![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
84 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Blood Connective Tissue
|
|

|
Compact Bone Connective Tissue
|
|
|
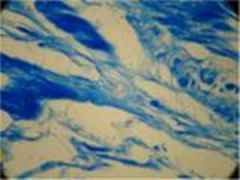
Fibrocartilage Connective Tisssue
|
|

|
Fibrocartilage Connective Tissue
|
|
|
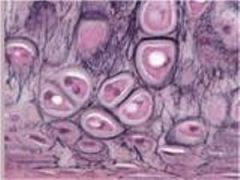
Elastic Cartliage Connective Tissue
|
|
|
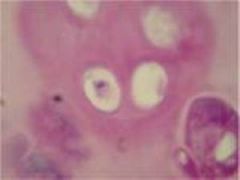
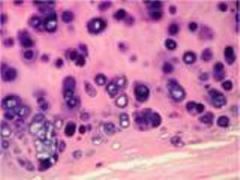
Hyaline Cartilage Connective Tissue
|
|
|
Hyaline Cartilage Connective Tissue
|
|
|
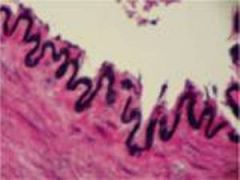
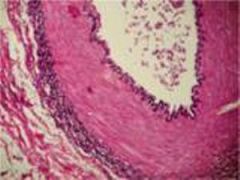
Dense Elastic Connective Tissue
|
|
|
Dense Elastic Connective Tissue
|
|
|
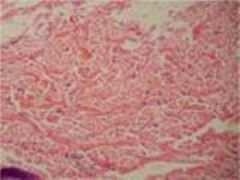
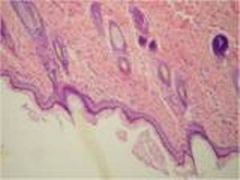
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
|
|
|
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
|
|

|
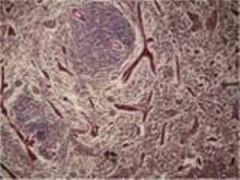
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
|
|
|
Loose Reticular Connective Tissue
|
|

|
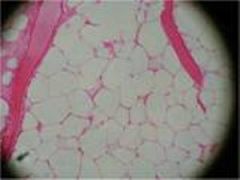
Loose Adipose Connective Tissue
|
|
|
Loose Adipose Connective Tissue
|
|
|
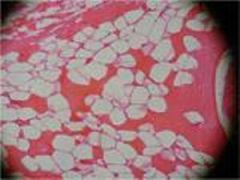
Loose Adipose Connective Tissue
|
|
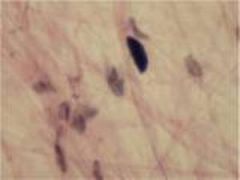
|
Loose Areolar Connective Tissue
|
|
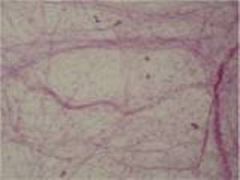
|
Loose Areolar Connective Tissue
|
|
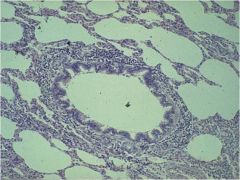
|
Simple Squamous Epitheluiem
|
|
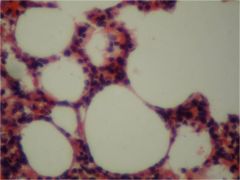
|
Simple Squamous Epitheluiem
|
|
|
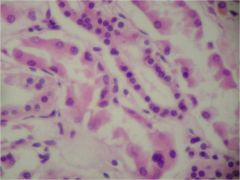
Simple Cuboidal Epithelueim
|
|
|
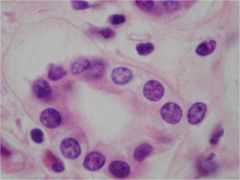
Simple Cuboidal Epitheluiem
|
|
|
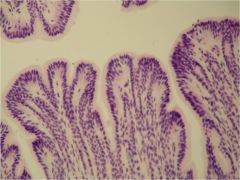
Simple Columnar Epithelueim
|
|
|
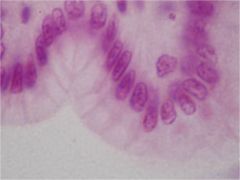
Simple Columnar Epitheluiem
|
|
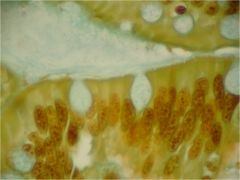
|
Pseudostratifed Ciliated Columnar Epitheluiem
|
|
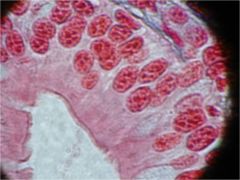
|
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epitheluiem
|
|
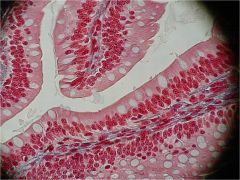
|
Goblet Cells
|
|
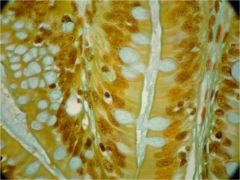
|
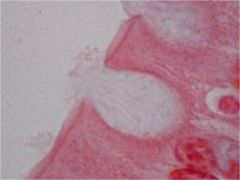
Goblet Cells Epitheluiem
|
|
|
Goblet Cells Epitheluiem
|
|
|
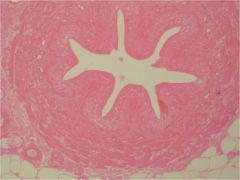
Transitional Epitheluiem
|
|
|
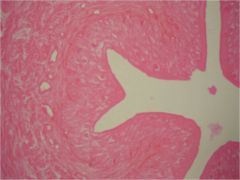
Transitional Epitheluiem
|
|
|
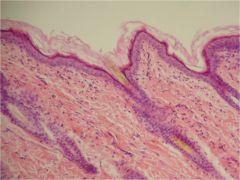
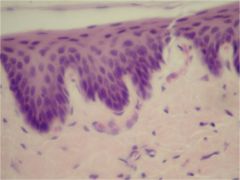
Stratified Squamous Epitheluiem
|
|
|
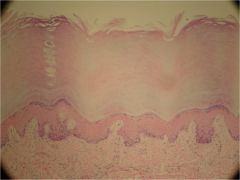
Stratified Squmous Epitheluiem
|
|
|
