![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
448 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the absolute contraindications to fibrinolysis in ACS
|
History of ICH
History of intracranial neoplasm History of intracranial structural lesion (AVM) History of ischemic stroke (<3mo except in the first 4.5h) Recent head trauma <3mo Recent facial trauma <3mo Suspected Aortic dissection Active bleeding |
|
|
What are the relative contraindications to fibrinolysis in ACS
|
History of chronic, severe, poorly controlled HTN
Severe uncontrolled HTN on presentation (SBP >180, DBP>110) History of prior ischemic stroke >3mo, dementia or known IC pathology not covered in absolute CI Traumatic or prolonged CPR Major surgery <3weeks Recent (within 2-4 weeks) internal bleeding Non compressible vascular punctures Pregnancy Active peptic ulcer Current use of anticoagulants: the higher the INR, the higher the risk of bleeding |
|
|
What are the absolute contraindications to fibrinolysis in ischemic stroke
|
-Evidence of ICH on pre-treatment CT heat
-History ICH -Clinical presentation suggestive of SAH even with normal CT head -CT shows multilobular infarction (hypo density >1/3 cerebral hemisphere) -uncontrolled HTN SBP >185, DBP >110 (despite repeated measures and treatment) -known AVM, neoplasm or aneurysm -blood glucose <2.7mmol/L -active internal bleeding or acute trauma -acute bleeding diathesis (Plt <100,000, recent heparin with PTT>Normal, current use of anticoagulant with INR >1.7) -Within 3 months of intracranial or intraspinal surgery, serious head trauma or previous stroke -arterial puncture at noncompressible site within 7 days |
|
|
What are the relative contraindications to fibrinolysis in ischemic stroke
|
-Only minor or rapidly improving stroke symptoms
-within 14 days of major surgery or serious trauma -recent GI or GU hemorrhage (within 21 days) -recent AMI (within 3 months) -postmyocardial infarction pericarditis -seizure at onset with postuctal residual neurologic deficits |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis of ST elevation
|
Infarction
Pericarditis Benign Early repolarization LV aneurysm LVH Hyperkalemia Osborn J wave of hypothermia Brugada syndrome Acute cerebral hemorrhage Post-electrical cardioversion Ventricular paced rhythm PE Normal variant |
|
|
Differential diagnosis of ST depression
|
infarction
pericarditis repolarization abnormality of ventricular hypertrophy (strain) ventricular paced rhythm BBB digoxin effect hyperkalemia hypokalemia PE ICH myocarditis rate-related ST depression PTX post cardioversion of tachydysrhythmias |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis of T wave inversion
|
myocardial ischemia
pediatric EKG PE CVA Pericarditis Myocarditis Wellen's syndrome |
|
|
What are the EKG changes seen in pericarditis?
|
ST elevation in multiple leads (usually concave)
PR depression seen in multiple leads Stages ST elevation (hrs to days) ST resolution (hrs to days) T wave inversion (hrs to days) T wave resolution (weeks) |
|
|
What are Sgarbossa's criteria?
|
For the diagnosis of AMI in the presence of LBBB
-ST elevation >/=1mm with concordant QRS in at least 1 lead (5pts) -ST depression of >/=1mm in V1-V3 (3pts) -ST elevation of >/=5 mm with discordant QRS (2pts) Scores of greater than or equal to 3 have 90% specificity |
|
|
What are the Brugada criteria for differentiating VT from SVT with aberrancy?
|
1.Absence of an RS complex in all precordial leads? YES-> VT, No ->goto step 2
2.R to S interval >100ms in one precordial lead? YES-> VT, no -> go to step3 3. Atrioventricular dissociation? YES-> VT, No -> go to step 4 4. Morphology criteria for VT present both in V1,V2 and V6? YES -> VT, if No -> SVT with aberrancy |
|
|
What are the morphology criteria for VT?
|
Tachycardia with RBBB-like QRS
V1 Monophasic R or QR or RS favors vT Triphasic RSR' favors SVT V6 R to S ratio <1 (R wave smaller than S wave) favors VT QS or QR favors VT Monophasic R favors VT Triphasic favors SVT R to S ratio >1 (R wave larger than S ave favors SVT) Tachycardia with LBBB like QRS V1 Any of the following R>30msec, >60msc to nadir S, notched S favors VT V6 Presence of any Q wave, QR or QS favors VT The absence of a Q wave in lead V6 favors SVT |
|
|
What are the clinical features of Wellen's criteria for differentiating VT from SVT with aberrancy?
|
VT
Age >50 History of MI, CHF, CABG, Atherosclerotic HD mitral valve prolapse Previous history of VT SVT Age 35 or less no heart disease Mitral valve prolapse (especially in WPW) Previous history of SVT |
|
|
What are the EKG features of Wellen's criteria for differentiating VT from SVT with aberrancy?
|
VT
Fusion beats AV dissociation QRS >0.14sec extreme LAD No response to vagal maneuvers SVT No fusion beats preceding P waves with QRS complexes QRS <0.14sec Axis normal or slightly abnormal arrhythmia slows or terminates with vagal maneuvers |
|
|
What are the specific QRS patterns in Wellen's criteria for differentiating VT from SVT with aberrancy?
