two carbon fragment and coenzyme A to form Acetyl CoA |
|
|
|
Acetyl CoA can now enter the CAC after which cycle? |
Pyruvate oxidation |
|
|
|
What does the CAC do? Where does it occur? |
Completes the breakdown of pyruvate to CO2 and it occurs in the Mito Matrix |
|
|
|
What output does the CAC generate in one cycle? |
1 ATP 3 NADH 1 FADH2 |
|
|
|
What happens to each pyruvate in the CAC? |
It becomes 3 CO2 - one in Pyruvate oxidation - two in CAC |
|
|
|
How many steps does the CAC have? |
8 |
|
|
|
How is citrate formed during the CAC? |
The Acetyl group of Acetyl CoA joins the cycle by combing with oxaloacetate. |
|
|
|
What do steps 2-8 in the CAC do? |
Decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate |
|
|
|
What do steps 2-8 in the CAC do? |
Decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate |
|
|
|
Where do the carbons in the CAC go after Acetyl CoA? |
They become carbons in oxaloacetate in a subsequent cycle? And are lost as carbon dioxide in the subsequent cycle |
|
|
|
What does each Acetyl CoA produce? |
1 ATP 1 FADH2 3 NADH |
|
|
|
What do NADH and FADH2 produced by the CAC do? |
They relay electrons extracted from food to the ETC |
|
|
|
What does the CAC produce per revolution? |
1 ATP 3 NADH 1 FADH2 |
|
|
|
Most of the energy extracted from food comes from where? |
NADH and FADH2 |
|
|
|
What does the ETC do? |
Powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation |
|
|
|
Where does the ETC occur? |
In the inner membrane of the mito |
|
|
|
What is the first step of the ETC? |
Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the ETC |
|
|
|
What are electrons passed through in the second step of the ETC? |
Proteins including cytochromes. Each one with an iron atom to oxygen |
|
|
|
What happens to the energy in electrons during the ETC? |
Electrons drop in free energy as they go down the chain and are finally passed to O2, forming water |
|
|
|
Are electron carriers reduced or oxidized states? |
They alternate between reduced and oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons |
|
|
|
What happens at the terminal electron acceptor? |
Oxygen, which strongly electronegative then forms water |
|
|
|
Does the ETC generate ATP? |
Not directly |
|
|
|
What happens to protons in the ETC? |
They are pumped from the mito matrix to the inter membrane space |
|
|
|
What does the ETC do in terms of protons? |
Increases the concentration of protons in the inter membrane space. |
|
|
|
What do the protons do once in the inter membrane space? |
They move down the concentration gradient back across the membrane. And they pass through the protein complex ATP Synthase |
|
|
|
What is Chemiosmosis? |
The use of energy in a proton gradient to drive cellular work |
|
|
|
HOw does Chemiosmosis work? |
Proton moves into binding sites on the rotor of ATP synthase, causing it to spin and catalyze phosphorylation of ADP and inorganic phosphate > ATP |
|
|
|
What are the first 2 of 5 steps of chemiosmosis? |
1. Hydrogen ions flow down concentration gradient 2. Hydrogen ions enter building sites in rotor, changing shape of subunit so rotor spins within the membrane |
|
|
|
What are steps 3 and 4 of 5 in chemiosmosis? |
3. Each proton makes one spin before exiting via a channel into the mito matrix 4. Spinning of rotor causes internal rod to spin |
|
|
|
What is the 5th step in chemiosmosis? |
Spinning rod causes catalytic sites in the catalytic knob to produce ATP from ADP and P |
|
|
|
What is the sequence of energy flow during CR? |
Glucose -> NADH -> ETC -> proton motive force -> ATP |
|
|
|
How much of the energy in a glucose molecule is transferred to atp? |
34% making 32 ATP |
|
|
|
What is oxidative phosphorylation and what does it contain? |
ETC and Chemiosmosis |
|
|
|
After what cycle and in the presence of Oxygen do cells use aerobic respiration? |
Glycolysis |
|
|
|
What makes electrons move down the ETC? |
Electronegative Oxygen |
|
|
|
Does anaerobic respiration use an ETC? |
Yes, but it does not use oxygen as final electron acceptor, so it doesn’t produce water at the end |
|
|
|
What is fermentation? |
Uses substrate level phosphorylation instead of an ETC to generate ATP Consists of glycolysis plus reactions that regenerate NAD+ which can be reused by glycolysis |
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of fermentation? |
Alcohol fermentation Lactic acid fermentation |
|
|
|
What happens in alcohol fermentation? |
Pyruvate is converted to ethanol in 2 steps |
|
|
|
What are the 2 steps of AF |
Release CO2 from Pyruvate Produce NAD+ and ethanol |
|
|
|
What happens in LAF? |
Pyruvate is reduced by NADH forming NAD+ and lactate as end products with no release of CO2 |
|
|
|
What do Fermentation, Aerobic Respiration, and Anaerobic Respiration have in common? |
Glycolysis. Used to oxidize glucose and harvest the chemical energy of food. |
|
|
|
In fermentation, what acts as the final electron acceptor? |
Organic molecule, pyruvate or acetaldehyde |
|
|
|
How many ATP does Fermentation produce? |
2 |
|
|
|
How many ATP are produced in CR? |
32 ATP |
|

