![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
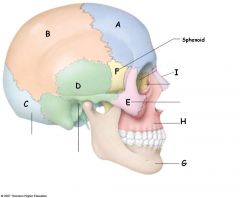
Label
|
A)frontal bone B) Parietal C) Occipital D) Temporal Bone E) Zygomatic bone F) Sphenoid G) mandible H)Maxilla I) Nasal Bone (next to I=lacrimal bone, then ethmoid bone) |
|
|
where does the spinal cord come out of the skull? |
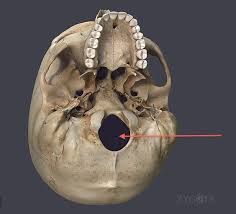
foramen magnum |
|
|
What is the join between the frontal and parietal bone? |
Bregma |
|
|
what is the join between the parietal and occipital bone? |
Lamba |
|
|
what part of the skull articulates with the atlas (C1)? |
occipital condyle |
|
|
what bones form part of the Pterion? |
parietal, frontal, temporal, sphenoid |
|
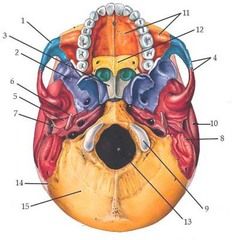
Name: 3, 11, 12 |
3: Vomer 11: maxilla (of hard palate) 12: palatine bone (part of hard palate) |
|
|
What is cranial nerve VII? where does it exit the skull? |
Facial Nerve internal acoustic meatus to stylomastoid foramen |
|
|
the facial nerve emerges as two divisions what are they? |
intermediate nerve: taste, PSNS, somatic sensory facial nerve proper: posterior auricular, parotid plexus (temporal, zygomatic, buccal, marginal mandibular, cervical) |
|
|
what are the 5 actions actions that test each branch of the trigeminal nerve? |
temporal: raise eyebrows breast forhead zygomatic: close eyes tightly against resistance buccal: puff out cheeks marginal mandibular: bear lower teeth cervical: shaving position |
|
|
what is facial artery a branch off? |
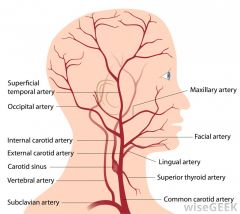
the external carotid |
|
|
what are the 4 branches of the facial artery? |
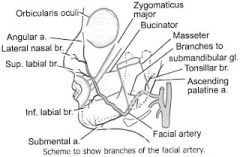
angular, lateral nasal, superior labial, inferior labial |
|
|
what is the primary superficial drainage of the eye? |
facial vein |
|
|
what is the facial nerve joined by what to drain into the internal jugular vein? |
retromandibular vein and the deep facial vein |
|
|
what the of gland is the parotid gland? |
serous gland with superficial and deep lobes |
|
|
what muscle does the parotid gland pierce? |
the buccinator and then enters the oral cavity opposite the 2nd maxillary molar |
|
|
what infections are associated with the parotid gland? |
parotiditis-imflammation mumps |
|
|
what is the parotid sheath formed from? |
deep investing cervical fascia |
|
|
what are the two parts of the cranium? |
neurocranium (containing the brain) viscerocranium (constituting the brain) |
|
|
what bones does the nasal bone articulate with? |
frontal, maxilla, ethmoid |
|
|
what bones does the maxilla articulate with? |
frontal, ethmoid, nasal, zygomatic, lacrimal, inferior concha, parietal, vomer |
|
|
what bones does the mandible articulate with? |
temporal bone |
|
|
what bones for them the nasal canal? |
ethmoid, vomer and inferior concha |
|
|
where do the emissary veins exit the skull? |
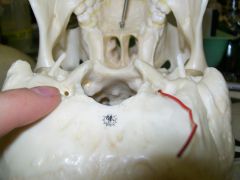
condylar canal |
|
|
where does the carotid artery enter the skull? |
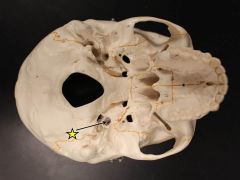
carotid canal (in temporal bone) |
|
|
where do the jugular veins leave the skull? |
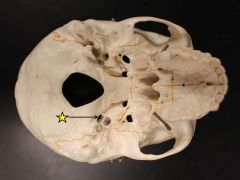
jugular foramen |
|
|
what exits the skull at the stylomastoid forame? |
the facial nerve and stylomastoid artery |
|
|
what exits through the foramen ovale in sphenoid bone? |
mandibular nerve, lesser petrosal nerve, accessory meningeal artery, emissary veins |
|
|
what exists through the foramen lacerum in the sphenoid bone? |
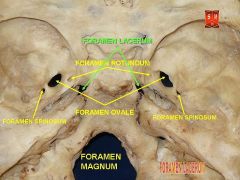
greater petrosal nerve, emissary veins, nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis |
|
|
what forms the temporomandibular joint? |
condylar process articulates with the articular tubercle of the temporal bone and the mandibular fossa separated by the articular disc |
|
|
what type of joint is the temporomandibular joint and what movements does it allow? |
loose synovial joint protrusion/retrusion elevation/depression side to side |
|
|
what are the two capsular ligaments of the temporomandibular joint and what are the two extra-capsular joint ligaments? |
capsular: lateral ligamen &synovial joint capsule
extra-capsular: sphenomandibular, stylomandibular |
|
|
what is the function of the temporomandibular ligaments? |
lateral ligamentum: strengthens the temporomandibular joint laterally and prevents posterior dislocation synovial joint capsule lig: contains the temporomandibular joint sphenomandibular : limits depression of mandible stylomandibular: limits depression of mandible |
|