|
VT
V1: R, qR, RS V6: S, rS or qR Identical to previous VT tracing concordance of positivity or negativity SVT V1: rsR' V6: qRs Identical to previous SVT tracing |
|
|
What are the indications for a 15 lead EKG?
|
Inferior STEMI
Any ST elevation or depression in V1 -V3 Equivocal ST elevation in inferior or lateral leads Hypotension in the setting of ACS |
|
|
Which coronary artery and leads are responsible for anterior wall AMI?
|
LAD
V1-V4 |
|
|
Which coronary artery and leads are responsible for lateral wall AMI?
|
Circumflex
V5-V6, I, aVL |
|
|
Which coronary artery and leads are responsible for inferior wall AMI?
|
RCA
II, III, aVF |
|
|
Which coronary artery and leads are responsible for right ventricular wall AMI?
|
RCA
V4R |
|
|
Which coronary artery and leads are responsible for posterior wall AMI?
|
RCA
V8, V9, V1-V3 depression |
|
|
What are criteria for STEMI on ECG?
|
ST elevation of 1mm or higher in 2 contiguous leads
except Men >/= 40 years - 2mm in V2 and V3 Men</= 40 years - 2.5mm in V2 and V3 Women 1.5mm in V2 and V3 Presumed new LBBB |
|
|
When is fibrinolytic therapy indicated?
|
When there is anticipated delay to performing PCI within 120 minutes of FMC and onset of symptoms within the previous 12 hours
-Reasonable to give if clinical and/or ECG evidence of ongoing ischemia within 12-24 hours of symptom onset and a large area of myocardium is at risk -only give in ST depression if true posterior mi or when associated with ST elevation in aVR |
|
|
When is Primary PCI indicated?
|
-Primary PCI should be performed in patients with STEMI and ischemic symptoms of less than 12 hours duration
-Ischemic symptoms <12 hours and contraindications to fibrinolytic therapy (irrespective of time delay from FMC) -cardiogenic shock or acute severe HF irrespective of time delay from first medical contact -primary PCI is reasonable in patients with STEMI if there is clinical and/or ECG evidence of ongoing ischemia between 12 and 24 hours |
|
|
What is the delta gap?
|
It is the
"Door to balloon time" minus the "Door to needle time" AHA guidelines suggest this should be max of 60minutes Ilcor guidelines suggest 90minutes if transferring to a high volume centre |
|
|
Which trial supports the Door to balloon time of <90 minutes?
|
Gusto IIb - NNT 24
Keeley - NNT 16 |
|
|
Which trial suggests that primary PCI is equal to lytic < 3hours (if door to ballon >90minutes)?
|
CAPTIM trial
|
|
|
Which trial suggests that primary PCI is superior to lytic if symptoms >3hours or complicated patient (age>65, IDDM, CHF, CVA, Prev PCI, AMI, CABG)?
|
Gusto IIb
Keeley |
|
|
What is facilitated PCI?
|
The use of thrombolytic drugs as pretreatment before PCI
|
|
|
Should facilitated PCI be used?
|
no
ASSENT-4 (2006) -increased mortality in facilitated PCI group- they had to stop the study early Keeley 2006 -facilitated PCI associated with significant mortality, reinfarction, bleeding and stroke |
|
|
What is the MOA of oxygen in AMI? What is the guideline?
|
Optimizes O2 delivery to the myocardium
Start oxygen if O2 sat <94% |
|
|
What is the MOA of ASA in AMI? What is the evidence for ASA in AMI?
|
Thromboxane A2 inhibitor - inhibits platelet aggregation
ISIS 2 NNT 42 to prevent early death NNT 100 to prevent recurrent MI |
|
|
What is the MOA of NTG in AMI? What is the evidence?
|
Peripheral and coronary vasodilation
No good large studies to show proven benefit |
|
|
What are contraindications to the use of NTG in AMI?
|
Hypotension
Recent phosphodiesterase inhibitor use Bradycardia Right-sided MI |
|
|
What is the role of morphine in ACS?
|
-CRUSADE observational trial showed increased mortality in patients with ACS, therefore AHA downgraded their recommendation
|
|
|
What is the perceived role of beta blockers in ACS?
|
decreased HR, BP and contractility therefore decreased O2 demand
|
|
|
What is the role of BB in the early management of ACS?
|
COMMIT trial (2005) showed increased death in patients with shock (group that is often tachycardic) thus the recommendation for BB is to wait until the patient is on the floor to start BB.
|
|
|
What is the evidence for the use of plavix in ACS?
|
In short, if PCI give load 600mg, if fibrinolysis load 300mg if <75 years and 75mg for those >75years.
