![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
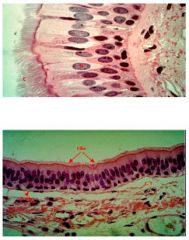
Pseudostratified Columnar
Location: lines nasal cavities, trachea, bronchi, and portions of male reproductive tract Function: Protection, Secretion, and Absorption ***Goblet Cells & Celia*** |
|
|
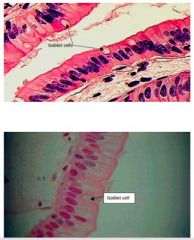
Simple Columnar
Location: Stomach, Gallbladder, Uterus, Small & large intestines Function: Secretes digestive fluids and absorbs nutrients from digested food *Goblet Cell** |
|
|
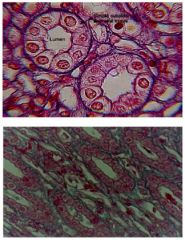
Simple Cuboidal
Location: Ducts of glands, Kidney (Renal) tubules, Bronchial, Thyroid gland... Function: Secretion and absorption. Secretes glandular products |
|
|
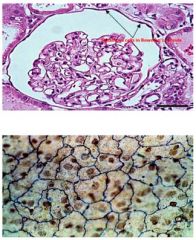
Simple Squamous
Location: Air sacs of lungs, Ventral cavities, Blood vessels, Lymphatics, Sections of renal tissue Function: Diffusion and Filtration |
|
|
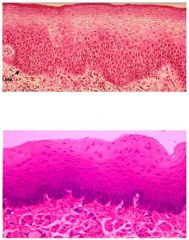
Stratified Squamous
Location: oral cavity, esophagus, and vagina Function: protection against abrasion, chemical damage and invasion of pathogens. It is located in oral cavity Modified for stretching |
|
|
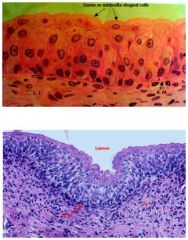
Transitional
Location: Renal Pelvis, Ureters, and Urinary Bladder Function: Capable of Stretching and Recoiling |
|
|
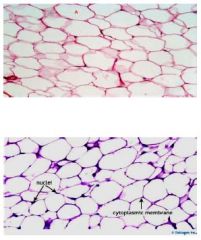
Loose Connective Tissue
Adipose Location: dermis, hypodermis, in between smooth muscle layers conforming blood vessels, in all types of mucous membranes Function: deep to the skin, especially at sides, buttocks, breasts. Can also be found around internal organs such as the eyes, heart, and kidneys |
|
|
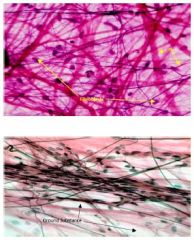
Loose connective tissue
Areolar Location: dermis, hypodermis, in between smooth muscle layers conforming blood vessels, in all types of mucous membranes Function: Fills internal spaces, and presence of elastic fibers makes it very resilient. Areolar connective tissue is the most ubiquitous of all. |
|
|
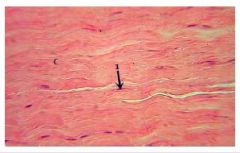
Dense connective tissue
Regular Location: tendons & ligaments Function: Connects tissue to one another |
|
|
Loose connective tissue
Reticular Location: liver, kidneys, spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow Function: provides support |

