![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is homeostasis? |
It is the maintenance of a stable internal environment |
|
|
What needs to be maintained in homeostasis? |
Core body temperature - 37℃ Blood pH - around pH 7 Glucose concentration |
|
|
Why must blood glucose concentration be maintained? |
Too high - water diffused out of cells causing cells to shrivel up and die. Too low - cells are unable to carry out normal activities. |
|
|
What is negative feedback? |

It is the mechanism that restores the level to normal. Although it has limits, that it may not be able to counteract |
|
|
Why do multiple negative feedback mechanisms give more control? |
Because you can actively increase and decrease a level so that it returns to normal |
|
|
When is positively feedback useful? |
Blood clot after an injury, platelets become activated, and release a chemical that triggers more platelets to be activated. Th process ends with negative feedback. |
|
|
What is the normal concentration of glucose in the blood? |
90mg per 100cm^3 of blood |
|
|
How is blood glucose monitored? |
By cells in the pancreas |
|
|
How does insulin lower blood glucose? |
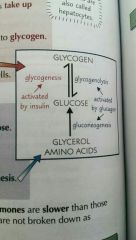
Beta cells secrete insulin, which binds to specific receptors on the cell membranes of liver and muscle cells. Which increases the permeability to glucose, and also activates enzymes that convert glucose into glycogen. |
|
|
How does glucagon increase blood glucose concentration? |

Binds to specific receptors on the cell membranes of liver cells and activates enzymes that breaks down glycogen into glucose. It also decreases the rate of respiration of glucose in cells. |
|
|
Negative feedback system for maintaining blood glucose |
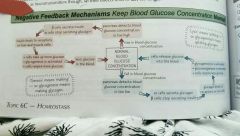
|
|
|
How does adrenaline increase blood glucose concentration? |
It binds to receptors in the cell membrane of liver cells: - It activates glycogenolysis - It inhibits glycogensis It als activates glucagon secretion and inhibits insulin secretion |
|
|
How do adrenaline and glucagon activate glycogenolysis? |

Binds to receptors and activate the enzyme called adenylate cyclase. Which converts ATP into a chemical signal called a 'second messenger' which is called cyclic AMP (cAMP). cAMP activates protein kinase A, an enzyme that activates a cascade that breaks down glycogen into glucose. |
|
|
What is type 1 diabetes and how is it controlled? |
The immune system attacks the beta cells in the islets of langerhans so they can't produce insulin. Treated with insulin therapy and controlling simple carb intake. |
|
|
What is type 2 diabetes and how is it controlled? |
Linked with obesity, lack of exercise, age and poor diet. Beta cells don't produce enough insulin/ cells are no longer responsive to it. Treated with healthy, balanced diet, losing weight and regular exercise. Glucose-lowering medication can be taken, and eventually insulin injections may be needed. |
|
|
What is the name of the arteriole that brings blood to the glomerulus in the kidneys |
Afferent arteriole and the efferent arteriole takes it away |
|
|
What is the role of the glomerulus? |
The blood passes through under high pressure, which forceps liquid and small molecules into the bowman's capsule. The liquid and small molecules must pass through three layers to get to the bowman's capsule, which larger molecules like proteins and blood cells can't pass through, so stay in the blood. |
|
|
What are the substancmes that enter the Bowman's capsule known as? |
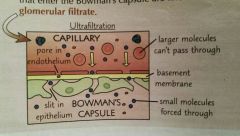
Glomerular filtrate |
|
|
The structure of the kidneys |
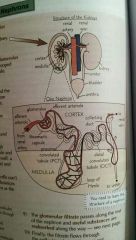
|
|
|
Describe the process of the nephron |
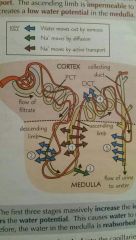
1- the ascending limb - Na+ ions are pumped out (AT), impermeable to water. 2- the descending limb - water moves out. 3- Na+ ions diffuse out 4- water moves out of the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) by osmosis 5- the first three stages increase the ion concentration in the medulla, which lowers the water potential and causes water to move out of the collecting duct. |
|
|
How is water reabsorption in the nephron controlled? |
It is controlled by hormones. Water potential of the blood is monitored by osmoreceptor in the brain called hypothalamus. It sends a signal to the pituitary gland which releases the hormone called antidiuretic hormone (ADH) into the blood. ADH makes the walls of the collecting duct more permeable to water |
|
|
What is ADH? |
Antidiuretic hormone Released by posterior pituitary gland Blood ADH level rises when you're dehydrated Blood ADH levels fall when you're hydrated |