Stratified Squmous Epitheluiem
|
|

|
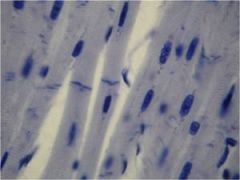
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
|
|
|
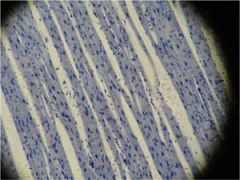
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
|
|
|
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
|
|
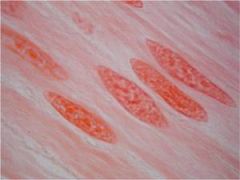
|
Smooth Muscle Tissue
|
|
|
Loose Areolar Connective Tissue
|
cell present:
fibroblasts macrophages adipocytes mast cells plasma cells Fibers Present: collagen elastic reticular Matrix Characteristics: loosely arranged fibers in gelatinous ground substance |
|
|
Loose Adipose Connective Tissue
|
Cells Present:
adipocytes Fibers Present: reticular collagen Matrix Characteristics: closely packed cells with a small amount of geltatinous ground substance; stores fat |
|
|
Loose Reticular Connective Tissue
|
Cells Present:
reticular cells Fibers Present: reticular Matrix Characteristics: loosely arranged fiber in gelatinous ground substance |
|
|
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
|
Cells Present:
fibroblasts Fibers Present: collagen (some elastic) Matrix Characteristics: parallel-arranged bundles of fibers with few cells and little ground substance; great tensile strength |
|
|
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
|
Cells Present:
fibroblasts Fibers Present: collagen (some elastic) Matrix Characteristics: Irregularly arranged bundles of fibers with few cells and little ground substance; high tensil strength |
|
|
Hyaline Cartilage Connective Tissue
|
Cells Present:
condrocytes Fibers Present: collagen ( some elastic) Matrix Characteristics: limited ground substance; dense, semisolid matrix |
|
|
Fibrocartilage Connective Tissue
|
Cells Present:
chondrocytes Fibers Present: collagen (some elastic) Matrix Characteristics: limited ground intermediate between hyaline cartilage and dense connective tissue |
|
|
Elastic Cartilage Connective Tissue
|
Cells Present:
chondrocytes Fibers Present: elastic Matrix Characteristics: limited ground substance; flexible but firm matrix |
|
|
Compact Bone Connective Tissue
|
Cells Present:
osteoblasts osteocytes Fibers Present: collagen Matrix Characteristics: rigid, calcified ground substance with (canal systems) |
|
|
Spongy Bone Connective Tissue
|
Cells Present:
osteoblasts osteocytes Fibers Present: collagen Matrix Characteristics: rigid, calcified ground substance (no osteons) |
|
|
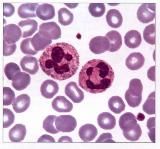
Blood Connective Tissue
|
Cells Present:
erythrocytes Fibers Present: "fibers" are soluble proteins that form during clotting Matrix Characteristics: liquid blood plasma |