COMMIT - small clinical benefit on composite end points at 28 days, NNT 111, no loading dose of plavix CLARITY - 300mg plavix load prior to PCI, composite outcome at 30 days, NNT 39 ARMYDA-6: 600mg plavix load prior to PCI, composite outcome at 30 days, NNT 11, no increase in bleeding |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of clopidogrel?
|
ADP-inhibitor
|
|
|
What is the role of GPIIb/IIIa inhibitors in STEMI?
|
AHA - Class IIb
It may be reasonable to administer in the precatheterization lab setting, but typically given by the cath lab ACUITY trial showed that there was no benefit in giving GPIIb/IIIa inhibitors in the ED over deferring to PCI some trials FINESSE, AGIR-2, I do not know them in detail |
|
|
What anticoagulant therapy should be given to support PCI in STEMI? Fibrinolysis in STEMI?
|
PCI
-UFH (with additional boluses administered as need to maintain activated clotting time levels) or - Bivalirudin (better in those with high risk of bleeding) (NEJM 2008) Fibrinolysis -UFH to APTT 1.5-2.0 times control or *preferred* -enoxaparin IV bolus followed by subcutaneous injection EXTRACT-TIMI-25 or -fondaparinux IV followed by SC injections |
|
|
What is bivalirudin?
|
It is a direct thrombin inhibitor.
|
|
|
What is the number of rescue breaths in a patient who is not breathing but has a pulse?
|
Adult - 10-12 breaths/min
Child and infant: 12-20 breaths/min |
|
|
What is the number of breaths/min in CPR with an advanced airway in place?
|
8-10 breaths/min
|
|
|
What should be done for relief of foreign body airway obstruction in a conscious patient/.
|
Adults - abdominal thrusts
Child - abdominal thrusts Infant - five back slaps and 5 chest thrusts |
|
|
Where do you perform pulse checks?
|
Adult and paediatric: carotid
Infant: brachial or femoral |
|
|
What is the compression landmark for CPR?
|
Adult: Lower half of the sternum (centre of the victims chest)
Paediatric: Lower half of the sternum Infant: below the inter-nipple line |
|
|
What is the compression depth in CPR?
|
Adult: 2 inches
Children: At least 1/3 AP diameter, 2 inches infant: At least 1/3 AP diameter, 1.5 inches |
|
|
What is the compression rate in CPR?
|
At least 100/min
|
|
|
What is the compression to ventilation ratio in CPR?
|
Adults: 30:2
Pediatric and Infant: 30:2 (2 rescuer), 15:2 (1 rescuer) |
|
|
What is the defibrillation dose for 1st monophasic defibrillation?
|
Adult: 360J
Pediatrics/infants: 2J/kg |
|
|
What is the defibrillation dose for 2nd monophasic defibrillation?
|
Adult: 360J
Pediatric/infants: 4J/kg |
|
|
What is the defibrillation dose for 1st biphasic defibrillation?
|
Adult: 120-200J
Pediatric/infant: 2J/kg |
|
|
What is the defibrillation dose for 2nd biphasic defibrillation?
|
Adult: 120-200J
Pediatric/infant: 4J/kg |
|
|
What is the epinephrine dose in cardiac arrest?
|
Adult: 1mg/kg
Pediatric: 0.01mg/kg |
|
|
What is the amiodarone dose in cardiac arrest?
|
Adult: 300mg then 150mg
Pediatric : 5mg/kg |
|
|
What is the adenosine dose?
|
Adult: 6-12-12
Child: 0.1mg/kg, 0.2mg/kg |
|
|
what is the magnesium dose in cardiac arrest?
|
Adult: 1-2g IV
Child: 25-50mg/kg IV |
|
|
Adult pulseless arrest. Describe management
|
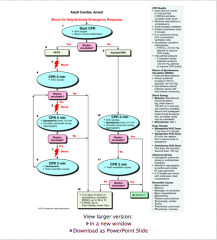
|
|
|
Child pulseless arrest. Describe management
|
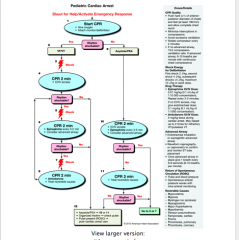
|
|
|
Adult Patient with pulse of 25
|
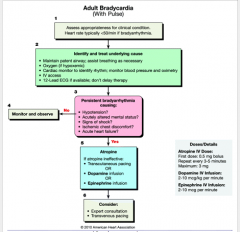
|
|
|
Adult with pulse 190
|
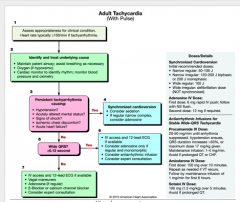
|
|
|
Pediatric patient with pulse of 25
|
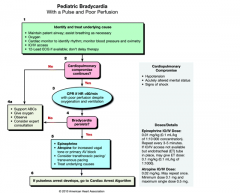
|
|
|
Pediatric with pulse of 190
|
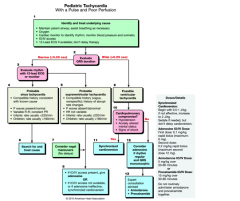
|
|
|
What is the neonatal resuscitation flow diagram
|
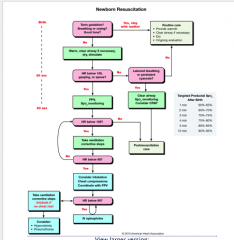
|
|
|
What are possible contributing factors to PEA/Asystole?
|
Hypoxia
Hypothermia Hypo/hyperkalemia Hypoglycemia Hydrogen ion thrombosis (coronary, pulmonary) trauma toxicology tension pneumothorax tamponade |
|
|
What are the indications for therapeutic hypothermia?
