![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Epithelial
|
-Lines, covers, and protects other tissues and organs. -Cells tightly packed together. -Contains a BASEMENT membrane. -One free surface faces a body fluid and the other faces the environment. |
|
|
Connective
|
-Provide support and keeps body parts together. -Most ABUNDANT tissues in the body. -Cells widely separated by MATRIX. |
|
|
Muscle
|
-Contract when stimulated to cause movement of body parts. -Consist of three subtypes: ~Skeletal ~Cardiac ~Smooth |
|
|
Nervous
|
-Provides communication between all organ systems -Found in the brain, spinal cords, and nerves |
|
|
Skeletal Muscle
|
-Attaches to move bones. -Long and striated (stripy). -Voluntary control (able to control movement). |
|
|
Cardiac Muscle
|
-Found only in the heart. -Cells are branching and striated. -NOT under voluntary control (not able to be controlled and movement takes place on its own. |
|
|
Smooth Muscle
|
-Found in soft internal organs. -Cells taper at the end and are NOT striated. |
|
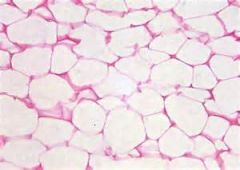
|
Connective Tissue (Adipose)
|
|
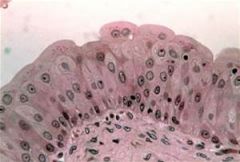
|
Epithelial Tissue
|
|
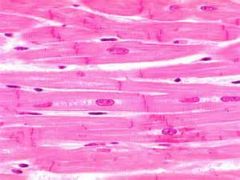
|
Muscle Tissue (Cardiac)
|
|
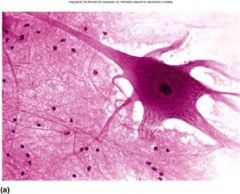
|
Nervous Tissue
|
|

|
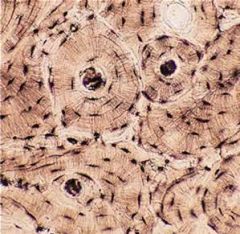
Muscle Tissue (Skeletal)
|
|
|
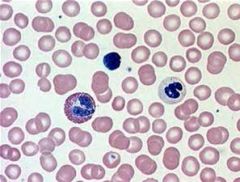
Connective Tissue (Blood)
|
|
|
Connective Tissue (Bone)
|
|

|
Muscle Tissue (Smooth)
|
|
|
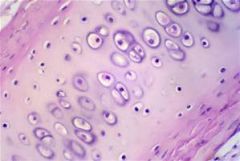
Connective Tissue (Cartlidge)
|
|
|
Attaches to the bone to move the body
|
Muscle
|
|
|
Lines major organs
|
Epithelial
|
|
|
Allows cells to communicate
|
Nervous
|
|
|
Makes up the majority of your heart
|
Muscle (Cardiac)
|
|
|
Cells are widely separated by a matrix
|
Connective
|
|
|
Tendons and Ligaments
|
Connective
|
|
|
Bone, fat, blood
|
Connective
|
|
|
Has a basement membrane
|
Epithelial
|
|
|
Found primarily in the brain/ spinal cord
|
Nervous
|
|
|
Cells may be striated
|
Muscle (Cardiac and skeletal)
|
|
|
Most abundant tissue in the body
|
Connective
|
|
|
Cells have long "arms" called axons
|
Nervous
|