|
|
Lymph Connective Tissue
|
Cells Present:
leukocytes Fibers Present: soluble liquid proteins that form during clotting Matrix Characteristics: |
|
|
Classification of Loose Connective Tissue
|
has abundant cells among few or loosely arranged fibers and a sparse to abundant gelatinous ground substance.
|
|
|
Classification of Dense Connective Tissue
|
has few cells among a dense network of fibers with little ground.
|
|
|
Classification of Cartilage Connective Tissue
|
has cells distributed among fibers in a firm jellylike ground substance. Cartilage is tough, but flexible, avascular, and without nerves.
|
|
|
Classification of Bone Connective Tissue
|
has cells distributed abundant fibers in a solid ground substance containing minerals, mostly calcium phosphate. Bone is organized in units, called osteons (Haversian system). Each osteon consists of a central canal (Haversian canal), which contains blood vessels and nerves, surrounded by concentric rings (lamellae) of hard matrix and collagen fibers. Between the lamellae are cavities (lacunae) that contain bone cells (osteocytes). Canals (canaliculi) radiate from the central canal and allow nutrient and waste exchange with osteocytes.
|
|
|
Classification of Blood Connective Tissue
|
is composed of various blood cells and cell fragments (latelets) distributed in a fluid matrix called blood plasma.
|
|
|
Four principle types of epithelial membranes
|
1. Serous membranes line interior organs and cavities. The serous membranes that line the heart, lungs and abdominal cavities and organs are called the pericardium, pleura, and peritoneum, respectively.
2. Mucous membranes line body cavities that open to the outside of the body. These include the nasal cavity and the digestive, respiratory, and urogenital tracts. 3. Synovial membranes line the cavities at bone joints. 4. The cutaneous membrane is the skin. |
|
|
Fibroblasts
|
are common in both loose and dense connective tissues.
|
|
|
Adipocytes
|
or flat cells, occur in loose connective tissue.
|
|
|
Reticular cells
|
resembles fibroblasts, but have long, cellular processes (extensions). They occur in loose connective tissue.
|
|
|
Chondtoblasts
Chondrocytes |
occur in cartilage
|
|
|
Osteoblasts
Osteocytes |
occur in bone
|
|
|
Hemocytoblasts
|
occur in the bone marrow and produce erythrocytes (red blood cells), leukocytes (white blood cells), and thrombocytes (blood platelets).
|
|
|
Macrophages
|
engulf foreign and dead cells.
|
|
|
Plasma cells produce
|
antibodies
|
|
|
Mast cells secrete
|
histamine, which stimulates immune responses.