|
-OOH VF arrest with ROSC
-in hospital cardiac arrest of any initial rhythm -OOH arrest with ROSC with initial rhythm asystole/PEA |
|
|
How do you cool a patient?
|
Ice packs to groin, axilla and neck
cold saline boluses cooling blankets fan & mist Paralyze and sedate |
|
|
What is the target temperature in therapeutic hypothermia?
|
32-34 degrees celsius for 12-24 hours
Cool over 2-8hours Rewarm over 12 hours |
|
|
What are criteria used to diagnose infective endocarditis?
|
Duke criteria
2 major 1 major and 3 minor 5 minor |
|
|
What are the major Duke criteria
|
Positive blood cultures (at least 2 separate cultures)
Evidence on echo (endocardial vegetation, paravalvular abscess, new partial dehiscence of prosthetic valve, new valvular regurgitation) |
|
|
What are minor Duke criteria?
|
-Predisposition (heart condition or IVDU)
-Fever >/=38 -vascular phenomenon (arterial emboli, septic pulmonary infarcts, mycotic aneurysm) -immunologic phenomena (osler nodes, Roth spots) -microbiologic evidence (single positive blood culture) -echo findings consistent with endocarditis but do not meet major criteria |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis of thrombocytopenia?
|
Spurius
-test is abnormal, inadequate anticoagulation of blood, dilutional due to massive RBC transfusion Real -decreased production (infection, chemo, BM suppression) -splenic sequestration (hematologic malignancy, portal hypertension, hereditary spherocytosis) -increased desctruction (ITP, TTP, HUS, DIC, HELLP), immunologic (SLE, HIT, Drug) |
|
|
List oncologic emergencies?
|
Febrile neutropenia
SVC syndrome Acute tumor lysis syndrome Hyperviscosity syndrome Hyperuricemia Hypercalcemia Neoplastic cardiac tamponade Spinal cord compression raised ICP |
|
|
What are clinical features of acute tumor lysis syndrome?
|
Hyperuricemia
Hyperkalemia Hyperphosphatermia Hypocalcemia |
|
|
What is the classic presentation of hyperviscosity syndrome?
|
Bleeding
visual disturbances neurologic manifestations |
|
|
Describe the Mallampati Score
|
I. soft palate, uvula, fauces, pillars visible
II. soft palate, uvula, faces visible no pillars visible III. soft palate and base uvula visible IV. only the hard palate |
|
|
Describe the cormack lehane score
|
Class I: vocal cords visible
Class II: the vocal cords are only partly visible Class III: only the epiglottis is seen Class IV: the epiglottis cannot be seen |
|
|
What are the pros and cons of volume control ventilation?
|
Known tidal volumes
High pressures can result in barotrauma |
|
|
What are the pros and cons of pressure control ventilation?
|
Known pressure (avoid barotrauma)
Potential for volume trauma |
|
|
What are the pros and cons of pressure support?
|
more comfortable for patient, good for weaning
Lack of control over volume relies on patients RR therefore can have apnea |
|
|
What are reasonable initial ventilator settings?
|
RR 10
I:E 1:3 If volume control 10cc/kg If pressure control start at 15cmH20 FiO2 100% PEEP 5-10 I will perform a VBG in 20 minutes and adjust as necessary |
|
|
What is the differential for the high pressure alarm on a ventilator?
|
Machine error
Mucus plug (airway or tube) kinked tube Right mainstem PTX/Hemothorax |
|
|
What is your differential if vent low pressure alarm goes off?
|
Vent broken
Vent disconnected Cuff Leak Open chest wound |
|
|
The apnea alarm goes off, what is your differential?
|
Apnea on pressure support
Equipment failure Disconnected |
|
|
List the congenital heart diseases that cause cyanosis?
|
Tetralogy of Fallot
Transposition of the great arteries Total anomalous pulmonary venous return Tricuspid atresia Tuncus arteriosus Ebsteins anomaly Pulmonary atresia Hypoplastic left heart syndrome Hypoplastic right heart syndrome |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis of acyanotic congenital heart disease?
|
Coarctation of the aorta
Mitral stenosis Aortic stenosis Atrial septal defect Ventricular septal defect Patent ductus arteriosus |
|
|
What are the four abnormalities of tetralogy of fallot
|
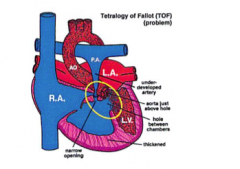
RV outflow tract obstruction
Large, unrestrictive VSD Overriding aorta (receives blood from both ventricles) RVH secondary to high pressure from RV outflow tract obstruction |
|
|
What is the treatment for a "tet spell"
|
-place infant in knee to chest position, provide supplemental O2
-morphine 0.1-0.2mg/kg -NaHCO3 1mEq/kg IV -Ketamine 1-2mg/kg -Propranolol 0.01-0.2mg/kg IV -Phenylephrine 0.01-0.2 mg/kg IV |
|
|
List CHDs that require a patent ductus and why?
|
To preserve flow from aorta to pulmonic circulation
-pulmonic atresia -tricuspid atresia -Tetralogy of fallot -Hypoplastic right heart syndrome To preserve flow from pulmonic circulation to aorta -Severe coarctation of the aorta -Severe aortic stenosis -Hypoplastic left heart syndrome |
|
|
What is the pharmacologic management to keep the ductus patent?
