![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
167 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A patient reports to your office with the following symptoms, pain on palpation of the left and right temporalis muscles, pain on palpation of the right massester muscle pain on palpation in joint area and body temperature of 101F.
Based on our lecture, your most likely diagnosis is a. Referred pain b. Temporal Arteritis c. Displaced disc with reduction with pain d. Anteriorly displaced disc without reduction |
Temporal Arteritis
|
|
|
A mother brings in her 10-year-old boy for consultation for his clicking TMJ's. Your treatment recommendation is
a. Stabilization appliance b. Anterior repositioning appliance c. Surgical consultation d. Monitor |
Monitor
|
|
|
You palpate a patient’s massester muscle and discover extremely tender localized painful areas, these are called
a. Pain centers b. Referral pain nodes c. Powerpoints d. Trigger Points e. Two of the above |
Two of the above
Referral pain nodes Trigger points |
|
|
A patient comes in as an emergency; their chief complaint is a moderate toothache in #14, which has no caries or restorations. Periapical radiograph is unremarkable, periodontal probing is WNL, no pain on chewing. Exam reveals several teeth with small occlusal restorations, crown on #30 with open margins. The patient reveals pain in her jaw
for the past three weeks and points to the left masseter, which is very sore on palpation, your tentative diagnosis is a. Heterotopic pain from the left Masseter Muscle b. Pulpitis, reversible or irreversible c. Cracked tooth #14 d. Open margin of #19 |
Heterotopic pain from the left Masseter Muscle
|
|
|
Symptoms of Atypical Odontalgia are usually very painful, continuous and burning; This burning, throbbing pain is
most commonly seen in all of the maxillary teeth. a. First statement is true, second is true b. First statement is true, second is false c. First statement is false, second is true d. First statement is false, second is false |
First is TRUE
Second is FALSE |
|
|
Which of the masticatory muscle disorders exhibits increased elevator activity on opening and increased depressor
activity in closing. a. Protective Co-Contraction b. Local Muscle Soreness c. Myospasm d. Myofascial Pain e. Fibromyalgia |
Protective Co-Contractions
|
|
|
Which of the following is a non-inflammatory pain disorder caused by a change in the environment of muscle tissues,
i.e. unusual muscle activity. a. Protective Co-Contraction b. Local Muscle Soreness c. Myospasm d. Myofascial Pain e. Fibromyalgia |
Local Muscle Soreness
|
|
|
Which of the following muscle disorders would you most commonly find heterotopic pain
a. Protective Co-Contraction b. Local Muscle Soreness c. Myospasm d. Myofascial Pain e. Fibromyalgia |
Myofascial Pain
heterotopic means you feel pain in one area, but a different source is creating the pain. Myofascial pain is trigger point myalgia. |
|
|
Which of the following are treated primarily by medical disciplines and not dentistry
a. Protective Co-Contraction b. Local Muscle Soreness c. Myospasm d. Myofascial Pain e. Fibromyalgia |
Fibromyalgia
|
|
|
You examine a patient in the clinic and their history reveals, signs and symptoms; mechanical locking/catching with
movement, excessive wear facets on the majority of the teeth and clicking with pain of the left and right TMJ’s on opening and closing. Your initial treatment should be a. Anterior repositioning appliance to “re-capture” or reduce the disc b. Eliminate bruxing c. Stabilization appliance d. Surgical consult e. Nothing, this is a self-limiting disease, disc is malformed and no longer has its’ normal anatomical form and can no longer function as a normal disc. |
Eliminate Bruxing
|
|
|
A patient states they were at the Cleveland Clinic for “TMJ”, but due to insurance limitations came to the dental
school for treatment. They receive a diagnosis of disc dislocation without reduction, with pain, of the left TMJ. Without examining the patient, you would except to see/discover the following on examination. a. Previous history of clicking temporomandibular joints. b. Normal lateral movement to the patient’s left c. Limited lateral movement to the patient’s right d. Deviation of the mandible on opening e. All of the above |
All of the above
|
|
|
The purpose of trimming the anterior portion of your splint (made in lab) at a different angle/plane than the posterior was to
a. Provide posterior disclusion b. Reduce muscle activity of the masseter and temporalis muscles c. Eliminate Bruxing d. A & B e. A & C |
A&B
Provide posterior disclusion Reduce muscle activity of the masseter and temporalis muscle |
|
|
Of the theories explained in class, all of the following are mechanisms of action of stabilization appliances EXCEPT
a. Decrease muscle activity b. A more musculoskeletally stable or structurally compatible, functional position of the condylar position c. Increase in vertical dimension of occlusion d. Cognitive awareness e. Decrease bruxing |
Increase in VDO
|
|
|
Your patient has been asymptomatic for several months while wearing a stabilization appliance. You instruct the
patient they no longer require the appliance and to stop wearing it. They return to your office for a follow-up and report they are completely asymptomatic as long as they wear the appliance when sleeping; they do not need to wear it during waking hours. Your chart entry reads a. Patient suffers from occasion emotional stress b. Patient suffers from High emotional Stress c. Patient suffers from daytime bruxing and occlusal non-adaptation d. Patient suffers from nocturnal bruxing, clenching or parafunctional activity e. Daytime parafucntion |
Patient suffers from nocturnal bruxing, clenching or parafunctional activity
|
|
|
What disorders listed below may cause long term/permenant hypomobility.
a. Severe bruxism b. Adhesions c. Acute Displaced Disc with reduction d. Chronic Displaced Disc with reduction |
Adhesions ???
|
|
|
Proplast was used by surgeons for what purpose
a. To repair the condylar head b. To repair the eminentia c. To reattach the collateral ligament d. To replace the disc |
To repair the condylar head
|
|
|
Proplast was found to be a disastrous choice for many patients because
a. Tefelon would breakdown and precipitate a severe immune response b. Cause severe fossae resorption c. Cause severe ligament damage d. A & B |
A&B
Teflon would breakdown and precipitate a severe immune response Cause severe fossae resorption |
|
|
Your exam of a patient reveals left lateral movement of 10mm, right lateral movement 9mm, horizontal
overlap(overjet) 2mm, vertical overlap(overbite) 6mm , protrusive 11mm, mandibular opening measured on a ruler of 45mm. You record in their chart a mandibular opening of? a. 39mm b. 43mm c. 45mm d. 47mm e. 51mm |
51 mm
|
|
|
Your examination of a severe pain patient reveals a restricted mandibular opening of 20mm and no joint sounds. You place your fingers on the mandibular centrals and attempt to assists the patients opening. The patient is able to open now to 40mm. Your tentative diagnosis of the patient is
a. Displaced disc with reduction with pain b. Displaced disc without reduction with pain c. Local Muscle soreness d. Sever degenerative arthritis e. Could be all of the above |
Local Muscle Soreness
|
|
|
What mal-occlusions has research found to have high association with temporomandibular disorders.