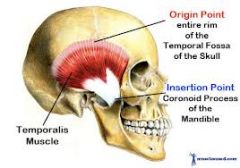
TEMPORALIS |
innervated by deep temporal nerve
elevates and retracts the mandible |
|
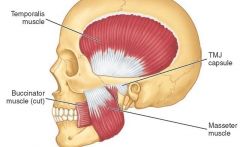
MASSETER |
inserts in to zygomtic arch
masseteric nerve
elevates and protracts the mandible |
|
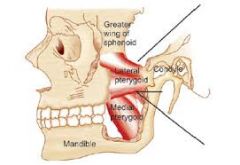
LATERAL PTERYGOIDS |
nerve to the lateral pterygoid
bilateral contraction: protracts the jaw and depresses the chin unilateral contraction: contraction moves the jaw laterally |
|
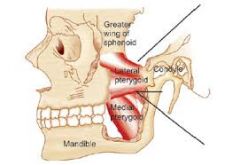
MEDIAL PTERYGOIDS |
nerve to the medial pterygoid
bilaterly: elevates and protracts the mandible unilaterally: moves the jaw laterally |
|
|
what muscles depress the mandible? |
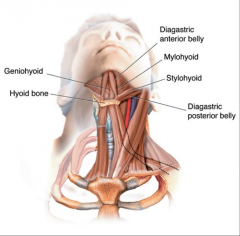
digastric, mylohyoid, geniohyoid |
|
|
what muscles elevate the mandible? |
temporalis, masseter and medial pterygoid
|
|
|
what muscles protrude the mandible? |
medial pterygoid, lateral pterygoid and masseter |
|
|
what muscles retrude the mandible? |
temporalis and masseter |
|
|
what muscles allow the mandible to move laterally? |
unilateral contraction of: temporalis, masseter and medial and lateral pterygoids |
|
|
where does the scalp extend up to on the skull? |
the zygomatic arches |
|
|
what are the 5 layers of the SCALP? |
Skin (swear, sebaceous glands, blood, lymph) Connective tissue (thick, dense, vasculated) Aponeurosis (sheath, attachment for muscles) Loose connective tissue (free movement of scalp) Pericranium (connective tissue) |
|
|
what is cranial nerve 5 and where does it originate from? |
trigeminal nerve, from the pons |
|
|
what generally does the trigeminal nerve innervate? |
muscles of mastication (small motor root) and sensory nerve of the head (large sensory route) |
|
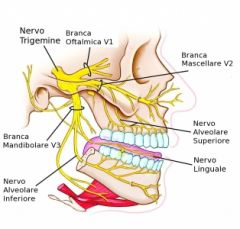
describe the course of the trigeminal nerve |
-exists from the pons into large sensory root and short motor root -moves from posterior to middle cranial fossa by passing over medial tip of petrous part of temporal bone -in middle cranial fossa, sensory root expand to form trigeminal ganglion in the trigeminal cave -divides into 3, each leaves at a different foramina
|
|
|
where do the different divisions of the trigeminal nerve leave the skull? |
V1:ophthalmic- superior orbital fissure V2: Maxillary- Foramne rotundum V3: Mandibular- Foramen ovale |
|
|
what does the ophthalmic nerve (V1) sense? |
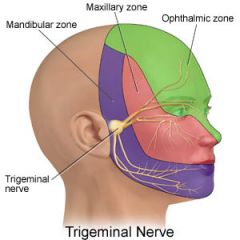
eyes, conjunctiva, orbital contents (lacrimal gland), nasal cavity, frontal sinus, anterior part of scalp
smallest branch |
|
|
What does the maxillary nerve (V2) sense? |
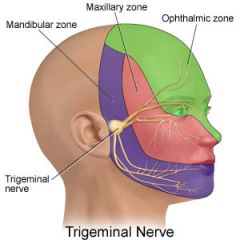
dura in middle cranial fossa, nasopharynx, palate, nasal cavity and nasal sinuses, teeth of upper jaw, maxillary sinus, skin over nose, cheek, upper lip and the lower eyelid. |
|
|
what does the mandibular nerve (V3) sense? |
SENSORY AND MOTOR, largest branch sensory: mylohyoid, digastric and muscles of mastication, anterior 2/3 of tongue, lower lip
motor: 4 MUSCLES OF MASTICATION (temporalis, masseter, medial and lateral pterygoids) |
|
|
what is trigeminal neuralgia? |
severe face pain, affects 1 in 25000 of normally on side of the face, casued by nerve compression from blood vessels |
|
|
the mandibular nerve divides into a anterior and posterior division, what nerves does it give off before this division? |
branches to medial pterygoid, tensory timpani and tensor veli palatini and the sensory meningeal branch |
|
|
the mandibular nerve gives of the motor branches to medial pterygoid, tensory timpani and tensor veli palatini and the sensory meningeal branch, then it divides into the anterior and posterior branch, what are the branches off these? |
anterior: sensory-buccal nerve motor: masseteric nerve, deep temporal nerve, nerve to lateral pterygoid Posterior: sensory: auriculotemporal nerve, lingual nerve moter and sensory: inferior alveolar nerve (sensory), mylohyoid nerve (motor)
|
|
|
when is an inferior alveolar nerve block used? |
extract or repair teeth, aesthetic supplied onto medial side of rams of mandible , lower teeth and lip and skin of chin affected. |
|
|
what is the sensory innervation of the tongue? |
anterior 2/3: sensory: lingual nerve (branch of V3) taste buds: chorda tympani (facial nerve branch)
psoterior 1/3: sensory and taste-glossopharyngeal nerve (CNIX) |
|
|
what is the motor innervation of the tongue? |
hypoglossal nerve (CNXII): intrinsic and extrinsic muscles, EXCEPT PALATOGLOSSUS M.
Vagus Nerve (CNX) palatoglossus m. |