|
Protaglandin E1 0.1ug/kg/min
(side effects include apnea and decreased BP) |
|
|
What are the etiologies of sudden cardiovascular death in young athletes?
|
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Various congenital coronary artery anomalies Prolonged QT Various pre-excitation syndromes (WPW) Commotio cordis Aortic rupture secondary to Marfans Idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy Myocarditis CAD secondary to Kawasaki's Aortic stenosis mitral valve prolapse |
|
|
What are the diagnostic criteria for Kawasaki's Disease?
|
Fever 38 degrees >/=5 days and at least 4 of the following:
-bilateral nonexudative bulbar conjunctivities -oropharyngeal mucus membrane changes (pharyngeal edema, red/cracked lips, strawberry tongue) -cervical lymphadenopathy -peripheral extremity changes (erythema, swelling of hands and feet) -polymorphous generalized rash |
|
|
What is the management of Kawasaki's disease and what is the complication
|
ASA 80-100mg/kg/day q6hrs
IVIG Admission Complication: coronary artery aneurysm, myocarditis |
|
|
What is the ABCD2 score and what does it predict?
|
It is a combination of the ABCD and California score and it designed to guide nonneurologists in the prehospital setting in predicting risk among patients with transient stroke like symptoms
A - age >60yrs B - blood pressure >140/90mmHg C - clinical features (incl. history of) - max 2 points (unilateral weakness +2 pts, speech difficulty without weakness +1) D - duration - max 2 points (>60min +2, 10-59min +1, <10min 0) D - diabetes Predicts risk at 2, 7 and 90 days, cut it has recently been shown to be poorly sensitive in ED patients and often miscalculated |
|
|
What are congenital causes of prolonged QTc?
|
Romano-Ward (AD)
Jervell-Lange-Nielson (AR, deaf) Sporadic |
|
|
What are acquired causes of prolonged QT?
|
Hypo K, Mg, Ca
Hypothyroid Diet CVA/SAH MI Drugs: Antiarrhythmics (Ia, Ic, III) Antipsychotics Antidepressants Antihistamines Antimalarials Antibiotics Antimotility Cocaine |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis of a hyperthermic patient with altered mental status?
|
NMS
SS MAOi interaction Malignant Hyperthermia Sympathomimetic Anticholinergic toxidrome Thyrotoxicosis Amphetamines ASA toxicity Anticholinergic toxidrome Heat stroke Withdrawal |
|
|
What is the pathophysiology and treatment of the "big 4" causes of hyperthermia and altered mental status?
|
NMS - decreased central dopamine action in thalamus
-fluids, cool, sedate, paralyze, bromocriptine, dantrolene SS - increased serotonin -fluids, cool, sedate, paralyze, ciproheptadine MAOi interaction - inhibited MAO, adrenergic overdrive -fluids, cool, sedate, paralyze Malignant hyperthermia - massive calcium release due to unstable sarcoplasm -fluids, cool, sedate, paralyze, dantrolene |
|
|
What is the differential for painless vision loss?
|
CRAO
CRVO Vitreous detachment/hemorrhage Retinal detachment Pre-chiasmal space occupying lesion Macular degeneration Amarosis fugax Malingering Conversion disorder |
|
|
What is the differential for delirium?
|
I WATCH DEATH
Infection Withdrawal Acute metabolic (high Ca, Mg, acidosis, hepatic, renal failure) Trauma CNS pathology Hypoxia Deficiencies Environmental Acute Vascular Toxins Heavy metals |
|
|
What are the indications for ED thoracotomy
|
Penetrating
-cardiac arrest with signs of life in the field -SBP<50mmHg after fluid resuscitation -Severe shock and clinical signs of tamponade Blunt -arrest in the ED Theoretical -suspected air embolus |
|
|
What are indications for urgent OR thoracotomy?
|
-Initial chest tube drainage >20cc/kg
-ongoing chest tube drainage of >7cc/kg/hr -increasing hemothorax on CXR -patient remains hypotensive despite adequate blood replacement and other sources of blood loss ruled out -patient decompensates after initial response to resuscitation |
|
|
What are tetanus prone wounds?
|
>6hours
stellate lesion depth >1cm missile crush burn frostbite devitalized tissue present contaminents (dirt, saliva) |
|
|
When is TIG given?
|
tetanus prone wound in a person who has not received at least 3 doses of tetanus in their life.
|
|
|
When is Td given?
|
tetanus prone wound and incomplete primary series or if it has been more than 5 years since received
non tetanus prone wound and incomplete primary series or if it has been more than 10 years since received |
|
|
What are the most concerning animals for rabies?
|
Bats
Raccoons Foxes Skunks Unknown wild dogs |
|
|
What are signs and symptoms of rabies?
|
-prodrome - pain, paresthesia at the site of bite/scratch, fever, HA
-neurologic (2-7days) aphasia, incoordination, lacrimation, paresis, paralysis, MS changes -late symptoms - decreased BP, DIC, arrhythmia DEATH |
|
|
Outline the PEP for Rabies and the immunization schedule
|
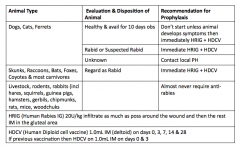
|
|
|
What are exposures considered to have negligible risk for HIV?
