![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
|
|
What is the drug list for tine and onchomycosis? |
Amorolfine Ciclopirox Fluconazole Griseofulvin Itraconazole Ketoconazole Naftifine Posaconazole Terbinafine Voriconazole |
|
|
What drugs are used for widespread tinea infections? How are they administered? |
Terbinafine, itraconazole, fluconazole, griseofulvin, ketoconazole (THIS IS THE ORDER)
Oral |
|
|
What drugs are used to treat tinea (localized)? How are they administered? |
Azoles, terbinafine, naftifine, ciclopirox
Topical |
|
|
What drugs are used to treat onchomycosis? How are they administered? |
Terbinafine, griseofulvin, itraconazole, fluconazole (same as tinea minus ketoconazole) = THIS IS THE ORDER ORUSE
Orally |
|
|
What drugs are used to treat onchomycosis topically? |
Ciclopirox, amorolfine |
|
|
What is the mechanism of naftitine? |
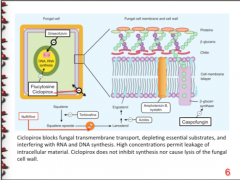
Blocks squalene epoxide to lanosterol (inhibition of 2,3 squalene epoxidase) (CELL WALL) |
|
|
What is the mechanism of terbinafine? |
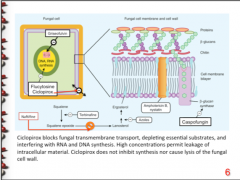
Blocks squalene to squalene epoxide (CELL WALL) |
|
|
What is the mechanism of the azoles? |
Blocks lanosterol to ergosterol (Lanosterol 14-alpha dehydrogenase enzyme) = (CELL WALL) |
|
|
What is the mechanism of amphoteracin, nystatin? |
Formation of pores in the cell wall (CELL WALL) |
|
|
Would there be an advantage to combine azoles, terbinafines, naftitine? |
No, all act on same pathway |
|
|
What is the mechanism of caspofungin? |
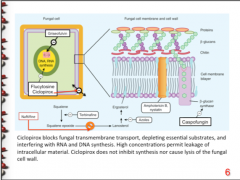
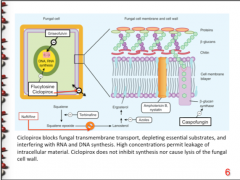
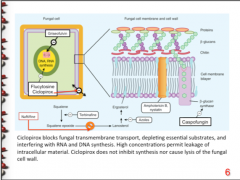
Inhibits B-glucan synthase, distrupting integrity of cell wall (CELL WALL) |
|
|
What is the added effect of ketoconazole? Which three enzymes are affected? Which three hormones are affected? |
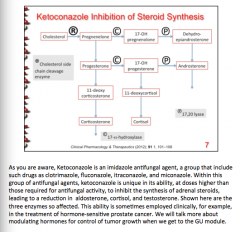
Sometimes used in hormone sensitive prostate cancer |
|
|
What are some adverse affects of ketoconazole? Think about effects on hormones |

|
|
|
What CYP to all azoles INHIBIT? Which two are azoles are substates for CYP3A4? Which two inhibit CYP2C9? Which inhibits CYP2C19? Which is a substrate for CYP2C19? |
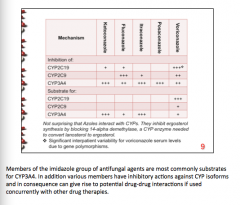
|
|
|
Which three azoles are class C pregnancy? (same as the three that inhibit CYP3A4) What is an adverse effect of Posaconazole? |
Ketoconazole Itraconazole Posaconazole = QT prolonged |
|
|
Which two azoles are class D pregnancy? What is another adverse effect of these two? |
Fluconazole Voriconazole
QT prolonged |
|
|
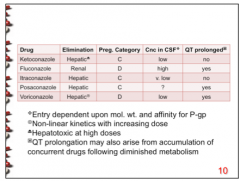
The one azole drug that has a high concentration in the CSF also is renally eliminated. What is this drug? |
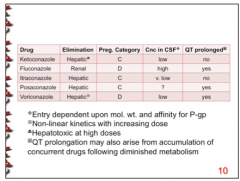
Fluconazole |
|
|
What azole drug is hepatotoxic at high doses? Which one exhibits non-linear kinetics with increasing dose? |
Hepatotoxic = ketoconazole
Non-linear kinetics = Voriconazole |
|
|
Is griseofulvin able to penetrate the skin? How do you have to administer it? How is it metabolized? Eliminated? |

Produced by certain species of penicillium |
|
|
What is the effect of griseofulvin on CYP3A4? How does this affect the action of the following: 1. Anticoagulant effect of coumarin and warfarin 2. Contraceptive effect with oral agents 3. Cyclosporine serum levels 4. Ethanol effects (tachycardia, diaphoresis, flushing) |
CYP3A4 inducer 1. Decrease 2. Decrease 3. Decrease 4. Increase |
|
|
What is the effect of griseofulvin on pregnancy? Liver? Porphyrin metabolism? What drugs will you see cross-sensitivity with? What is the effect on the skin? |

|
|
|
Terbinafine is generally well tolerated. What are two possible side effects however? What population would you want to avoid giving this drug to? |
Blood dyscrasias (lymphopenia, neutropenia) => increases susceptibility to opportunistic infections
Immunosuppressed patients |
|
|
How is terbinafine metabolized and eliminated? |
Hepatic metabolism, renal elimination
(long half life, no hepatotoxicity) |
|
|
What is the advantage of naftitine over the other azoles? |
Fungicidal activity at low doses (locally bactericidal => gram - and gram +), faster onset of action |
|
|
How does naftitine have anti-inflammatory properties? Does this lead to vasoconstriction or dilation? |

|
|
|
Why should you not combine topical azoles with naftitine? |
Pharmacodynamic interference: Inhibits sterol production at earlier point than azoles => diminishes effectiveness |
|
|
What two drugs have minimal adverse effects? What type of skin would causes worsened effects? Which one of the two drugs inhibits ergosterol synthesis? |

` |
|
|
What problems with terbinafine? Can you take it during pregnancy? |
Liver problems, blood dyscrasias (possibly need LFTs and CBCs)
YES, not teratogenic |
|
|
Which age groups tend to have decreased barrier function in skin and diminished capacity to excrete (same amount of topical cream would give much higher concentrations and systemic effects)? |
The very young and the very old |