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle
|
consist of long cylindrical cells, that under a microscope, apperar striated with bands perpendicular to the length of the cell.
The many nuclei in each cell (multinucleated cells) are located near the outside along the plasma membrane. |
|
|
Cardiac muscle
|
is striated and have single, cntrally located neuleus, and the fibers branch often.
Where two cardiac muscle cells meet, they form an intercalated disc containing gap junctions, which bridge the two cells. |
|
|
Smooth muscle
|
consists of cells with a single, centrally located nucleus.
The cells are elongated with tapered ends and do not appear striated. Smooth muscle lines the walls of blood vessels and certain organs such as the digestive and urogenital tracts, where it serves to advance the movement of substances. |
|
|
Three kinds of muscle tissue
|
1. Skeletal muscle
2. Cardiac muscle 3. Smooth muscle |
|
|
Stratified squamous epithelial tissue
|
Cells:
squamous cells apically, but basal layers vary from cuboidal to columnar Nuclei: centrally located Functions: protectection |
|
|
Stratified cuboidal epithelial tissue
|
Cells:
two layers Nuclei: centrally located, and spherical Functions: absorption, secretion |
|
|
Stratified columnar epithelial tissue
|
Cells:
single layer of columnar cells on several layers of cuboidal (or many sided) cells Nuclei: basal and oval Functions: protection, secretion |
|
|
Transitional epithelium
|
Cells:
vary depending on stretch, apical cells often large, round, and bi-nucleated Nuclei: centrally located Functions: distention (occurs only in bladder, ureter, and urethra) |
|
|
Numer of cell layers in epithelium tissues
|
Simple - describes a single layer of cells
Stratified - describes epitheluim consisting of multiple layers. Pseudostratified - describes a single a single layer of cells of different sizes, giving the appearance of being multilayered. |
|
|
Neurons
|
are the basic structural unit of the nervous system.
|
|
|
Each neuron cell consist of
|
1. Cell body - contains the nucleus and other cellular organelles.
2. Dentrites - are typically short, slender extensions of the cell body that receive stimli. 3. Axon - is typically a long, slender extension of the cell body that sends stimuli. 4. Neuroglia or glial cells - provide support functions for the neurons, such as insulation or anchoring neurons to blood vessels. |
|
|
The sum of all chemical reactions in the body is termed:
a) homeostasis b) physiology c) dyamic feedback d) metabolism |
d) metabolism
|
|
|
A vertical plane through the body dividing it into right and left is termed:
a) sagittal b) lateral c)trasverse d)frontal |
a) sagittal
|
|
|
Which of the folowing is an example of applied physiology:
a) measing the length of the femur on a fetus using ultasound b) locating an injury to a tendon in the shoulder using CT imaging c) describing the process of how a toxin interferes with nerve impulse conduction d) identifying the types of cells found in a biopsy sample of lung tissue |
c) describing the process of how a toxin interferes with nerve impulse conduction
|
|
|
The elbow is ___ to the wrist.
a) distal b) lateral c) ventral d) proximal |
d) proximal
|
|
|
The heart is ___ to the lungs.
a) superior b) dorsal c) medial d) lateral |
c) medial
|
|
|
What is the function of serous membranes?
a) to prevent fluid loss from an organ b) to reduce friction between internal organs c) to circulate blood around the organ d) to conserve heat within the organ |
b) to reduce friction between internal organs
|
|
|
Histology is the study of:
a) cells and membranes b) skin c) organs and organ systems d) tissues |
d) tissues
|
|
|
Which of the following involves the injection of radioisotopes into the body:
a) radiography b) PET c) CT imaging d) MRI |
b) PET
|