|
Urine
Saliva Nasal secretion Sweat Tears if NOT visibly contaminated with blood |
|
|
What are exposures considered to have substantial risk?
|
Vagina
Rectum Eye Mouth Mucus membrane non-intact skin Percutaneous contact with: Blood semen vaginal secretions rectal secretions breast milk |
|
|
What is HIV PEP
|
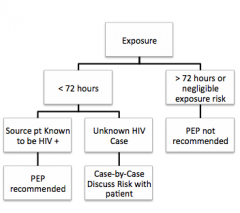
|
|
|
What does PEP consiste of ?
|
2 drug regimen - combivir (2 NRTI)
3 drug regiment - combivir and indimavir (2 NRTI + PI) |
|
|
What are the side effects of PEP?
|
NRTI - bone marrow suppression, peripheral neuropathy, pericarditis
PI - GI effects, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, fat redistribution |
|
|
What is the estimated risk of acquisition of HIV by blood transfusion?
|
90% per act
|
|
|
What is the estimated risk of acquisition of HIV by needle sharing injection drug use?
|
0.67% per act
|
|
|
What is the estimated risk of acquisition of HIV by receptive anal intercourse?
|
0.5% per act
|
|
|
What is the estimated risk of acquisition of HIV by percutaneous needle stick?
|
0.3% per act
|
|
|
What is the estimated risk of acquisition of HIV by receptive penile vaginal intercourse?
|
0.1% per act
|
|
|
What is the estimated risk of acquisition of HIV by Insertive anal intercourse?
|
0.065% per act
|
|
|
With regards to intercourse what are the risks (highest to lowest) of acquiring HIV
|
Anal receptive
vaginal receptive Anal insertive Penile insertive Oral receptive oral insertive |
|
|
What are AIDS defining illnesses?
|
CD4 <200
Candidiasis (esophageal or pulmonary) Cervical CA Coccidiomycosis (extrapulmonary) Cryptosporidium (extrapulmonary) Crytosporidiosis CMV infection (any organ other than liver, spleen, lymph) HSV HIV associated dementia HIV wasting syndrome Isosporiasis Kaposi Lymphoma PCP PML |
|
|
What should you think of in a patient with HIV, HA and fever?
|
Toxoplasmosis
Histoplasmosis CNS lymphoma Cryptococcus Neoformans |
|
|
List diseases that may cause focal lesions on an enhanced CT of the brain in an HIV+ patient?
|
Toxoplasmosis
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy Lymphoma HSV Cryptococcus TB |
|
|
What is Hepatitis B post-exposure prophylaxis?
|
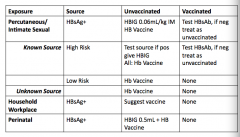
|
|
|
What are the 3 zones of a burn injury?
|
Zone of hyperaemia
zone of stasis Zone of coagulation |
|
|
Describe the various depths of burns?
|
First degree - minor epithelial damage of the epidemis
Second degree Sup partial thickness - epidermis and superficial dermis Deep partial thickness - extends into the reticular dermis Third degree - full thickness burns that destroy both epidermis and dermis Fourth degree - full thickness destruction plus destruction of underlying fascia, muscle and bone |
|
|
What is the rule of 9s for peds and adult
|
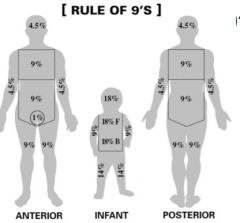
|
|
|
What formula is used to determine fluid replacement in burn patients?
|
Parkland:
4cc/kg/%BSA burned, 1/2 over 8 hours, 1/2 over 16 hours |
|
|
What are indications for transfer to a burn centre?
|
-any burn BSA >10% for age <10 and >50
-Any burn with BSA >20% any age -Full thickness BSA 5% -significant burn: face, perineum, hands, feet, perineum, genitalia, major joint -significant electrical burn -significant chemical burn -significant inhalational burn, mechanical injury or pre-existing medical disorder -special psychosocial or rehab care |
|
|
What is the START triage system?
|
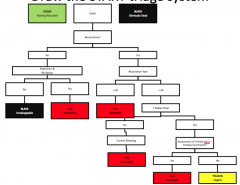
|
|
|
What is the PICE grading system
|
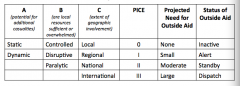
|
|
|
Which patients with STEMI receiving lytics should be transferred to a PCI-capable hospital
|
immediate
-cardiogenic shock or acute severe HF urgent -evidence of failed repercussion or reocclusion -> <50% decrease in ST elevation 60-90minutes after lytics As part of an invasive strategy in stable patients with PCI between 3 and 24hrs |
|
|
What are the 5 components of the incident command system?
|
Command
Logistics Finance Planning Operations |
|
|
What are the stages of ossification in the pediatric elbow and their age of appearance?
|
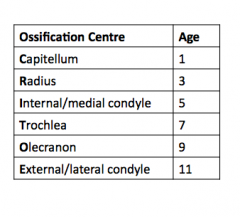
|
|
|
What are the ECG findings in PE?
