![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
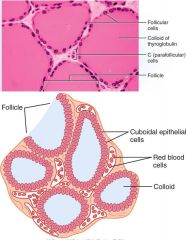
Thyroid Gland
|
Largest - lots blood supply (temp and blood soluteregulation) -- Follicle (cuboidal epithelial cells --> colloid (thyroglobulin protein: pre-thyroid --- C cells – secrete calcitonin (discussed later)
|
|
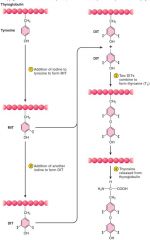
Hydrophobic – Class I -- (long half life #1 -- LATENT period)
|
Derived from two tyrosine -- with 2 Iodines -- T4 (Thxione) cleaved into T3 (Trioi -- active form)
|
|
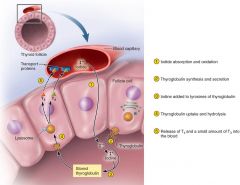
Thyroid synthesis
|
Iodine trapping infollicle (adding I to T-globulin) --- T3: 1 monoiodinated (MIT) and 1 DIT -- T4: 2 DIT added -- Most released in T4 and less T3
IonRequirements: Iodine, Iodine peroxidase and thyroglobulin |
|
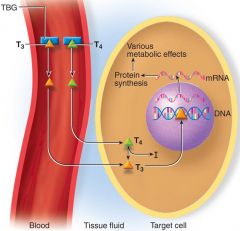
Transport class I Hydrophobic
|
need TBG (thyroxine binding globulin – synthesized by the liver) ----- and transthyretin and albumin (less than 30%: --> Slow release from blood proteins) ---- Stored in target cells bound to intracellular proteins -- Long lasting effects – latent periods
|
|
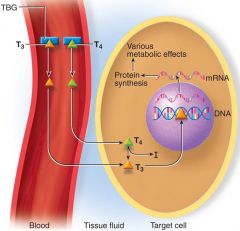
Physiological Actions general
|
T4 --> T3 (in target cell) -- Binds to nuclear receptors to alter gene expression --> 1) Na+/K+ ATPase --- 2) b-adrenergic receptors -- 3) Muscle myosin
|
|
|
Physiological Actions detail
|
Cardiovascular: incr blood flow and cardiac muscle strength --- Respiratory – increases resting ventilation and minute ventilation (breathing rate) --- Nervous system – regulates development, increases synaptic firing, enhances wakefulness and alertness ---- Muscoskeletal – more activity (small rise in thyroid levels) -- Endocrine – increases glucocorticoid release -- increases insulin release, parathyroid hormone
|
|
|
Physiological Effects
|
Increase metabolic (O2 - heat (Calorigenic effect) -protein turnover/ synthesis (cross Placenta fetus growth or else cretinism) - carb/ lipid metabolism (dec choles, phospholipids and TG’s in blood), increased vitamin utilization
|
|
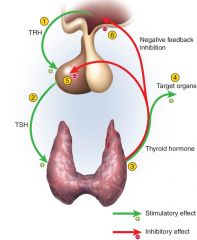
Regulation of Secretion
|
Release (Cold - Night for heat and growth) ---- Inh (Excitement - Anxiety - Burns - Starvation - Fever - Corticosteroids --> stress fight and flight -- need to survive not not growth)
|
|
|
Hypothyroidism disease --
|
Hashimoto’s (autoimm -- Thyroiditis) -- Congenital Hypothyroidism – cretinism (can't growth) -- Defect thyroid or pituitary, ↓hormone synthesis --- Iodine deficiency (Endemic colloid goiter) -- Elevated TSH stimulates TG secretion into follicles -- Idiopathic colloid goiter – normal levels of iodine -- Problems with the enzymes in the follicle -- Anti-thyroid compounds – can be found in foods (Thiocyanate – inhibits iodine transport ---- Propylthiouracil – peroxidase enzyme inhibitor)
|
|
|
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism:
|
Cold intolerance -- Weight gain -- Fatigue, excessive sleeping -- Increase cholesterol -- Depressed cardiovascular -- Myxedema
|
|
|
Treatment vs Diagnosis of Hypothyroidism:
|
Treatment: T4 hormone replacement therapy – extremely effective Synthroid (levothyroxine) -- Diagnosis: Radioimmunoassay (measurement of free plasma T3 (T4) --- Decreased BMR -- Circulating TSH levels elevated above normal -- Clinical observation: goiter and swollen face
