![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
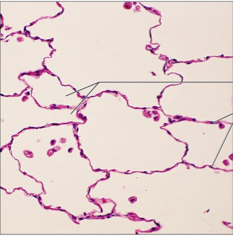
simple squamous epithelium
simple layer of flattened cells, disk-shaped central nuclei allows passage of materials by diffusion in sites where protection isn't important. Secretes lubricating substances lining of heart, air sacs of lungs, blood vessels |
|

|
simple cuboidal epithelium
single layer of cube-like cells, large spherical central nuclei secretion and absorption ducts and secretory portion of small glands, kidney tubules |
|
|
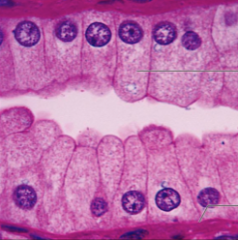
simple columnar epithelium
single layer of tall cells with round to oval nuclei absorption, secretion of mucus/enzymes, ciliated and nonciliated nonciliated lines digestive tract, ciliated line uterus |
|

|
psudostratified columnar epithelium
single layer of cells with differing heights, nuclei at different heights secretion of mucus, ciliated and nonciliated celiated lines trachea, nonciliated lines ducts of large glands |
|
|
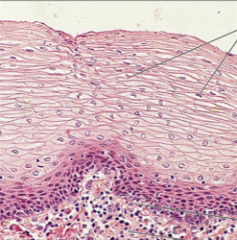
stratified squamous epithelium
thick membrane composed of several cells layers protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion, keratinized and nonkeratinized nonkeratinized lines esophagus, keratinized forms epidermis |
|
|
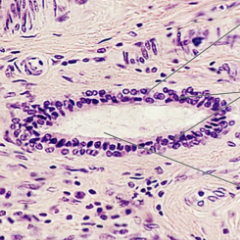
stratified cuboidal epithelium
two layers of cuboidal cells protection lines largest sweat gland ducts |
|
|
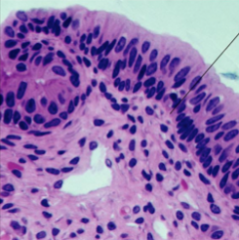
stratified columnar epithelium
several layers, basal cells are cuboidal and superficial cells are columnar protection, secretion rare in body, male urethra |
|
|
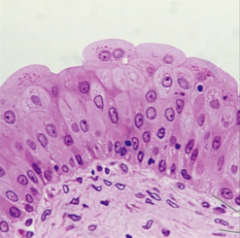
transitional epithelium
resembles stratified squamous and stratified cuboidal, basal cells cuboidal/columnar, surface cells are squamouslike stretches readily line urinary bladder, urethra |
|
|
areolar loose connective
gel-like matrix with cells (fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells) wraps and cushions organs forms lamina propia under the epidermis, wraps capillaries and organs |
|

|
adipose loose connective
closely packed adipocytes, have nuclei pushed to side provides reserve fuel, insulates in breasts |
|

|
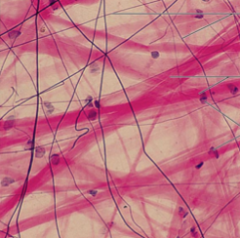
reticular loose connective
network of reticular fibers in ground substance fibers form soft internal skeleton (stroma) that supports other cell types lymph nodes, bone marrow |
|
|
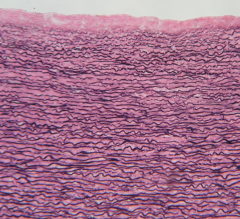
dense regular
parallel collagen fibers attaches muscles to bones, withstands tensile stress in one direction tendons, ligaments |
|
|
elastic dense
high proportion of elastic fibers allow recoil of tissue after stretching walls of large arteries, aorta of heart |
|
|
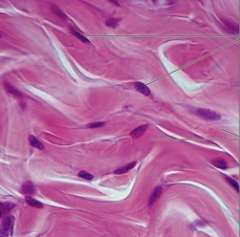
dense irregular
irregularly arranged collagen and elastic fibers withstands tension in many directions fibrous joint capsule |
|
|
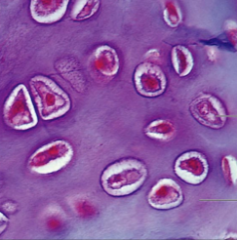
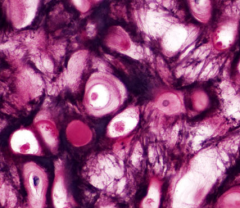
hyaline cartilage
matrix, chondrocytes in lacunae supports, reinforces, cushions ends of long bones, ribs, nose |
|
|
elastic cartilage
more elastic fibers than hyaline maintains shape while being flexible ear |
|
|
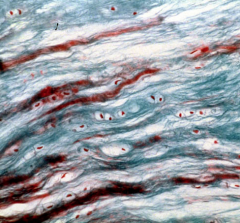
fibrocartilage
less firm than hyaline, thick collagen fibers tensile strength, absorbes compressive shock intervertebral disks |
|
|
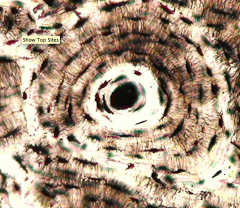
osseous tissue
hard calcified matrix, collagen fibers, osteocytes bones |
|
|
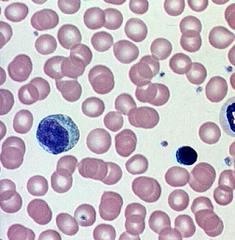
blood
red and white blood cells in plasma |
|

|
nervous tissue
branching neurons transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors brain, spinal cord, nerves |
|
|
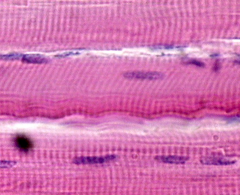
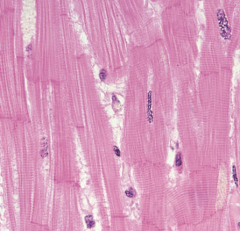
skeletal muscle
long, cylindrical cells, striations, parallel voluntary movement skeletal muscles attached to bones |
|
|
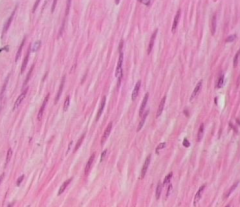
cardiac muscle
branching, striated involuntary control walls of heart |
|
|
smooth muscle
no striations, sheets of closely placed cells propels substances along passageways, involuntary control walls of hollow organs |