a. Class II Div II deep overbite b. Reduced or anterior openbite c. Severe Class II Div I; >5mm horizontal overlap d. Unilateral maxillary posterior crossbite e. All of the above |
All of the above
|
|
|
Muscles in the head, face and neck region can elicit heterotopic pain with the perceived pain site in all of patients’ teeth.
a. TRUE b. FALSE |
True
|
|
|
A patient comes to your office with pain in the upper right but is unable to identify the area specifically. They reveal continuous pain, burning sensation, aching and sometimes throbbing. You take 2 periapical radiographs to image all the roots. Periapicals are within normal limits. Examination of the patients teeth reveal, very conservative occlusal restorations in 2,4 &5. Periodontal examination is all within normal limits, multiple severe wear facets. Results of an anesthetic block of the area are ambiguous Your tentative diagnosis is:
a. Irreversible pulpitis in 2, 4 or 5 b. Acute Periodontitis c. Atypical Odontalgia d. Occlusal trauma from severe bruxism e. Could be all of the above |
Atypical Odontalgia
|
|
|
STATEMENT 1: Only when posterior disclusion is obtained by an appropriate anterior guidance can the elevating activity of the temporal and masseter muscles be reduced; STATEMENT 2: It is not the contact of the canines that decreases the activity, but the elimination of posterior contacts.
a. First statement if true; Second statement is true b. First statement if true; Second statement is false c. First statement if false; Second statement is true d. First statement if false; Second statement is false e. None of the above is true |
First Statement is TRUE
Second Statement is TRUE |
|
|
You are seeing a patient for the first time, you diagnose a patient with a Chronic Displaced Disc w/ Reduction with Pain, which is not improving. Your first treatment recommendation should be. (Hint: you forget how to treat the patient, so you leave the operatory and go to your private office where you have stored all your TMD notes. You pull out the flowsheet for the treatment of the disorder which reads??)
a. Relief of the patients pain with anterior repositioning appliance b. Relief of the patients pain with NSAID’s and an oral surgery referral c. Relief of the patients pain with stabilization appliance d. A & B |
Relief of the patients pain with stabilization appliance
|
|
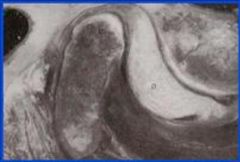
What is your diagnosis based on the MRI below differentiate between displaced and dislocated
a. Acute Displaced disc with reduction b. Chronic Displaced disc with reduction c. Acute Displaced disc without reduction d. Chronic Displaced disc without reduction |
Chronic Displaced disc without reduction???
|
|
|
The treatment recommendation for the patient in previous question is
a. Recapture disc (reduction of disc) b. Surgical consult because of disc’s non-anatomical shape c. Monitor and/or Stabilization appliance d. Anterior repositioning appliance |
Monitor and/or Stabilization appliance
|
|
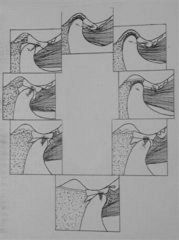
What is this condition in the picture on the right----------------------!
a. Normal Joint b. Displaced Disc with reduction c. Displaced Disc without reduction d. Hypomobility e. Hypermobility |
Displaced Disc WITHOUT reduction
|
|
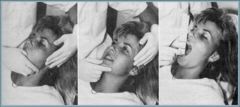
In this picture the patient is being treated for what disorder
a. Acute Displaced disc with reduction b. Chronic Displaced disc with reduction c. Acute Displaced disc without reduction d. Chronic Displaced disc without reduction e. Displaced disc Hypermobility |
Acute Displaced disc WITHOUT reduction
|
|
|
On examination of your patient you record the following values: maximum opening 35mm, lateral movement left
9mm, lateral movement right 4mm; your tentative diagnosis is? a. Right displaced disc b. Left displaced disc c. Muscle restriction of the right masseter muscle d. Local muscle soreness of left masseter muscle e. Hypomobility |
Left displaced disc
Disc displacement w/o reduction Patients deviates towards affected side |
|
|
A situation in which a stabilization appliance would most likely fail to resolve symptoms would be a patient with
a. Bipolar disease b. Death of a family member c. A recent diagnosis of ameloblastoma d. Local Muscle Soreness e. A, B, C |
A,B,C
|
|
|
Heterotopic pain is common with TMD patients. This can be seen as referred pain from:
a. The shoulder to the TM joint b. Masseter muscle to anterior teeth c. Digastric muscle to premolars d. Buccinator muscle to the TMJ |
???
|
|
|
Hard appliances are preferred over soft “rubbery” type because:
a. Soft appliances may increase bruxing in some patients. b. Soft appliances may intrude posterior teeth. c. Soft appliances do not provide cuspid (canine) disclusion. d. All the above |
All of the above
|
|
|
You prescribed an appliance for treatment of your patient’s TMD problems. Several months later they call your office
and state their upper anterior teeth are sore, “a little” loose and a diastema forming. The most likely appliance the patient is wearing is: a. Maxillary full coverage stabilization appliance b. Mandibular full coverage stabilization appliance c. Mandibular posterior coverage stabilization appliance d. NTI e. Posterior coverage stabilization appliance |
???
|
|
|
A mandibular full coverage stabilization appliance is a very esthetic appliance for patients that must wear an appliance
14-16 hours per day, what is the most significant disadvantage associated with this type of appliance? a. Statistically less effective than a maxillary full coverage appliance b. Must see patient more frequently for adjustments than a maxillary full coverage appliance c. Intrusion of mandibular posterior teeth d. More difficult to wear vs. maxillary full coverage appliance |
???
|
|
|
You just finished preparing #2 for a crown. You ask your patient to close and they can’t. Your tentative diagnosis would most likely be:
a. Displaced disc without reduction b. Displaced disc with reduction c. Spontaneous dislocation d. Local Muscle Soreness e. All of the above |
Spontaneous dislocation
|
|
|
Your patient states they were in a fight a year ago receiving a blow to the mandible. He still has pain in the jaw joints
and clicking. Your initial treatment would be a. Vapocool spray and stretching b. Stabilization appliance c. Anterior repositioning appliance d. Massage e. Surgical consulatation |
Stabilization Appliance
|
|
|
A stabilization appliance should have all of the following characteristics except:
a. Disclusion b. Forces over the long axis c. Coverage of all teeth on arch the splint is fabricated on d. Indentation of posterior surface to prevent excessive mandibular movement e. Prevent tooth eruption |
Indentation of posterior surface to prevent excessive mandibular movement
|
|
|
Scientific literature does not support occlusal problems as primary etiological factors in TMD, but in class we
discussed several occlusal problems with strong occlusion/TMD associations. Indicate the possibilities from below. a. Severe Class II Division I occlusion Excessive horizontal overbite b. Severe Class II Division II occlusion Excessive Vertical overbite (overlap) c. More than 5 missing posterior teeth d. Posterior unilateral crossbite. e. Non-working interferences in lateral |
All of these
|
|
|
A patient of yours is seen 1 week after a crown prep for tooth #18. They complain of pain in the jaw and sensitivity to
cold with #18. Your differential diagnosis is a. Local muscle soreness b. Buccinator and Medial ptyergoid muscle injury c. Mucosa injury d. Closed lock, displaced disc e. Dislocation of joint |
???
