![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Equation for photosynthesis |

|
|
|
|
ATP molecule |

|
|
|
|
Properties that make ATP a good energy source |
->Energy is released in small, amounts, so energy is not wasted as heat energy. ->Small and soluble, so east to transport. ->Easily broken down, so energy can be released instantaneously. ->Can be re-made quickly. ->Can make other molecules more reactive (phosphorylation) ->ATP can't pass out of the cell |
Size, energy, is it soluble? |
|
|
Metabolic pathway |
A series of small reactions controlled by enzymes |
|
|
|
Phosphorylation |
Adding phosphate to a molecule. |
|
|
|
Photophosphorylation |
Adding phosphate to a molecule using light |
|
|
|
Photolysis |
The splitting (lysis) of a molecule using light (photo) energy |
What is lysis? |
|
|
Photoionisation |
When light energy 'excites' electrons in an atom or molecule, giving them more energy and causing them to be released. The release of electrons causes the atom or molecule to become a positively-charged ion |
|
|
|
Hydrolysis |
The splitting (lysis) of a molecule using water (hydro) |
|
|
|
Decarboxylation |
The removal of CO2 from a molecule |
|
|
|
Dehydrogenation |
The removal of hydrogen from a molecule |
|
|
|
Redox reactions |
Reactions that involve oxidation and reduction - OIL RIG - oxidation is loss reduction is gain |
What is oxidation and reduction |
|
|
What is a coenzyme? |
It is a molecule that aids the function of an enzyme. They work by transferring a chemical group from one molecule to another.
Examples: NADP, NAD, coenzyme A and FAD |
Examples |
|
|
Where does photosynthesis take place? |
In the chloroplasts. The pigments for photosynthesis are found in the thylakoid membranes |
Where are the pigments found? |
|
|
How many photosytems are there? |
Two. Photosystem I (PSI) which absorbs light with a wavelength of 700nm and photosystem II (PSII) which absorbs the light best at 680nm. |
|
|
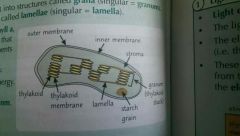
Why is the stroma (in the chloroplasts useful? |
It contains enzymes, sugars and organic acids. |
|
|
|
What is the Light-independent reaction (of photosynthesis) also called? And where does it take place? |
It is also called the Calvin cycle. It takes place in the stroma |
|
|
|
The light-dependant and light independent reactions |

|
|
|
|
What does non-cyclic photophosphorylation produce? |
ATP, reduced NADP AND O2 |
|
|
|
Describe the process of non-cyclic photophosphorylation (light-dependant reaction) |

|
1- light energy excites electrons in chlorophyll 2- photolysis of water produces protons (H+ ions), electrons and O2 3- energy from the excited electrons makes ATP... 4-...and generates reduced NADP |
|
|
Describe the Calvin cycle |

|
1- carbon dioxide is combined with ribulose bisphosphate to form two molecules of glycerate 3-phosphate. 2- ATP and reduced NADP are required for the reduction of GP to triose phosphate. 3- Ribulose bisphosphate is regenerated. |
|
|
How many ATP AND reduced NADP ARE needed for 6 turns in the Calvin cycle |
18 ATP and 12 reduced NADP |
|
|
|
What is produced by the Calvin cycle |
ADP + Pi, NADP, triose phosphate |
|
|
|
What are triose phosphate (TP) and glycerate 3-phosphate (GP) from the Calvin cycle useful for? |
Useful for make: carbohydrates - hexose sugars are made by joining two TP molecules together Lipids - glycerol is synthesized from TP and fatty acids are synthesized from GP Amino acids - some amino acids are made from GP |
Carbs, lipids and amino acids |
|
|
How many triose phosphate (TP) is produced in each turn of the Calvin cycle, and in how many turns is one TP produced to be used to make useful organic substances? |
Two TP are produced on each cycle of the Calvin cycle. For every three turns of the cycle, only one TP is produced to be used as a useful organic substances. |
|
|
|
What are the optimum conditions for photosynthesis? |
Light - red and blue (green is reflected) Temperature - around 25℃ Carbon dioxide - 0.4%, too high causes the stomata to close. |
|
|
|
What photosynthesis experiments are there? |
Chromatography to investigate pigments in leaves Investigate the activity of dehydrogenase in chloroplasts |
|
|
|
How do you investigate the pigments in leaves? |
Chromatography. -Grind up the leaves with anhydrous sodium sulfate then add a few drops of propanone. -Transfer the liquid to a test tube, add some petroleum ether, and gkently shake. Two layers - top layer is pigments mixed with petroleum ether. -place spot on chromatography paper (as usual) -Put paper in a jar with solvent in, put lid on and leave to develop -calculate Rf values and compare |
Chromatography |
|
|
How do you calculate the Rd value? (Chromatography) |
Distance travelled by spot/distance travelled by solvent |
|
|
|
How do you investigate the activity of dehydrogenase in chloroplasts? |

