![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
83 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Transitional Epithelium of Ureter |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Polarity |
Two surfaces that differ in structure and function |
|
|
|
Apical Surface |
Upper surface exposed to the body's exterior of cavity of an internal organ |
|
|
|
Microvilli |
Fingerlike extensions of the plasma membrane that increase surface area |
|
|
|
Cilia |
Tiny hairlike projections that moves substances along the surface |
|
|
|
Basal Surface |
Internal surface |
|
|
|
Tight junction |
Helps fuse the membranes of adjacent cells together |
|
|
|
Desmosomes |
Keeps cells anchored so they are not separated |
|
|
|
Basal Lamina |
Selective filter adjacent to the basal surface and a scaffolding which can be used by epithelial cells for wound repair |
|
|
|
Reticular lamina |
Extracellular connective tissue |
|
|
|
Avascular |
Contains no blood vessels |
|
|
|
Simple epithelial |
Single layer of cells |
|
|
|
Stratified epithelia |
Two or more layers |
|
|
|
Squamous Cells |
Flat and scalelike |
|
|
|
Cuboidal cells |
Box like |
|
|
|
Columnar cells |
Tall and column shaped |
|
|
|
Apical surface desired for... |
Filtration, secretion, and absorption |
|
|
|
Simple squamous epithelia function |
Passes materials through diffusion and filtration. Protect is not important. Secretes lubricating substances in serosa. |
|
|
|
Simple squamous epithelia location |
Kidney glomeruli Air sacs of lungs Linings of heart Blood vessels Lymphatic vessels Lining of ventral body cavity |
|
|
|
Simple squamous epithelia |
|
|
|
|
Endothelium |
Inner covering Lines lymphatic vessels Lines blood vessels Lines hollow organs Very thin for nutrient and waste exchange |
|
|
|
Mesothelium |
Middle covering Located in Serosa lining of ventral body cavity |
|
|
|
Simple Cubodial epithelia |
|
Cubelike Large nuclei |
|
|
Simple cubodial epithelia function |
Secretion and absorption |
|
|
|
Simple cubodial epithelia location |
Kidney tubules Ducts and secretory portions of small glands Ovary surface |
|
|
|
Simple columnar epithelia location |
Lines digestive tract, stomach to rectum. Gallbladder Lines small bronchi, uterine tubes and some regions of uterus |
|
|
|
Simple columnar epithelia function |
Absorption Secretion of mucous, enzymes, and other substances Ciliated type propels mucus |
|
|
|
Simple squamous epithelia function |
Passes materials through diffusion and filtration. Protect is not important. Secretes lubricating substances in serosa. |
|
|
|
Simple squamous epithelia location |
Kidney glomeruli Air sacs of lungs Linings of heart Blood vessels Lymphatic vessels Lining of ventral body cavity |
|
|
|
Simple squamous epithelia |
|
|
|
|
Endothelium |
Inner covering Lines lymphatic vessels Lines blood vessels Lines hollow organs Very thin for nutrient and waste exchange |
|
|
|
Mesothelium |
Middle covering Located in Serosa lining of ventral body cavity |
|
|
|
Simple Cubodial epithelia |
|
Cubelike Large nuclei |
|
|
Simple cubodial epithelia function |
Secretion and absorption |
|
|
|
Simple cubodial epithelia location |
Kidney tubules Ducts and secretory portions of small glands Ovary surface |
|
|
|
Simple columnar epithelia location |
Lines digestive tract, stomach to rectum. Gallbladder Lines small bronchi, uterine tubes and some regions of uterus |
|
|
|
Simple columnar epithelia function |
Absorption Secretion of mucous, enzymes, and other substances Ciliated type propels mucus |
|
|
|
Simple squamous epithelia function |
Passes materials through diffusion and filtration. Protect is not important. Secretes lubricating substances in serosa. |
|
|
|
Simple Columnar Epithelium |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Simple squamous epithelia location |
Kidney glomeruli Air sacs of lungs Linings of heart Blood vessels Lymphatic vessels Lining of ventral body cavity |
|
|
|
Simple squamous epithelia |

