![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Nutrition |
Taking in of nutrients which are substances and mineral ions, containing raw material or energy for growth and tissue repair, absorbing them and assimilating them. |
|
|
|
Excretion |
The removal of toxic material from organisms, the waste product of metabolism |
|
|
|
Respiration |
This involves chemical reactions which break down nutrient molecules in living cells. |
|
|
|
Sensitivity |
This is the ability of organisms to detect or sense change in the environment and to make responses |
|
|
|
Reproduction |
This is the process which makes mode of the same kind of organism |
|
|
|
Growth |
This is the perminent increase in size and dry mass by an increase in the cell number, size or both |
|
|
|
Movement |
This is an action by an organism or part is an organism causing a change in position or place |
|
|
|
Diffusion |
Thus is the net movement of molecules from a region of their higher to their lower concentration down a concentration gradient, as a result of their random movement |
|
|
|
Osmosis |
This is the movement of water from a region of high to low concentration through a partially permeable membrane, down a water potential gradient. |
|
|
|
Hypotonic solutions |
A solution that has a higher water potential and a lower solute concentration compared to it's surroundings |
|
|
|
Hypertonic solutions |
A solution that had a lower water potential and a higher concentration compared with it's surroundings |
|
|
|
Isotonic solutions |
A solution that has equal water and skits concentration compared with it's surroundings |
|
|
|
Cell membrane |
Contracts the entry and exit of substances into and of of the cell |
|
|
|
Cell wall |
Gives plant Creek rigidity and strength |
|
|
|
Cytoplasm |
It contains the cell organelles in which the chemical reactions occur. This provides energy and chemical for cerulean function |
|
|
|
Chloroplast |
It contains chlorophyll to capture solar energy and concert CO2 and H2O into glucose |
|
|
|
Nucleas |
It regulates all cell activity. Ur contains chromosomes, structures made up of genetic information, that direct a cells Grier and reproduction |
|
|
|
Vacuole |
It gives the plant cell rigidity as water pushed against the membrane. It can also act as a storehouse for things such as water and sugar. |
|
|
|
Preparing a slide of a onion cell |
1. Clean slide 2. Take a piece of membrane from inner leaf 3. Must be thin and small 4. Lay fair to remove air bubbles 5. Add iodine 6. Add cover skip from one side to eliminate air bubbles |
|
|
|
Plant cell |
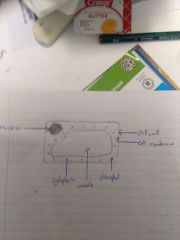
|
- chloroplast present - large vacuole - cell wall present |
|
|
Animal cell |
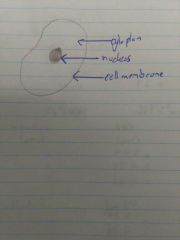
- no chloroplast - small or no vacuole -no cell wall |
|