|
|
|
You prepare to seat Procera crowns #6-11. Your patient says they are gorgeous, she starts crying, and states you are
the greatest dentist, you agree humbly. But since your head is now swelled, you seat the crowns forgetting to check the occlusion. She calls back 1 week later and says some of the teeth you worked on are sore. As discussed in class, what are other problems she may develop? a. Chipping of teeth b. Diastemas forming c. Mobility of teeth d. Painful teeth |
All of these
|
|
|
The treatment of the patient in the previous question would be (THIS QUESTION HAS ONLY ONE ANSWER)
a. Adjust occlusion on the opposing tooth b. Adjust occlusion on the crown c. Stabilization appliance, as symptoms are only temporary d. Remake the crown to the proper occlusion e. All of the above would be satisfactory |
Adjust occlusion on the crown
|
|
|
In class we discussed major disadvantages in using a soft “rubbery” “bleaching-type” mouth guards for bruxing
patients, they are a. Too soft and thus wear through easily (many students picked this answer even though we never mentioned this answer as a disadvantage, only stated increase bruxing and intrude) b. Increase bruxing c. Intrude posterior teeth d. All the above |
d. All the above
|
|
|
A displaced disc with reduction is characterized by:
a. Mechanical locking, patient may report “catching” until disc returns to normal position b. Reciprocal Clicking c. Protrusive opening usually eliminates clicking d. Open Locking e. Previous history of clicking |
a. Mechanical locking, patient may report “catching” until disc returns to normal position
b. Reciprocal Clicking c. Protrusive opening usually eliminates clicking |
|
|
A displaced disc without reduction is characterized by:
a. Disc is permanently displaced b. Characterized by “Closed Lock” c. Previous history of joint noises d. Mechanical locking, until disc returns to normal position |
a. Disc is permanently displaced
b. Characterized by “Closed Lock” c. Previous history of joint noises |
|
|
Which of the following disorders would you expect to find in a patient with permanent limited or restricted
mandibular opening, a. Spontaneous dislocation b. Hyper-mobility c. Adhesions of the TMJ d. Adherences of the TMJ e. Ankylosis |
Adhesions of the TMJ??
or maybe hypermobility |
|
|
Which of the following disorders would you expect to find in a patient with permanent limited or restricted
mandibular opening, a. Spontaneous dislocation b. Hyper-mobility c. Adhesions of the TMJ d. Adherences of the TMJ e. Ankylosis 10. Treatment of the previous question would be (this question has only 1 answer) a. Stabilization appliance b. Anterior repositioning appliance c. Monitor d. Surgical consultation |
I think this might be hypermobility. Which we tell patients hust not to open too far, otherwise no treatment
(w/o reduction Stabilization appliance then if that doesn't work Surgical Consultation) |
|
|
The which of the following is an example of Growth Disorders of the TMJs .
a. Hyperplasia b. Neoplasia c. Hypoplasia d. Agenesis e. Hypotrophy |
???
|
|
|
Full coverage mandibular stabilization appliances are effective in treatment of TMD, but have addition concerns that
maxillary stabilization appliances do not, they are: a. Development of a diastemas b. Intrusion of posterior teeth c. Lack of canine disclusion d. Must see patient more frequently for adjustments vs. maxillary appliance |
.
|
|
|
What are the 2 most common imaging techniques for viewing the temporomandibular joint, mentioned in Dr. Ruch’s
lecture: (THERE ARE ONLY TWO ANSWERS FOR THIS QUESTION) a. Panoral b. Transcrainal c. CT scan d. Arthrography e. MRI |
I think
Panoral CT scan |
|
|
A patient complains of pain in his TMJ’s after an auto accident. Your exam reveals bilateral opening and closing
clicks, which the patient states happened immediately after the accident. Your recommended treatment is? a. Soft Diet and warm and/or cold compress b. Stabilization Appliance c. Repositioning Appliance d. NTI e. MRI |
Stabilization appliance???
|
|
|
A patient complains of pain in his TMJ’s after an auto accident. Your exam reveals bilateral opening and closing
clicks, which the patient states happened immediately after the accident. Your recommended treatment is? a. Soft Diet and warm and/or cold compress b. Stabilization Appliance c. Repositioning Appliance d. NTI e. MRI 15. Your diagnosis of the patient in the previous question is (this question has only 1 answer) a. LOCAL MUSCLE SORENESS b. Displaced disc w/ reduction c. Disc displacement w/o reduction d. Disc locking e. Adhesions |
Displaced disc WITH reduction
|
|
|
You cement an anterior crown #7 and although there is posterior tooth contact, the patient states the contact on the crown is heavy; this may cause:
a. Wear of anterior teeth b. Fracture of anterior teeth c. Displaced anterior teeth d. Development of diastemas e. Increased vertical dimension of occlusion |
a. Wear of anterior teeth
b. Fracture of anterior teeth c. Displaced anterior teeth d. Development of diastemas |
|
|
The following would indicate a diagnosis of what: monitor condition, pseudo-disc formation, joint adaptation.
a. Acute displaced disc with reduction b. Acute displaced disc without reduction c. Chronic disc displaced with reduction d. Chronic disc displaced without reduction |
c. Chronic disc displaced with reduction
|
|
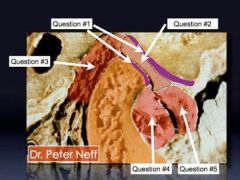
What is #1
|
.
|
|
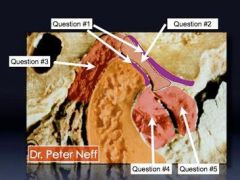
What is #1?
|
?
|
|
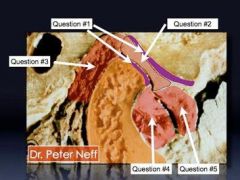
What is #2?
|
?
|
|
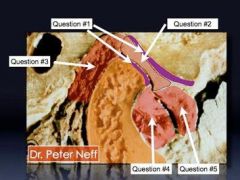
What is #3?
|
Retrodiscal area
bilaminar zone |
|
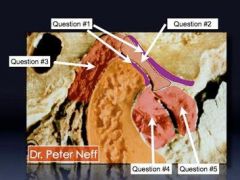
What is #3?
|
Retrodiscal pad
|
|
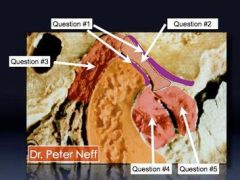
What is #4?