|
|
|
|
Endothelium |
Inner covering Lines lymphatic vessels Lines blood vessels Lines hollow organs Very thin for nutrient and waste exchange |
|
|
|
Mesothelium |
Middle covering Located in Serosa lining of ventral body cavity |
|
|
|
Simple Cubodial epithelia |
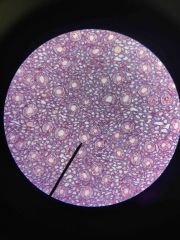
|
Cubelike Large nuclei |
|
|
Simple cubodial epithelia function |
Secretion and absorption |
|
|
|
Simple cubodial epithelia location |
Kidney tubules Ducts and secretory portions of small glands Ovary surface |
|
|
|
Simple columnar epithelia location |
Lines digestive tract, stomach to rectum. Gallbladder Lines small bronchi, uterine tubes and some regions of uterus |
|
|
|
Simple columnar epithelia function |
Absorption Secretion of mucous, enzymes, and other substances Ciliated type propels mucus |
|
|
|
Simple squamous epithelia function |
Passes materials through diffusion and filtration. Protect is not important. Secretes lubricating substances in serosa. |
|
|
|
Simple Columnar Epithelium |
|
|
|
|
Simple squamous epithelia of lungs |

|
|
|
|
Simple squamous epithelia location |
Kidney glomeruli Air sacs of lungs Linings of heart Blood vessels Lymphatic vessels Lining of ventral body cavity |
|
|
|
Simple squamous epithelia |

|
|
|
|
Endothelium |
Inner covering Lines lymphatic vessels Lines blood vessels Lines hollow organs Very thin for nutrient and waste exchange |
|
|
|
Mesothelium |
Middle covering Located in Serosa lining of ventral body cavity |
|
|
|
Simple Cubodial epithelia |

|
Cubelike Large nuclei |
|
|
Simple cubodial epithelia function |
Secretion and absorption |
|
|
|
Simple cubodial epithelia location |
Kidney tubules Ducts and secretory portions of small glands Ovary surface |
|
|
|
Simple Columnar Epithelium |
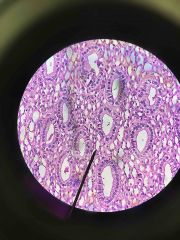
|
|
|
|
Simple Columnar Epithelia of Intestines |
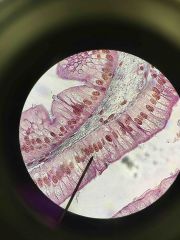
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Simple Columnar Epithelium Collecting ducts of Kidney |
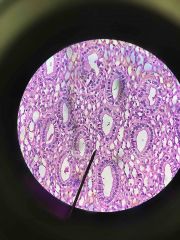
|
|
|
|
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelia of Trachea |
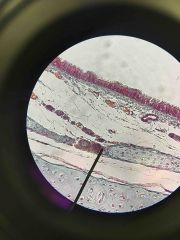
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelia function |
Secretion of mucus Propelled by ciliated action |
|
|
|
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelia location |
Non ciliated in male sperm and ducts of large glands Ciliated found in trachea and UPPER respiratory tract |
|
|
|
Non keratinized Stratified squamous epithelium of esophagus |
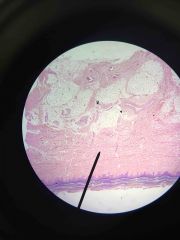
|
|
|
|
Keratinized stratified Epithelium of sole of the foot |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Keratinized stratified Epithelium of sole of the foot |
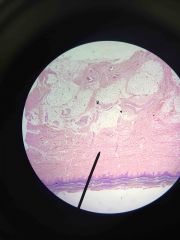
|
|
|
|
Non keratinized Stratified squamous epithelia location |
Mouth, esophagus, vagina, rectum |
|
|
|
Keratinized Stratified squamous epithelium location |
Epidermis of skin A dry membrane |
|
|
|
Stratified squamous epithelium function |
Protection of tissue subject to abrasions |
|
|
|
Transitional Epithelium of Ureter |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Transitional Epithelium of Ureter |
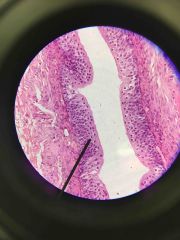
|
|
|
|
Transitional Epithelium location |
Lines the ureter, bladder, and part of the urethra. |
|
|
|
Transitional Epithelium function |
Coils (cubodial) and uncoils (Columnar) to permit urine to distend |
|
|
|
Merocrine Glands |
Secrete by exocytosis Doesn't alter cell |
|
|
|
Holocrine Glands |
Accumulate product until they rupture |
|
|
|
Tubular |
Secretory cells for tube like structure |
|
|
|
Tubular |
Secretory cells for tube like structure |
|
|
|
Alveolar |
Secretory cells form small flask like sacs |
|
|
|
Tubuloalveloar |
Secretory cells having both tube and flask like sacs |
|
|
|
Tubuloalveloar |
Secretory cells having both tube and flask like sacs |
|
|
|
Non keratinized Moist |
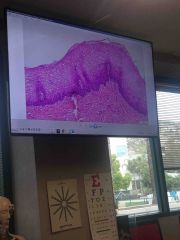
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Keratinized |
Back (Definition) |
|

