![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Epithelium |
lines, protects and secretes
Named by number of layers
Named by shape of cells |
|
|
Muscle Tissue |
excitable, contractile tissue for movement |
|
|
Nervous tissue |
excitable tissue used to send short term signals throughout the body |
|
|
Connective tissue |
living cells in a non-living matrix |
|
|
Tissue |
group of cells with common function |
|
|
Simple Squamous Epithelium |
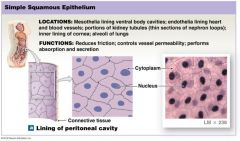
One layer of cells, squished
Located: ventral body cavity, lining of heart, blood vessels |
|
|
Stratified |
Many layers |
|
|
Stratified Squamous Epithelium |
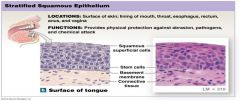
Many layers, squished
Located: throat, lining of mouth |
|
|
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium |
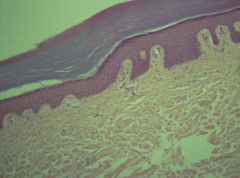
dead cells, you will not see a nuclei on most superior layer |
|
|
Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium |
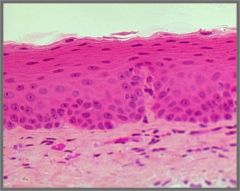
No dead cells, you will see nuclei all the way to the top |
|
|
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium |
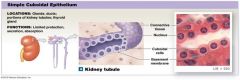
One layer and cube shaped
Located: glands, ducts |
|
|
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium |
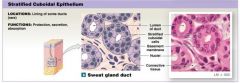
Many layers and cube shaped |
|
|
Simple Columnar Epithelium |
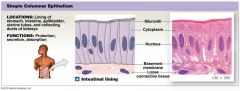
One layer and column shaped
Located: lining of stomach, intestine |
|
|
Stratified Columnar Epithelium |
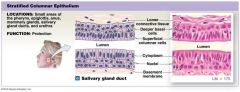
Many layers and column shaped
Located: glands |
|
|
Endocrine |
secretes into body directly
|
|
|
Exocrine |
secrete through ducts. Products go to places "outside" (surface of) the body
Examples: sweat glands, salivary glands, mammary glands, liver |
|
|
Basics of tissues picture |
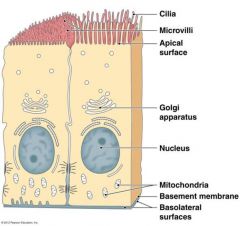
|
|
|
Apical surface |
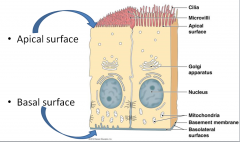
top of cell |
|
|
Basal surface |
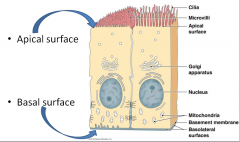
near bottom of cell, but not the most distal part |
|
|
Basement membrane |
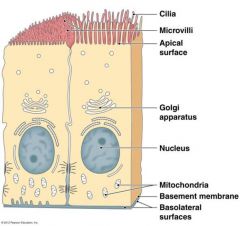
Layer of fibers that attach an epithelium to the underlying connective tissue |
|
|
Pseudostratified Ciliated Coumnar Epithelium |
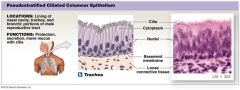
Located: lining of nasal cavity and trachea
*look for cilia |
|
|
Goblet Cells |
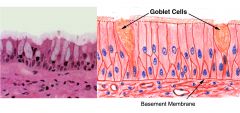
goblet shaped, mucus-producing, unicellular exocrine gland |
|
|
Cilia |
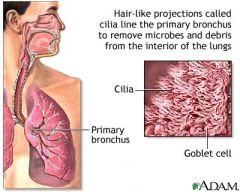
Slender organelle that extends above the free surface of an epithelial cell, generally undergoe cycles of movement and are composed of basal body and microtubules |
|
|
Merocrine secretion (exocrine secretion classification) |
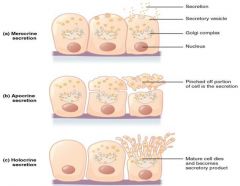
method of secretion in which the cell ejects materials from vesicles through exocytosis |
|
|
Apocrine secretion (exocrine secretion classification) |
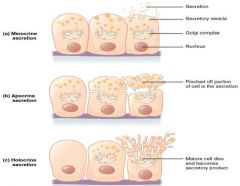
A mode of secretion in which the glandular cell sheds portions of its cytoplasm |
|
|
Holocrine secretion (exocrine secretion classification) |
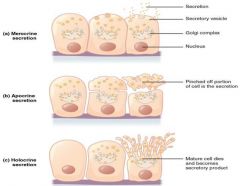
secretory cell becomes swollen with vesicles and then ruptures, the mature cell dies as a result |
|
|
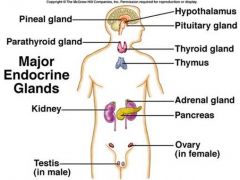
Major Endocrine Glands (picture) |
|