|
Inferior head of lateral pterygoid
|
|
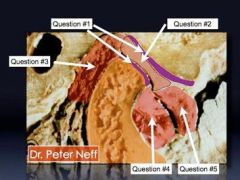
What is #5?
|
Superior head of lateral pterygoid.
|
|
|
What is the most important reason a stabilization appliance should cover the posterior and
provide posterior occlusion? a. To prevent indentations in the acrylic from locking the mandible in place b. With heavy anterior occlusion teeth can wear, fracture, move, become mobile and be symptomatic c. Stabilization of teeth to allow patient to “get into” CR d. Prevent the potential need for orthodontic treatment e. None of the above |
c. Stabilization of teeth to allow patient to “get into” CR
|
|
|
7. A patient walks into your office with signs and symptoms of TMD. Exam reveals excessive
vertical overlap of 10mm, lateral movement left – 10mm right – 12mm, lateral working interference #5, missing teeth #2, 3, 4,13,14,15. Definitive treatment for this patient would most likely be: a. Stabilization appliance, occlusal equilibration, implant retained crowns and/or removable partials and stabilization appliance b. Stabilization appliance, orthodontic consultation, implant retained crowns and/or removable partials c. Stabilization appliance, implant retained crowns and/or removable partials d. Complete Maxillary denture |
b. Stabilization appliance, orthodontic consultation, implant retained crowns and/or
removable partials |
|
|
8. Some studies have shown that soft appliances (“bleaching type” appliances) can intrude
posterior teeth; these types of appliances can be routinely used for patients that can’t tolerate standard stabilization appliances. a. First statement is true; second statement is true b. First statement is true; second statement is false c. First statement is false; second statement is true d. First statement is false; second statement is false |
b. First statement is true; second statement is false
|
|
|
9. In class we discussed major disadvantages in using a soft “rubbery” “bleaching-type” mouth
guards for bruxing patients, they are a. Too soft and thus wear through easily (many students picked this answer even though we never mentioned this answer as a disadvantage, only stated increase bruxing and intrude) b. Increase bruxing c. Intrude posterior teeth d. All the above |
All of the above
|
|
|
10. Migraine headaches are characterized by all of the below EXCEPT
a. activation of the trigeminal vascular system b. vascular changes c. affects the endogenous pain control mechanisms d. associated with tearing, rhinorrhea, vasodilatation e. None of the above |
d. associated with tearing, rhinorrhea, vasodilatation
|
|
|
Which of the following headaches is typically not associated with pain in or around the eye?
a. Temporal arteritis b. Maxillary sinusitis c. Tension-type headache d. Migraine with aura e. Cluster headache |
Temporal Arteries?
|
|
|
12. Which of the following headaches is typically not associated with increased pain with head
movement? a. Meningitis b. Migraine with aura c. Sinusitis d. Tension type headache e. Migraine without aura |
d. Tension type headache
|
|
|
13. The occurrence of a persistent headache associated with systemic signs and symptoms for the
first time in a person over the age of 50 is significant. The primary concern is the possible diagnosis of: a. Migraine with aura b. Cluster headache c. Meningitis d. Sphenoidal sinusitis e. Temporal arteritis |
e. Temporal arteritis
|
|
|
14. Which type of pain is classically associated with a vascular headache?
a. dull, aching b. sharp, shooting c. throbbing, pounding d. electric shock-like e. soreness, tightness |
Throbbing, Pounding
|
|
|
15. Stress has been identified as a precipitating factor in both migraines and tension type
headaches. Which of the following statements is true? a. Tension - type headaches typically occur after the stressful situation. b. Migraine headaches typically occur after the stressful situation. c. Migraine headaches typically occur during the stressful situation. d. Both migraine and tension headaches typically occur during the stressful situation. e. Both migraine and tension-type headaches occur after the stressful situation. |
B
Tension headaches occur DURING STRESS |
|
|
16. Photophobia, phonophobia and osmophobia are commonly associated with which type of
headache? a. Tension-type headache b. Migraine c. Temporal arteritis d. Meningitis e. Maxillary sinusitis |
b. Migraine (light noise and odors)
(note: meningitis also has photophobia, but not the other two) |
|
|
17. Which important chemical mediator has been associated with the development of migraine
and tension-type headaches? a. norepinephrine b. dopamine c. serotonin d. histamine e. interleukin |
serotonin
|
|
|
18. The TMJ is supported by
a. temporomandibular ligament b. bilateral zone c. retrodiscal tissue d. all of the above |
.
|
|
|
19. Which of the following would the patient most likely report an inability to “open wide”
a. anterior displaced disc with reduction of left joint b. anterior displaced disc with reduction of right joint c. anterior displaced disc without reduction d. All of the above e. None of the above |
Anterior displaced disc without reduction.
(closed lock 25-30mm) |
|
|
20. Centric relation is used as a treatment position because it is
a. Stable position under considerable stress at the joint for many years b. a repeatable position c. It is a treatment position, which will not change with time d. All of the above |
All of the above
|
|
|
21. Your patient opens 20mm unassisted. You can increase their opening to 40mm by pressing
down on the mandibular centrals. a) the patient exhibits an anterior displaced disc without reduction b) muscle restriction of mandible c) shortening of TMJ ligaments d) all of the above |
Muscle restriction of mandible
|
|
|
22. You examine teeth #8 & #9 and detect fremitus. Most likely etiology could be
a. heavy contact in maximum intercucspation on lingual of crown #9 by mandibular central(s) b. Mandibular stabilization appliance unmonitored c. Patient was in a fight and was severely punched in the mouth d. All of the above |
.
