![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is the definition of tissue? |
A group of cells that work together to perform a specific function/set of functions |
|
|
|
What are the 4 main types of tissue? |
1) Epithelial or lining tissue 2) Connective tissue - these hold structures together and provide support eg. Blood, bone and cartilage 3) Muscle tissue - made of cells that are specialised to contract and cause movement 4) Nervous tissue - made of cells specialised to conduct electrical impulses |
|
|
|
What is the function of epithelial tissue? |
This covers and lines free surfaces in the body such as skin, cavities of the digestive and respiratory systems, blood vessels, heart Chambers and walls of organs |
|
|
|
Name five characteristics of epithelial tissue |
1) Epithelial tissue is made up of almost entirely of cells 2) Cells are very close together and form continuous sheets 3) No blood vessels instead cells receive nutrients by diffusion from tissue fluid 4) Epithelial cells have a short cell cycle dividing up to 2 or 3 times a day 5) These carry out functions of protection, absorption, filtration, excretion and secretion |
Remember to name the 5 main function as well |
|
|
What are the 2 characteristics of squamous epithelial tissue? |
1) These tissues are made up of squamous cells which are flat and thin 2) The tissue is only one cell thick to allow for rapid diffusion eg. alveoli and villi |
|
|
|
Name the 4 characteristics of ciliated epithelium? |
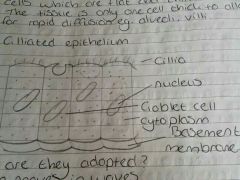
1) Cilia moves in waves 2) Mucus made to trap dust and bacteria 3) Cilia moves mucus away from the lungs where it can be swallowed 4) When swallowed, the bacteria is killed by the acid in stomach |
|
|
|
Name 5 characteristics of cartilage |
1) The connective tissue found at the ends of bones reduces friction 2) It is firm and flexible 3) Made up of chondrocytes embedded in a matrix 4) It contains fibres of the proteins elastin and collagen 5) It protects bones being damaged when they rub together at joints |
|
|
|
Muscle tissue has many blood vessels what is another word for this? |
Muscle tissue is well vascularised |
|
|
|
What are muscle cells also called? |
Fibres |
|
|
|
What is the function of muscle? |
Muscle tissue needs to shorten in length (contract) to move parts of the body |
|
|
|
Muscle tissue allows movement what are the three types? |
1) Skeletal muscles 2) Cardiac muscle 3) Smooth muscle |
|
|
|
What are skeletal muscles? |
These are packaged by connective tissue sheets, joined to bones by tendons; these muscles when they contract cause bones to move. |
|
|
|
What is cardiac muscle? |
These makes up the walls of the heart and allows the heart to beat and pump blood |
|
|
|
What is smooth muscle? |
This occurs in the walls of intestine, blood vessels, uterus and urinary tracts and it propels substances along these tracts |
|
|
|
Plant tissues |
Plant tissues |
|
|
|
What is the definition of meristem? |
An area of unspecialised cells within a plant that can divide and differentiate into other cell types |
|
|
|
What is the definition of organ? |
A collection of tissues working together to perform a function/related functions |
|
|
|
Name the five characteristics of a epidermal tissue |
1) These have cells that are closely packed and cover leaf surfaces 2) They often have a waxy layer to reduce water loss 3) Consists of flattened cells 4) Stomata formed by a pair of guard cells that are present to allow a gas exchange (CO2 in and O2 out) 5) At night stomata will close to stop water loss |
|
|
|
Name three characteristics of xylem |
1) The xylem vessel transports water and minerals from roots to all parts of the plant 2) These contain parenchymas cells (dead cells) which is a waterproof material called lignin in the cell walls 3) These also provide the plant support |
|
|
|
Name three characteristics of phloem |
1) These transfer the products of photosynthesis (mainly sucrose sugar) in solution from the leaves to parts of the plant that do not photosynthesise such as roots, flowers and growing shoots 2) It has parenchymas cells and sieve tube cells which are separated by sieve plates 3) Phloem also has companion cells that help support the sieve tube cells which lack of organelles |
|
|
|
What 5 tissues make up the lungs? |
They contain squamous epithelial tissue (in the alveoli) and ciliated epithelium tissue (in the bronchi) they also have elastic tissue, connective tissue and vascular tissue (in the blood vessels) |
|
|
|
What 4 tissues make up the leaves? |
They contain palisade tissue for photosynthesis as well as epidermal tissue (to prevent water loss from the leaf) and xylem and phloem tissues in the veins. |
|
|
|
What 6 organs make up the respiratory system? |
1) lungs 2) trachea 3) larynx 4) nose 5) mouth 6) diaphragm |
|
|
|
What 4 organs make up the circulatory system? |
1) heart 2) arteries 3) veins 4) capillaries |
|
|
|
What is meristematic tissue? |
It contains stem cells. It is from the tissue that all other plant tissues are derived by cell differentiation. It is found at root and shoot tips and in the cambium of vascular bundles. These areas are called meristems |
|
|
|
Name the features that meristems have |
1) Have thin walls containing very little cellulose 2) Do not have chloroplasts 3) Do not have a large vacuole 4) Can divide by mitosis and differentiate into other cell types |
|
|
|
How are xylem vessels made from meristems? |
Some cambium cells differentiate into xylem vessels. 1) Lignin is depostied in their cell walls to reinforce and waterproof them; however this also kills the cells 2) The ends of the cells break down so that the xylem forms continuous columns with wide lumens to carry water and dissolved minerals |
|
|
|
How are phloem vessels made from meristems? |
Other cambium cells differentiate into phloem sieve plates or companion cells 1) Sieve tubes lose most of their organelles, and sieve plates develop between them 2) Companion cells retain their organelles and continue metabolic functions to provide ATP for active loading of sugars into the sieve tubes |
|

