![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Diastema |
Any spacing between teeth |
|
|
Torus palatinus |
Large body growth in hard palate |
|
|
Ankyloglossia |
Condition where lingual frenum is short and attached to tip of tongue making normal speech difficult |
|
|
Uvula |
Small hanging fold of tissue in back of small pallate |
|
|
Hard palate |
Boney roof of the mouth |
|
|
Exostoses |
Small extra growths of bone on a bone surface usually seen on the buccal cortical plate |
|
|
Torus palatinus |
Large bony growth in hard palate |
|
|
Mandibular tori |
Bony growths on the lingual cortical plate of bone opposite the mandibular canines |
|
|
Alveolar mucosa |
Mucosa bw the mucobuccal fold and gingiva |
|
|
Mucojingival junction |
Point at which the alveolar mucosa becomes the gingiva |
|
|
Labial frenum |
Fold of tissue that attaches the lip to the labial mucosa @ midline of the lips |
|
|
Sublingual caruncle |
Small elevation of soft tissue @ base of the lingual frenum that is the opening for the submandibular duct |
|
|
Lingual frenum |
Fold of tissue that attaches the undersurface of the tongue to the floor of the mouth |
|
|
Rugae |
Small ridges of tissue extending laterally across the anterior of the hard palate |
|
|
Fordyce granules |
Misplaced sebaceous glands in the lips cheek or retromolar pad area |
|
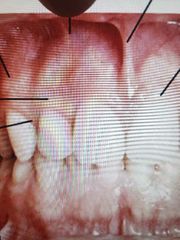
What area is my thumb pointing too |
Muccobuccal fold ot is covered by the alveolar mucosa |
|
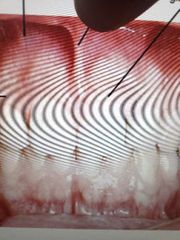
What area is my thumb pointing too |
Maxillary frenum |
|
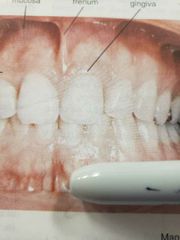
What area |
Mandibular labial frenum |
|
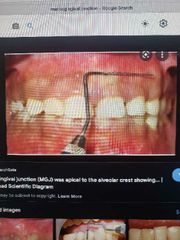
What area is this showing |
The mucogingival junction |
|
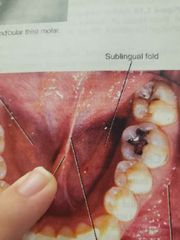
What area |
Lingual frenum |
|
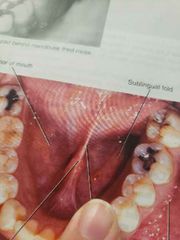
What area |
Sublingual fold |
|
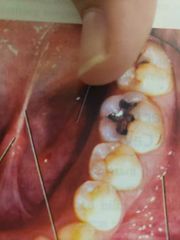
What area |
Sublingual caruncle |
|
|
Pulp |
Dentin reparitive system of tooth |
|
|
Enamel |
Hard calcified tissue that covers the dentin of the crown portion of tooth |
|
|
Dentin |
Hard calcifiedbtissue forming the inside body of tooth underlying the cementum and enamel surrounding the pulpal tissue |
|
|
Cementum |
Layer of bine like tissue covering root of the tooth |
|
|
Anterior teeth surfaces How many ? What are they called |
4 surfaces and a ridge 1) Lingual -facing tongue 2) Labial -anterior surface facing cheek or Buccal - posterior facing cheek ( these can also be called facial) 3) 4) proximal left and right side surfaces of tooth will either be mesial or distal depending on which side is closer to the midline |
|
|
Occlusal surfaces how many what are they called |
Lingual Facial/labial/ buccal Proximal distal Proximal measial Occlusal |
|
|
Pulp canals |
Canal in root of tooth that leads from apex to root chamber contains dental pulp tissue |
|
|
Cingulum |
Lingual lobe of anterior teeth |
|
|
Contents of pulp (5) |
Blood vessels Lymph vessels Connective tissue Nerve tissue Ondoblast |
|
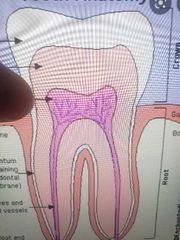
|
Pulp |
|
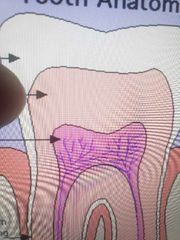
|
Dentin |
|
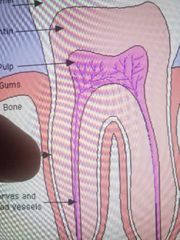
|
Cementum |
|
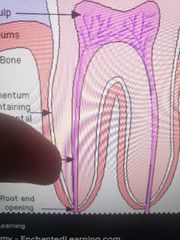
|
Pulp canals |
|
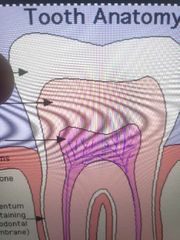
|
Enamel |
|
|
Mylohyoid muscle |
Suprahyoid muscle that forms the floor of the mouth |
|
|
Structures on tounge |
Filiform Fungiform Village Circumvallate papillae Rudimentary foliate papillae |
|
|
What should be carefully examined because it may be difficult or hide early signs of cancer |
Foliate papillae |
|
|
Inlargments of lymphoid tissue at the base of the tounge collectively referred to as |
Lingual tonsils |
|
|
2 major salivary glands |
Submandibular and sublingual salivary glands |
|
|
What is floor of the mouth supported by |
Paired mylohyoid muscles |
|
|
Flange |
Projecting edge edge of denture |
|
|
Crown and root are joined at the |
Cementoenamel junction |
|
|
Four tooth tissues |
Enamel dentin cementum nd pulp |
|
|
Hardest tissue in the body |
Enamel |
|
|
Chemical composition of enamel |
96 inorganic 4 organic |
|
|
Main portion of tooth |
Dentin |
|
|
Chemical composition of dentin |
70 inorganic and 30 organic |
|
|
Cementum chemical composition |
50 inorganic 50 to 55 organic |
|
|
2 types of cementum |
Cellular cementum Acellular cementum |
|
|
What is acellular cementum confined too ? What can it do special |
Apical 3rd root Reproduce itself |
|
|
What type of cementum covers the entire anatomic root |
Acellular cementum |
|
|
Pulp is located ? What surrounds it |
Housed in center of tooth Dentin |
|
|
Fossa |
Area on tooth that is indented or concave |
|
|
Pit |
When pinpoint hole is evident within the fossa or anywhere on the tooth |
|
|
Cusp |
Mound on the crown portion of the tooth that makes up a major division of its occlusalor insisal surface |
|
|
Where are cusp found |
Premolars and molars |
|
|
Fourth developmental lobe of anterior teeth |
Cingulum |
|
|
Makes up bulk of the cervical third of the lingual surface |
Cingulum |