|
|
|
23. A patient reports symptoms; pain, tightness, inability to open wide, inability to move left and
right in the muscles of mastication. Appropriate treatment is a. Stabilization Appliance covering maxillary arch b. Stabilization Appliance covering mandibular arch c. Stabilization Appliance covering mandibular posterior teeth d. A & B e. All of the above |
d. A & B
|
|
|
24. In class we discussed 5 occlusal problems which may predisposes a patient to TMD. Which
of the following would not predispose a patient to TMD a. Anterior open bite b. Class II division with lateral non-working interferences and severe horizontal overlap c. Maxillary unilateral cross bite d. Bilateral missing mandibular posterior teeth d. Class I with lateral non-working interferences e. More than of the above |
d. Class I with lateral non-working interferences
|
|
|
25. A patient reports pain in masseter muscles; mandible deviates severely to the left on wide opening and has an opening and closing click. The diagnosis is most likely
a. Displaced disc with reduction of right TMJ b. Displaced disc with reduction of left TMJ c. Displaced disc without reduction of left TMJ d. Displaced disc without reduction of right TMJ e. A & D |
Displaced disc with reduction because As the patient opens, the condyles translate and "reduction" of the disc
occurs. During closing, the disc again displaces Collateral ligaments elongate and the disc displaces anterior and medially, so I believe that it would be the RIGHT TMJ |
|
|
26. While examining a new patient, they state their chief complaint as pain in jaw muscles,
clicking of both joints and numerous posterior teeth. Multiple non-working interferences are documented. Your initial treatment recommendations are: a. Endodontic consultation of symptomatic posterior teeth b. Adjustment of non-working interferences c. Stabilization appliance d. Anterior repositioning appliance e. All of the above are acceptable initial treatments |
.c. Stabilization appliance
|
|
|
27. You just finish preparing a tooth #31 for a crown, which took you 2 ! hours. You ask your patient to close and they can’t. Your diagnosis would most likely be:
a. displaced disc without reduction b. displaced disc with reduction c. spontaneous dislocation d. two of the above e. all of the above |
Displaced disc without reduction
Spontaneous dislocation |
|
|
28. Your patient presents with opening and closing clicking with intracapsular pain. Your
primary treatment goal should be: a. increase inter-incisal opening b. reduction of pain c. reposition disc in it’s proper relation d. surgery e. all of the above |
c. reposition disc in it’s proper relation
|
|
|
29. You would order radiographs for your patient for:
a. insurance companies b. base line information c. diagnosis d. two of the above e. all of the above |
Two of the above
|
|
|
30. The disc is attached to the ramus of the mandible by
a. collateral ligaments b. posterior attachment c. oblique ligaments d. all of the above e. none of the above |
.
|
|
|
31. Your patient require crown and bridge treatment on all of the maxillary teeth, which of the
following is true when sending case to the lab. a. mount case with maximum intercuspation interocclusal record b. mount case with a regular interocclusal record c. mount case with centric relation interocclusal record d. all of the above are acceptable for this case e. Depends on Preceptor |
c. mount case with centric relation interocclusal record
|
|
|
32. Which of the following may increase a patients bruxism
a. occlusal splint constructed at CR b. occlusal splint constructed at maximum intercuspation c. mandibular occlusal splint d. anterior stop e. soft “rubbery-type” mouth guard occlusal splint |
e. soft “rubbery-type” mouth guard occlusal splint
|
|
|
33. The primary purpose of the stabilization phase of splint construction is
a. mandibular support b. prevent tooth movement c. posterior tooth guidance d. all of the above |
d. all of the above
|
|
|
34. When adjusting an anterior stop, the contact area on the mandibular centrals should be where
a. lingual surface of centrals b. facial surface of centrals c. incisal edge of centrals d. contact should allow thin articulating paper to pull between appliance and teeth |
c. incisal edge of centrals
|
|
|
36. Which of the following characteristics best describes the type of pain found in trigeminal
neuralgia? a) Throbbing, pulsing pain b) Deep, aching pain c) Diffuse, poorly localized pain d) Sharp, shooting pain, electric shock-like pain e) Deep, burning, pounding pain |
d) Sharp, shooting pain, electric shock-like pain
|
|
|
36. Which of the following characteristics best describes the type of pain found in trigeminal
neuralgia? a) Throbbing, pulsing pain b) Deep, aching pain c) Diffuse, poorly localized pain d) Sharp, shooting pain, electric shock-like pain e) Deep, burning, pounding pain |
d) Sharp, shooting pain, electric shock-like pain
|
|
|
37. An anterior repositioning appliance generally is used only when sleeping because
a. Extrustion of mandibular teeth b. Poor esthetics and phonetics c. Posterior tooth intrustion d. Permanent joint changes |
I think B
(others think A) |
|
|
38. Which muscle is involved in maintaining the appropriate relationship of the disc to the head
of the condyle during opening and closing? a. Superficial masseter b. Superior head of the medial pterygoid c. Inferior head of the medial pterygoid d. Superior head of the lateral pterygoid e. Inferior head of the lateral pterygoid |
d. Superior head of the lateral pterygoid
|
|
|
39. TMD splint therapy is effective in relieving the symptoms of bruxism because if the TMD
splint is properly designed, it will eliminate the bruxism. a. True b. False |
??unsure. it would relieve symptoms of bruxism.
|
|
|
40. What is the most important reason a maxillary stabilization appliance should cover the
posterior teeth? a.To prevent indentations in the acrylic from locking the mandible in place b. With heavy anterior occlusion teeth can wear, fracture, move, become mobile and be symptomatic c. Stabilization of teeth to allow patient to “get into” CR d. Prevent posterior extrusion e. None of the above |
b. With heavy anterior occlusion teeth can wear, fracture, move, become mobile and be symptomatic
|
|
|
41. Reduced activity of the Temporalis and Masseter occurs by elimination of?
a. Opening very wide and hyperactivity of those muscles b. Elimination of posterior lateral working and non-working contacts c. Elimination of posterior contacts d. Elimination of anterior contacts in working and non-working contacts e. More than one of the above |
Reduced activity of the Temporalis and Masseter occurs by elimination of lateral working and non-working contacts.
|
|
|
42. Some studies have shown that soft appliances (“bleaching type” appliances) are acceptable
appliances; therefore, these types of appliances can be routinely used for patients that can’t tolerate standard stabilization appliances. a. First statement is true; second statement is true b. First statement is true; second statement is false c. First statement is false; second statement is true d. First statement is false; second statement is false |
d. First statement is false; second statement is false
|
|
|
43. Which of the following would not be primary site of pain referral to the maxillary posterior
teeth a.Temporalis b. Masseter c. Tension-Type Headache d. Atypical odontalgia e. Sinusitis |
Tension type headache
|
|
|
44. Which of the following would indicate a Temporal Arteritis
a. Muscle pain, b. Fever c. Severe headaches d. Pain when chewing e. disc displacement due to swelling |
Fever
|
|
|
45. Treatment of TMD is mostly confined to treatment of:
a. Masticatory Muscles b. Temporomandibular joint derangements c. Associated Structures d. Headaches e. All of the Above |
All of the above
|
|
|
46. FIRST STATEMENT: TMD symptoms can be triggered by mandibular blocks. SECOND
STATEMENT: Potential tissues affected are mucosa, buccinator muscle medial Pterygoid mucle, connective tissue, adipose tissue and Sphenomandublar ligament. a. FIRST STATEMENT IS TRUE, SECOND STATEMENT IS FALSE b. FIRST STATEMENT IS TRUE, SECOND STATEMENT IS TRUE c. FIRST STATEMENT IS FALSE, SECOND STATEMENT IS TRUE d. FIRST STATEMENT IS FALSE, SECOND STATEMENT IS FALSE |
b. FIRST STATEMENT IS TRUE, SECOND STATEMENT IS TRUE
|
|
|
47. Which of the following occlusal problems are not considered primary etiology for TMD
patients a. Class II Division II occlusion b. Anterior Open Bite c. Severe Class II Division I occlusion d. Unrestored Kennedy I partial denture case replacing all posteriors e. Group function with working interferences |
.