|
-usually provides more info about alternative diagnoses
-tachycardia -simultaneous T-wave inversions in the anteroseptal and inferior leads -rightward axis -S1Q3T3 -incomplete RBBB |
|
|
What are CXR findings in PE?
|
-unilateral basilar atelectasis
-Hampton hump - pleural based area of increased opacity -Westermark sign - unilateral lung oligemia -Pleural effusion -Enlarged hilum |
|
|
What are Wells criteria for PE?
|
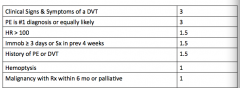
0-4 - PE unlikely -> D-dimer would be enough
>4 - PE likely -> cannot use only D-dimer |
|
|
What are the PERC criteria
|
Age <50
HR <100 SPO2>94% on RA no exogenous estrogen use no hemoptysis no previous VTE no recent surgery or trauma no unilateral leg swelling |
|
|
Describe the elements of the GCS
|
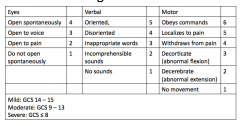
|
|
|
What is a pharmacoinvasive strategy for STEMI?
|
PCI 2-6 hours after lytics
supported by TRANSFER-AMI (a Canadian study) |
|
|
What are the Canadian CT head rule high risk criteria?
|
GCS <15 within 2 hours
suspected open skull # suspected basal skull # vomiting >/=2 Age >/=65 100% sensitive |
|
|
What are the Canadian CT head rule medium risk criteria?
|
Amnesia before impact >30 minutes
Dangerous mechanism -pedestrian struck, ejection from vehicle, fall from height (>3ft or 5 steps) 98.4% sensitive |
|
|
What are high risk factors in the Canadian C-spine rules?
|
Age >65
Paresthesias Dangerous mechanism -Fall from >5 stairs -Axial load to the head -High speed >100km/h -ejection -rollover -ATV/bike collision |
|
|
What are the low risk factors in the Canadian C-spine rules?
|
-simple rear end MVC (except bus, truck, highspeed, pushed into traffic, rollover)
-ambulatory, sitting in ED -delayed onset of neck pain -absence of midline c-spine tenderness |
|
|
What is the NEXUS rule for c-spine injury?
|
No distracting injury
Not intoxicated No midline tenderness Normal level of alertness/mental status No neurological abnormality |
|
|
Describe the injury, MOI and stability of a Jefferson fracture
|
C1 burst
Axial load Unstable |
|
|
Describe the injury, MOI and stability of a Hangman's fracture
|
C2 pars interarticularis #
distraction of C2-C3 Extension Unstable |
|
|
Describe the injury, MOI and stability of a odontoid fracture
|
Dens (3 types)
Flexion Unstable |
|
|
Describe the injury, MOI and stability of a unilateral jumped facet dislocation
|
Flexion/rotation
stable |
|
|
Describe the injury, MOI and stability of a bilateral jumped facet dislocation
|
flexion
unstable |
|
|
Describe the injury, MOI and stability of a flexion teardrop fracture
|
Usually lower c-spine
flexion unstable |
|
|
Describe the injury, MOI and stability of an extension teardrop fracture
|
Usually upper c-spine
extension unstable |
|
|
Describe the injury, MOI and stability of an atlantoaxial dislocation
|
flexion
unstable |
|
|
Describe the injury, MOI and stability of a clay shoveler's fracture
|
fracture of the end of a spinous process
flexion stable |
|
|
Describe the injury, MOI and stability of a burst #
|
Vertical compression/flexion
stable |
|
|
What are differences in the pediatric c-spine
|
-increased mobility (increased laxity of ligaments, anterior wedging of vertebrae, shallow facet joints predisposes to subluxation, poorly formed uncinate process increases risk of SCIWORA)
-larger head and weaker neck muscles (60-70% of fractures occur in the C1/C2 region) -more room around the spinal cord in children (decreased incidence of neuro deficit) -more radiolucent cartilage in children makes xrays difficult to interpret -variable interspinous distances esp C6/C7, C1/C2 |
|
|
What is the San Francisco syncope rule?
|
C - CHF
H - HCT <30% E - EKG abnormality S - SOB on history S - SBP <90mmHg at triage If score = 0 then low risk for serious outcome If >/=1 then high risk and should admit Recent CJEM 2007 article external validation in Australia, SFSR performed as well as clinical judgement |
|
|
What primary disease processes result in heart failure
|
CAD
Dilated cardiomyopathy (viral, EtOH, familial, idiopathic) Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Restrictive cardiomyopathy Myocarditis Acute valvular disease (Acute MR secondary to papillary muscle rupture, acute aortic insufficiency secondary to bacterial endocarditis) Chronic valvular disease (mitral insufficiency, aortic stenosis) Aortic dissection Pericardial disease Pulmonary disease Renal failure |
|
|
What is the NYHA classification of CHF
|
I - asymptomatic on ordinary physical activity
II - symptomatic on ordinary physical activity III - symptomatic on less than ordinary physical activity IV - symptomatic at rest |
|
|
What are evidence based treatments for CHF?
