![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
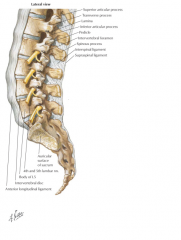
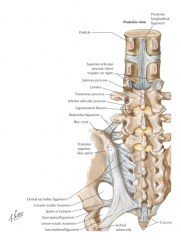
posterior ligamentous complex
|
supraspinous ligament (SSL)
interspinous ligament (ISL) ligamentum flavum (LF) facet joint capsules |
|
|
liagmentus nuchae
|
interspinous ligament
supraspinous ligament |
|
|
ASIA grading
|
Grade A: complete - no motor or sensory
Grade B: no motor, sensory present Grade C: motor <3/5, sensory present Grade D: motor >/=3/5, sensory present Grade E: normal |
|
|
sensory present on ASIA scale
|
sensation at anal mucocutaneous junction
deep anal sensation |
|
|
motor present on ASIA scale
|
voluntary anal schincter contraction
|
|
|
motor grading
|
0 = no visible or palpable contraction
1 = any visible or palpable contraction 2 = able to move with gravity eliminated 3 = able to move against gravity 4 = able to move against some resistance 5 = able to move against resistance |
|
|
anterior column
|
anterior longitudinal ligament
anterior part of the vertebral body anterior portion of the annulus fibrosis |
|
|
middle column
|
posterior longitudinal ligament
posterior part of the vertebral body posterior portion of annulus fibrosis |
|
|
posterior column
|
facet joints
laminae pedicles supraspinous ligament (SSL) interspinous ligament (ISL) ligamentum flavum (LF) facet joint capsules |
|
|
SLIC components
|
morphology
ligamentous neurologic status |
|
|
SLIC morphology
|
no abnormality = 0
compression = 1 burst = 2 distraction = 3 (perch, hyperex) rotation/translation = 4 (facet dislocation, unstable teardrop) |
|
|
SLIC ligamentous
|
intact = 0
indeterminate = 1 (interspinous widening, MRI signal change) disrupted = 2 (disc space wide, facet perch/dislocation) |
|
|
SLIC neurologic
|
intact = 0
root injury = 1 complete = 2 incomplete = 3 continuous cord compression = 4 |
|
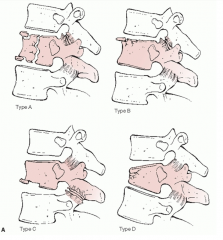
|
Denis scheme: compression
A: both endplates B: superior endplate C: inferior endplate D: anterior body |
|
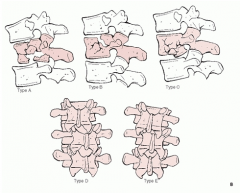
|
Denis scheme: burst
A: both endplates B: superior endplate C: inferior endplate D: rotational deformity E: lateral translation |
|
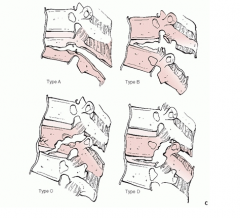
|
Denis scheme: flexion-distraction
A: bony involving one segment B: soft tissues of one segment C: bony involving two segments D: soft tissues of two segments |
|
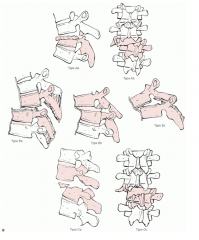
|
Denis scheme: fracture-dislocations
A: bony involving one segment B: soft tissues of one segment C: two level injuries |
|
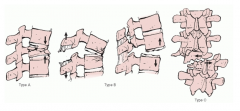
|
AO/Magerl classification based on vector forces
A: compression B: distraction C: rotation |
|
|
TLICS
|
thoracolumbar injury classification and severity score
- morphology - neurologic status - posterior ligamentous complex |
|
|
TLICS morphology grading
|
compression = 1
burst = 2 translational/rotational = 3 distraction = 4 |
|
|
TLICS neurologic status grading
|
intact = 0
nerve root injury = 2 spinal cord/conus medullaris injury complete = 2 incomplete = 3 cauda equina = 3 |
|
|
TLICS PLC grading
|
intact = 0
indeterminate = 2 disrupted = 3 |
|
|
TLICS treatment recommendations based on score
|
</=3 nonoperative
4 indeterminate >/=5 operative |
|
|
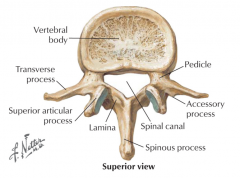
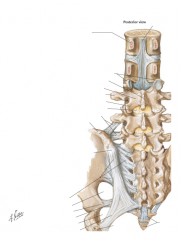
posterior elements making up protective neural arch
|
pedicles
laminae transverse processes spinous processes facet (zygoaphophyseal) joints |
|
|
primary thoracic spinal cord vascular supply
|
artery of Adamkiewicz
|
|
|
why artery of Adamkiewicz is in danger
|
perfuses retrograde
enters single intervertebral foramen between T9-L2 |
|
|
level conus medullaris ends
|
L1-L2
|
|
|
at what point are compression fractures considered unstable?
|
>50% vertebral body height loss
>20-30 degrees angulation multiple adjacent compression fractures |
|
|
thoraco lumbar injury associated with intrabdominal injuries
|
flexion-distraction
(chance fractures, seat belt-type injuries) |
|
|
when is spinal injury considered unstable?
|
normal physiologic loads cause further neurologic damage, chronic pain, and unacceptable deformity
|
|
|
factors indicative of instability of burst fracture
|
50% canal compromise
15-25 degrees of kyphosis >40% anterior body height loss |
|
|
L1-S1 motor exam
|
L1: hip flexor
L2: hip adductor L3: quadriceps L4: anterior tibialis L5: extensor hallucis longus S1: flexor hallucis longus |
|
|
L1-S1 sensory exam
|
L1: anterior proximal thigh
L2: middle proximal thigh L3: inferior to patella L4: just above medial malleolus L5: 1st web space S1: lateral border of foot |
|
|
L1-S1 reflex exam
|
L1: none
L2: none L3: patella L4: patella L5: none S1: achilles |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