|
|
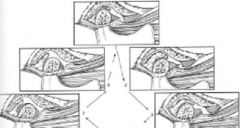
48. The diagram on right depicts what type of
temporomandibular disorder a. Normal TMJ b. Disc displacement with reduction c. Disc displacement without reduction d. Spontaneous dislocation e. Closed Lock |
Disc displacement with reduction
|
|
|
49. Joint sounds are very common and not usually associated with pain or decreased joint
mobility. TMJ joints usually progress to more severe conditions as the patient ages. a. First Statement is False, Second is False b. First Statement is False, Second is True c. First statement is True, Second is False d. First statement is True, Second is True |
c. First statement is True, Second is False
|
|
|
50. A patient reports to your office with the following chief complaints: clicking of the left and right joint with pain, tenderness to palpation of the right joint. Maximum opening you measure at 55mm, left lateral 9mm and right lateral 10mm. What is your recommended treatment for your
patient. a. Monitor b. Stabilization Appliance c. Anterior Repositioning Appliance d. Surgical Consultation |
Stabilization Appliance
|
|
|
b. Stabilization appliance, orthodontic consultation, implant retained crowns and/or
removable partials 51. After 6 months of treatment of the above patient (question #50), are still in pain, what is your recommended treatment. a. Monitor b. Stabilization Appliance c. Anterior Repositioning Appliance d. Surgical Consultation |
.c. Anterior Repositioning Appliance
|
|
|
51. After 6 months of treatment of the above patient (question #50), are still in pain, what is your
recommended treatment. a. Monitor b. Stabilization Appliance c. Anterior Repositioning Appliance d. Surgical Consultation 52. The same patient above (question #50 and #51) is at your office 3 years later with no pain and a maximum opening of 30mm. Your treatment recommendations are a. Monitor b. Stabilization Appliance c. Anterior Repositioning Appliance d. Surgical Consultation |
.
|
|
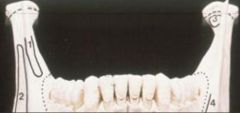
53. Name the muscle that attaches to the mandible
at point (1) on the diagram at the right a. Later Pterygoid b. Buccinator c. Masseter d. Temporalis e. Muscles of facial expression |
a. Later Pterygoid
|
|
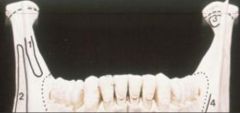
54. Name the muscle that attaches to the mandible at point (2) on the diagram at the right
a. Later Pterygoid b. Buccinator c. Masseter d. Temporalis e. Muscles of facial expression |
Masseter
|
|
|
55. Name the muscle that attaches to the mandible at point (3) on the diagram at the right
a. Later Pterygoid b. Buccinator c. Masseter d. Temporalis e. Muscles of facial expression |
.
|
|
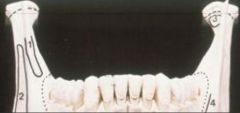
56. Name the muscle that attaches to the mandible at point (4) on the diagram at the right
a. Lateral Pterygoid b. Buccinator c. Masseter d. Temporalis e. Muscles of facial expression |
Buccinator
|
|
|
1. The outcome of conservative muscle treatment with disc disc placed joints is
generally poor; therefore more aggressive treatment is usually warranted. a. First statement is true; Second statement is true b. First statement is true; Second statement is false c. First statement is false; Second statement is true d. First statement is false; Second statement is false |
d. First statement is false; Second statement is false
|
|
|
2. The treatment goals of a stabilization appliance include
a. All of the below b. The condyles should be in their musculoskeletally stable position (CR), the disc should be properly interposed c. Teeth should have even simultaneous contact directing forces through the long axis of the teeth d. Anterior guidance should have eccentric contacts on the anterior teeth e. Occlusion ideals are the posterior teeth contact heavier than the anterior teeth |
a. All of the below
|
|
|
3. Which of the following is TRUE regarding Disc Dislocation w/ Reduction
a. A disorder usually requiring anterior positioning or surgical consult b. Opening and closing the mandible in a retruded posture, eliminates reciprocal clicking c. Elongation of collateral ligaments d. Reduction of the TMJ disc on closing e. More than one of the above |
d. Reduction of the TMJ disc on closing
c. Elongation of collateral ligaments |
|
|
4. Which of the following most differentiates correctly a disc dislocation without
reduction from a disc dislocation with reduction a. Mandibular opening that is usually normal b. Loss of normal disc anatomy c. Loss of posterior teeth causing collapse of occlusion placing undue stress on the temporomandibular joints d. Chronic trauma |
b. Loss of normal disc anatomy
|
|
|
5. Which of the following muscle disorders is characterized by heterotopic pain
a. Protective Co-Contraction b. Local Muscle Soreness c. Myospasm d. Myofascial Pain e. Chronic Centrally Mediated Myalgia |
d. Myofascial Pain
|
|
|
6. A patient is in your office for TMD pain. You ask the patient to directly point to the
effected area and they point to the right TMJ area, a tentative conclusion could be made that the patient has a. Joint problem b. Muscle pain c. Joint pain d. A and B e. A and C |
e. A and C
|
|
|
7. In the acute pain patient the problems are generally quite visible; Where as in the
chronic pain patient often we donʼt often find what we are expecting to find. a. The first statement is true; the second statement is true b. The first statement is true; the second statement is false c. The first statement is false; the second statement is true d. The first statement is false; the second statement is false |
a. The first statement is true; the second statement is true
|
|
|
8. The Stabilization Phase in the construction of a Stabilization appliance includes all
below except a. Provides optimal occlusion b. Prevents posterior tooth eruption c. Group function occlusion d. Lateral balance on excursive movements |
c. Group function occlusion
|
|
|
9. You are about to deliver crown #18 to your patient. After your remove the
provisional restoration and clean the preparation, your next step should be a. Verify the contacts are acceptable b. Verify the margins are acceptable c. Verify the occlusion is acceptable d. Verify the shade match is acceptable |
a. Verify the contacts are acceptable
|
|
|
10. A patient reports to your office with the following signs and symptoms; 30mm
mandibular opening, previous history of bilateral TMJ clicking, scar on chin from car accident 1 year ago, initial pain in joints but patient says “I have had no pain for the past 3 months”, “about a month ago it was very hard to open to eat normally, but I can open better now”, no signs or symptoms of parafunction. Your treatment recommendations for the patient would be? a. Stabilization appliance b. Anterior repositioning appliance c. “Recapture disc” and Stabilization appliance d. Physical therapy to increase opening e. Monitor the condition, it is self limiting and healing |