|
|
|
Hyperthyroidism Etiology:
|
Graves’ Disease (autoimm. makes thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) stimu Thyroid gland over Thyroid --> neg fb --> Suppressed TSH levels -- Thyroid adenoma – thyroid cancer -- Suppressed TSH levels : decreases non-adenoma thyroid hormone release
|
|
|
Thyrotoxicosis - Goiter
|
Thyrotoxicosis – excess thyroid hormone in the blood and tissues ----Goiter – enlarged thyroid gland due to hypersecretion of thyroid hormone (toxic) – growth effects of thyroid hormone
|
|
|
Hyperthyroidism Symptoms:
|
Heat intolerance
Weight loss High state of excitability Muscle weakness (too much protein catabolism) Increased cardiovascular Fatigue, inability to sleep Exopthalmos |
|
|
Hyperthyroidism Treatments:
|
Block iodine uptake or synthesis – (pertechnetate, percholorate, thiocynate) -- Prevent iodination – thioamides --- Radioactive Iodine – destroys thyroid
|
|
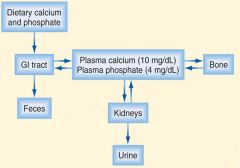
Calcium Hormones extracellular Ca2+ bound to plasma proteins – remains in narrow range – Regulatory Points
|
Calcitriol, Calcitonin, Parathyroid hormone
|
|
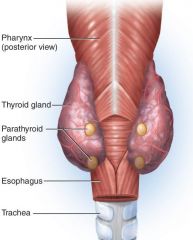
Parathyroid Glands
|
– secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH) in response to hypocalcemia
|
|
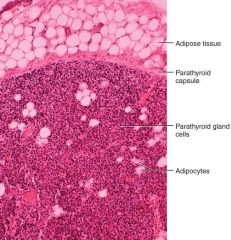
Cells of the parathyroid gland
|
Chief cells – synthesis and secretion of PTH -- Clear cells – chief cells with increased glycogen -- Adipocytes – 60-70% of glandular mass
|
|
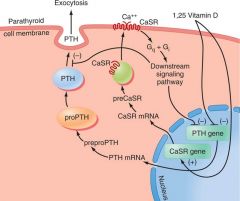
Parathyroid Synthesis
|
Synthesis (pro-PTH synthesized in ER and golgi -- PTH produced in secretory vesicles ) ----- Hormone Release – Ca2+-sensing receptor – represses release
|
|
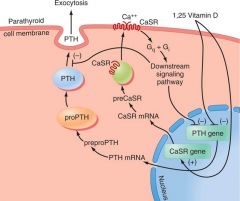
Parathyroid regulation
|
High Ca outside -- Gs-Gi --> less PTH gene express AND
High Vitamin D (Calcitriol) – directly Suppress PTH gene express AND more CaSR more Ca Receptor to signal GsGi |
|
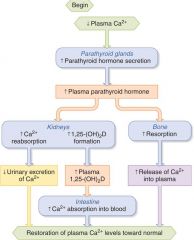
PTH Physiological Effects:
|
Kidneys: INC. gene exp enz (make VitD act form) -- REabsorb more Ca2+ -- Bone: Break Bone for Ca (osteoclasts) --- Take P in --- USING G-protein coupled receptor activation - cAMP and PLC signaling pathways
|
|
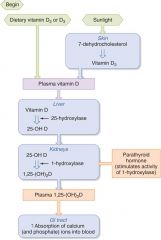
Calcitriol (1,25 – OH2D) – form of vitamin D with physiological effects
|
INdirectly regulated by PTH -- Increase absorption of Vitamin D from GI tract
|
|
|
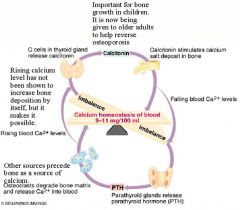
Calcitonin – secreted by C-cells of the thyroid gland follicle
|
Peptide hormone (type 2 soluble) -- Release: SPIKE High Ca -- Block REabsorp Ca2+ to MAKE bone (osteoblasts)
|
|
|
Prim and 2nd Hyperparathyroidism
|
Prim: less Ca2+ receptor or PTH secreting tumors ---
2nd: hypo-calc-emia -- Vitamin D deficiency, malabsorption, pregnancy |
|
HyperPTH Symptoms - Treatment
|
Weakness --Depression -- Osteopenia-- Kidney stones --
Treatments – diet LESS Ca- VitD -- surgical (required Ca supp) |
|
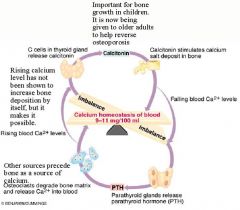
Hypoparathyroidism and Treatment
|
Autoim -- Genetic disease - Surgery -- Symptoms: Hypocalcemia -- Muscle cramping -- Tetany -- Treatment: Ca2+ supplementation and vitamin D supplementation
|