|
|
|
|
What does theinvestigation of the activity of dehydrogenase in chloroplasts show? |
In the light dependant reaction, NADP acts as an electron acceptor, and is reduced. This reaction is catalysed by a dehydrogenase enzyme. If the dye DCPIP is added, it will act as an electron acceptor. As it gets reduced it changes colour from blue to colourless. This investigation therefore shows how light intensity affects the rate of the dehydrogenase enzyme (ie the light dependant stage of photosynthesis) |
|
|
|
What are the four stages of respiration? |
Glycolysis Link reaction Krebs cycle oxidative phosphorylation |
|
|
|
What ere the two stages in glycolysis and describe the process of glycolysis. |

|
Phosphorylation and oxidation |
|
|
How many ATP arrived made and used up in glycolysis? how many NAD are reduced? |
2 are used 4 are made. 2 NAD are reduced |
|
|
|
In anaerobic respiration, what is pyruvate (from glycolysis) converted to, and how? |

|
|
|
|
Describe the link reaction |

|
After glycolysis. Start - pyruvate End - acetyl CoA |
|
|
How many times does the link reaction occur for every glucose molecule? |
Twice |
|
|
|
When does the Krebs cycle occur in respiration and describe the process. |

|
Glycolysis, Link Reaction, ______, Oxidative Phosphorylation8 |
|

Where do the products of the Krebs cycle go? |
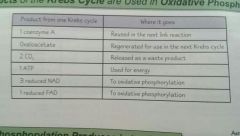
|
|
|
|
What are the products of the Krebs cycle? |

|
|
|
|
How many ATP are made from each reduced NAD and reduced FAD in oxidative phosphorylation? |
2.5 ATP are made from each reduced NAD 1.5 ATP are made from each reduced FAD |
|
|
|
Describe oxidative phosphorylation |

- electrons move down the electron transfer chain, losing energy at each carrier - this energy is used to pump protons from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space. - the protons then move along their concentration gradient, back into the matrix of mitochondrion via ATP synthase. - this movement drives the synthesis of ATP. - at the end of the transport chain, the protons, elections and O2 combine to form water. Oxygen is said to be the final electron acceptor. |
|
|
|
What does oxidative phosphorylation involve? |
Electrons transport chain and chemiosmosis |
|
|
|
What is chemiosmosis |
The process of ATP production driven by the movement of H+ ions across a membrane, this is due to elections moving down an electron transfer chain |
|
|
|
How many ATP are made from one glucose molecule |

32 |
|
|
|
How do mitochondrial diseases affect the functioning of mitochondria? |
They affect how proteins involved in oxidative phosphorylation or the Krebs cycle function, reducing ATP production. - anaerobic respiration increases - increases lactate produced - cause muscle fatigue and weakness - leads to high lactate concentrations in the blood |
|
|
|
What measures rate of oxygen consumption |
Respirometer |
|