e. Monitor the condition, it is self limiting and healing
|
|
|
11. The diagnosis of the patient in question #13 would be
a. Atypical Odontalgia b. Chronic anterior displaced with reduction c. Acute anterior displaced without reduction d. Chronic anterior displaced without reduction |
d. Chronic anterior displaced without reduction
|
|
|
12. The pain in frontal sinusitis most commonly occurs in the __________ and
__________as the day progresses. a. morning; increases b. morning; decreases c. afternoon; increases d. afternoon; decreases |
b. morning; decreases
|
|
|
13. What type of headaches are referred to as “Suicide Headache” and associated with
excruciating pain of short duration, 30-90 minutes. a. Tension-type b. Migraine with aura c. Temporal Arteritis d. Cluster headache e. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage |
d. Cluster headache
|
|
|
14. When adjusting a new crown #9, the occlusion should be adjusted so that:
a. It lightly contacts the facial of #23 b. It lightly contacts the lingual of #24 c. Contact should be on #6 and #11, not #23 or #24 d. It lightly contacts the Incisal edge of #24 |
d. It lightly contacts the Incisal edge of #24
|
|
|
15. The muscle condition associated with Chronic Global Musculoskeletal problems is
a. Protective Co-Contraction b. Local Muscle Soreness c. Myospasm d. Myofascial Pain e. Fibromyalgia |
e. Fibromyalgia
|
|
|
16. A patient is assigned to you by emergency. The health history and examination
reveal the following: injury to the jaw this past weekend, pain in both temporomandibular joints, mandibular opening of 10mm, no history of temporomandibular joints clicking. Your tentative diagnosis is: a. Acute disc dislocation with reduction b. Acute disc dislocation without reduction c. Chronic disc dislocation without reduction d. Chronic disc dislocation with reduction |
b. Acute disc dislocation without reduction
|
|
|
17. Your initial treatment prescribed for the patient in question #16 would be
a. Stabilization appliance b. Anterior repositioning appliance c. Cold / Hot compresses - self limiting injury, will heal normally on itʼs own d. Recapture of disc e. Physical therapy |
d. Recapture of disc
|
|
|
18. Teeth most affected due to G.E.R.D. most likely appears as all the following
EXCEPT a. Extent of wear similar on both arches b. All maxillary linguals c. All mandibular occlusals d. Lingual asymmetrical wear e. Extensive wear lingually on mandibular anteriors |
e. Extensive wear lingually on mandibular anteriors
|
|
|
19. In the clinic you prepare 2 posterior crowns on the maxillary arch and 1 on the
mandibular arch. To articulate the mandibular cast to the maxillary cast your next step most likely would be, assuming the patient has an accurate maximal interspation a. None of the below b. Take a centric relation interocclusal record c. Facebow transfer d. Mount case with leaf gauge or anterior stop like the anterior stop on step one of your stabilization appliance laboratory project |
a. None of the below
|
|
|
20. Attrition can be differentiated from erosion by
a. Concavities on smooth surfaces b. “Cupped-like concavities on cusp tips c. Pulp exposure in adults d. “Raised” restorations e. None of the above |
e. None of the above
|
|
|
21. A patient seen by our admitting department has a chief complaint of burning and
throbbing pain, sensitive to chewing, sensitivity to palpation for the past several months in the areas of #2, #3, #4 & #5. Peiodontal examination reveal pockets depths of 4 & 5 mm generally with #15 6mm. Periapical radiographs reveal moderate to deep restorations on all teeth indicated with #4 treated with endodontics, post and core and crown, with no apparent radiographic apical pathology. Your tentative diagnosis would be: a. Reversible Pulpitis b. Irreversible Pulpitis c. Acute periodontal inflammation d. Atypical Odontalgia e. Fractured tooth |
d. Atypical Odontalgia
|
|
|
22. Etiology of the chief complaint of patient in question #21 would be
a. Moderate depth restorations b. Nerve deafferentation c. Deep depth restorations d. Periodontal Chronic inflammation e. Severe nocturnal bruxism and/or clenching |
b. Nerve deafferentation
|
|
|
23. Treatment of the patient in question #24 would most likely be:
a. Scaling Root Planning b. Inform patient of deep restorations and associated sensitivity, Rx Sensodyne Tooth paste use c. Medical Referral d. Endodontic therapy e. Oral surgery consultation |
c. Medical Referral
|
|
|
24. The stabilization laboratory appliance should have all of the following criteria except:
a. Canine guidance b. Anterior guidance c. Moderately deep occlusal indentations for a stable “appliance” maximal intercuspation d. Complete posterior occlusal coverage e. All of the above are proper criteria for a stabilization appliance |
c. Moderately deep occlusal indentations for a stable “appliance” maximal
intercuspation |
|
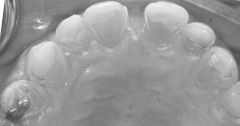
25.
This photo shows severe wear on the maxillary anterior linguals and no where else in the maxillary or mandibular arches, this is indicative of a. Bruxism b. G.E.R.D c. Bulimia d. Carbonated drink abuse e. Abrasion |
c. Bulimia
|
|
|
26. Injury to which of the following soft tissues it possible with a tradition inferior alveolar
anesthetic block a. All the below b. Mucosa & Sphenomandibular Ligament c. Buccinator Muscle & Medial Ptyergoid d. Connective Tissue e. Adipose Tissue |
a. All the below
|
|
|
27. In the appropriate situation in which an anterior repositioning appliance is
prescribed, the instructions to the patient on wearing should be a. Wear 24 hours a day to prevent disc dislocations and to promote healing b. Wear only when sleeping and during day time to control pain as needed c. Wear only during the daytime since most clenching occurs during this time d. With adaptive changes, most patients can reduce appliance use it 12-14 months |
b. Wear only when sleeping and during day time to control pain as needed
|
|
|
28. The posterior clearance between the mandibular last molar and the maxillary
substructure for the lab project should at lease be a. 0-2mm b. 2-4mm c. 4-6mm d. 6-8mm |
b. 2-4mm
|
|
|
29. In general the incident in developing temporomandibular disorders
a. All the below b. Decreases with time for all patients c. Decreases with time for males d. Decreases with time for females |
a. All the below
b. Decreases with time for all patients |
|

30.
The patient in this photo is most likely being treated for a. Local Muscle Soreness b. Acute dislocation without reduction c. Acute dislocation with reduction d. All of the above |
b. Acute dislocation without reduction
|
|
|
31. which of the following TMDʼs would an initial treatment for a surgical consultation be
the recommendation recommended treatment choice a. Acute disc dislocation without reduction b. Spontaneous dislocation with severe pain c. Atypical Odontalgia d. Chronic disc dislocation without reduction e. None of the above |
e. None of the above
|
|
|
32. Throbbing, pulsing, pounding pain is typically associated with which condition?
a. musculoskeletal pain b. neurogenic pain c. vascular pain d. arthralgia e. chronic sinus pain |
c. vascular pain
|
|
|
33. A patient opens 20mm unassisted. You can increase their opening to 40mm by
pressing down on the mandibular centrals a. the patient exhibits an anterior displaced disc without reduction b. muscle restriction of mandible c. shortening of TMJ ligaments d. all of the above |
b. muscle restriction of mandible
|
|
|
34. The tmj discs are held in place by
a. TMJ capsule b. Discal ligaments c. Collateral ligaments d. Temporomandibular ligaments |
b. Discal ligaments
c. collateral ligaments |
|
|
35. Valid treatment protocols for a bruxing patient would include all listed except:
a. Maxillary Complete Posterior tooth coverage Stabilization Appliance b. Anterior Repositioning Appliance for failed treatment of a disc dislocation with reduction, with continuing pain c. Soft “Bleaching-tray” type of an appliance d. Mandibular Complete Posterior tooth coverage Stabilization Appliance |
c. Soft “Bleaching-tray” type of an appliance
|
|
|
36. It is generally accepted that most TMD is caused by occlusal relationships;
equilibration or grinding of the occlusion is thus justified in the initial treatment phase a. first statement is true, second statement is false b. first statement is false, second statement is true c. both statement are true d. both statements are false |
d. both statements are false
|
|
|
37. Which of the following is associated with Trigger Points
a. Local Muscle Soreness b. Protective Co-contraction c. Myfasical Pain d. Fibromyalgia |
c. Myfasical Pain
|
|
|
38. Trigger point Clinical Characteristics are
a. Consistent patterns of referral b. Palpation relieve Pain c. Constant burning-type ache d. None of the above |
a. Consistent patterns of referral
|
|
|
39. Which type of headache is associated with pain in and around the eye and the
patient presents with tearing, bloodshot eye, nasal discharge and redness of the affected side of the head. a. migraine with aura b. temporal arteritis c. maxillary sinusitis d. cluster headache e. tension type headache |
d. cluster headache
|
|
|
40. Occlusal indentations on a stabilization appliance should be:
a. All the below b. Deep posterior indentations to provide and accurate stable occlusion c. A complex technique only achievable by AGED d. Deep anterior indentations to provide and accurate stable Anterior Guidance e. Flat to allow muscles to guide closure and condylar position |
e. Flat to allow muscles to guide closure and condylar position
|
|
|
41. Which headache has a central mechanism similar to that of migraine headaches
a. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage b. Cluster Headaches c. Tension-Type d. Frontal Sinusitis e. Maxillary Sinusitis |
c. Tension-Type
|
|
|
42. Which neuro-chemical mediator is associated with migraine headaches?
a. substance P b. serotonin c. prostaglandins d. dopamine e. norephinephrine |
b. serotonin
|
|
|
43. The primary goal in the treatment of disc dislocation w/ reduction w/ pain is:
a. Treatment of the dislocation with anterior repositioning appliance b. Surgical consult c. Reduce intracapsular pain d. MRI to obtain a definitive diagnosis |
c. Reduce intracapsular pain
|
|
|
44. Which of the following muscle disorders is not commonly seen in the muscles of
mastication a. Protective Co-Contraction b. Local Muscle Soreness c. Muscle Spasms d. Myofascial Pain e. Fibromyalgia |
c. Muscle Spasms
|
|
|
45. Treatment indications for the use of a stabilization appliance include
a. All of the Below b. Decrease parafunctional activity c. Local muscle soreness d. Retrodiscitis secondary to trauma e. Fixed Prosthodontics with the treatment position at Centric Relation |
a. All of the Below
|
|
|
46. Which of the commonly exhibit heterotopic characteristics
a. Fibromyalgia b. Atypical Odontalagia c. Local Muscle Soreness d. Myofasical Pain e. All of the above |
d. Myofasical Pain
|
|
|
47. A review of the literature reveals, the following have been identified as having
strong occlusion-TMD associations except a. Deep Bite Angles Class II Division II Occlusion b. Severe Angles Class II Division I Occlusion c. Loss of Posterior teeth d. Open Posterior Bite |
d. Open Posterior Bite
|
|
|
48. You are on oral surgery rotation and are assigned an emergency patient. The
patient states they have pain in masseter muscles, tenderness in the temporalis area, headaches, stiffness and a body temperature measured at 105o F. Your initial tentative diagnosis would be: a. Acute disc dislocation without reduction b. Spontaneous dislocation with severe pain c. Vasculitis d. Atypical Odontalgia e. Chronic disc dislocation without reduction |
c. Vasculitis
|
|
|
49. A disadvantage of a complete ****----> mandibular <----**** coverage stabilization
appliance is a. Less esthetic than itʼs maxillary counterpart b. General tooth intrusion c. Possible heavy anterior contact over time causing maxillary anterior teeth to move |
c. Possible heavy anterior contact over time causing maxillary anterior teeth
to move |
|
|
50. Aggravating factors in Myofasical Pain are
a. Lack of effective Anterior Guidance b. Parafunctional Habits c. Anxiety/Depression d. Severe Wear/Attrition e. All of the above |
e. All of the above
|
|
|
51. What determines the position of centric relation
a. ligaments b. teeth c. hyoid muscles d. TMJ disc e. a & d |
e. a & d
|
|
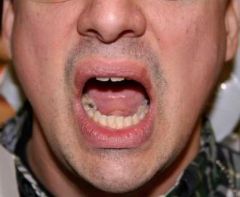
52.
This photograph shows the patient deviating to their left on opening. Select the most correct answer a. Left temporomandibular disc displacement b. Muscle dysfunction c. Right temporomandibular disc displacement d. Bilateral disc displacements |
a. Left temporomandibular disc displacement
|
|
|
53. Anterior Repositioning Appliances may cause permanent joint changes if used for
an extended period of time a. True b. False c. Neither true or false as research has not reached a definitive conclusion |
a. True
|
|
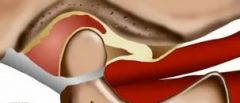
54.
In the photo above, the patientʼs definitive treatment in the **absence of pain** would be: a. Stabilization appliance b. Anterior repositioning appliance c. A condition to monitor d. Depend on the length of time of itʼs presence and the presence or absence of parafunction |
d. Depend on the length of time of itʼs presence and the presence or absence
of parafunction |
|
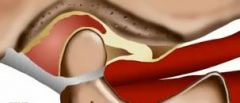
55. In the photo for question #54, the patientʼs definitive treatment **with pain** would
be: a. Stabilization appliance b. Anterior repositioning appliance c. A condition to monitor d. Depend on the length of time of itʼs presence and the presence or absence of parafunction |
a. Stabilization appliance
|
|
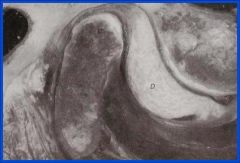
56. Diagnosis of this patient based on the above MRI image above would be
a. Acute disc dislocation without reduction b. Chronic disc dislocation without reduction c. Acute disc dislocation with reduction d. Chronic disc dislocation with reduction e. Normal a |
b. Chronic disc dislocation without reduction
|