|
NTG - start 20ug/min and titrate to effect maintaining SBP >80mmHg
Levy et al Ann EM 2007 (decreased BiPAP, decreased intubation, decreased ICU, decreased adverse effects) BiPaP 12/5 with 60% 02 (decreased mortality NNT 10, decreased intubation NNT 6-7) ACE-I (if increased BP) Captopril 25mg PO or Enalapril 6.25mg PO Lasix IV - two times regular IV dose No Morphine |
|
|
Define hypertensive emergency and hypertensive urgency
|
Hypertensive emergency: severe HTN with acute impairment of an organ system (CNS, CVS, renal)
Hypertensive urgency: severe HTN but no organ system impairment |
|
|
What is the classification for aortic dissection
|
Stanford classification
-type A: involve the ascending aorta -type B: does not involve the ascending aorta |
|
|
What are the goals of management in aortic dissection
|
Decrease BP
Decrease the rate of rise of the arterial pulse (dP/dt) to diminish the shearing force -Labetolol or esmolol and nitroprusside Type A - STAT vascular surgery consult Type B - Medical with Vascular surgery consult |
|
|
What are the 5Ps of acute arterial occlusion and managment
|
Pain
Pallor Pulselessness Paresthesias Paralysis Immediate heparinization and embolectomy |
|
|
What are causes of fever in a returned traveler?
|
Malaria
Dengue Japanese encephalitis Yellow fever colitis HIV typhoid Hepatitis TB Amebic liver abscess RMSF Leptospirosis trypanosomiasis |
|
|
What is the vector of malaria?
|
Anopheles mosquito
|
|
|
What are the different species of malaria?
|
Falciparum
Vivax Ovale Malariae |
|
|
What are the classic fever patterns in malaria?
|
q48h - falciparum, vivax, ovale
q72h - malariae |
|
|
How do you diagnose malaria?
|
Thick and thin smears (6-12 hours spar)
The highest yield is in the middle of the night in the time zone they came from |
|
|
What is the treatment of malaria
|
Not sick: atovaquine 1000mg + proguanil 400mg x 3 d ( Malarone 4 tabs per day)
Sick or falciparum: quinidine IV -> on a cardiac monitor |
|
|
What is the difference between a thick and thin smear?
|
Thick: 10-40x more sensitive than thin smears (used for screening)
Thin: allows precise identification of plasmodium species and the degree of parasitemia |
|
|
What are 5 complications of malaria?
|
Anemia
cerebral malaria (seizures, encephalitis, edema) glomerulonephritis splenic rupture hypoglycemia |
|
|
What is the vector of dengue?
|
Aedes mosquitos
|
|
|
What is the presentation of dengue fever?
|
biphasic fever
chills malaise HA bone pain |
|
|
What is the treatment of dengue
|
supportive care
shock may require intensive monitoring |
|
|
When do people typically get hemorrhagic fever from dengue?
|
2nd infection
|
|
|
What is the vector of typhoid
|
fecal-oral transmission with salmonella typhi
|
|
|
What is the presentation of typhoid fever
|
sustained or remittent fever
HA mailaise abdo pain diarrhea or constimation Rose spots Hepatomegaly or splenomegaly |
|
|
How is typhoid fever diagnosed?
|
blood cultures, bone marrow aspiration
|
|
|
What is the treatment of typhoid fever
|
Ceftriaxone 1g IV
or Cipro 400mg IV BID or Cefixime 400mg PO or cipro 500mg PO |
|
|
What is the vector for Lyme disease?
|
Borrelia burgdorferi
|
|
|
What is early lyme disease
|
erythema migrans
hematogenous spread migrating lesions malaise, fatigue Ttx with doxycycline 100mg PO BID x 21 days |
|
|
What is early disseminated lyme disease?
|
Neuro: meningoencephalitis, cranial neuropathy, peripheral neuropathy or radiculopathy
Cardiac: carditis Arthritis Doxycycline 100mg PO BID x 30d or if severe IV ceftriaxone |
|
|
Who do you prophylactically treat for Lyme disease?
|
tick on <72 hours, not engorged -> NO
tick on <72hours, engorged -> YES tick on >72 hours -> YES Doxycycline 200mg PO x 1 |
|
|
What are TB drugs and their side effects?
|
INH - hepatitis, peripheral neuropathy, seizures (pyridoxine treats neuropathy and seizures)
Rifampin - tears an urine turn orange Ethambutol - green-red blindness, retrobulbar neuritis Pyrazinamide - hepatitis |
|
|
ABG interpretation
|
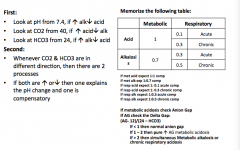
|
|
|
What are the treatments, dose, frequently and mechanism of action of treatments for primary angle closure glaucoma
|
Timolol 0.5% 1 drop q 30 min x 2
beta blocker, decreases aqueous humor production Pilocarpine 1% 1 drop q 15min x 2 miotic, contracts the ciliary muscle apraclonidine 1% 1 drop x 1 alpha agonis - decreases aqueous humor production Prednisolone acetate 1.0% 1 drop q15min x 4 Acetazolamide 500mg IV Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, decreases aqueous humor production Mannitol 1g/kg over 45 min increases osmotic gradient between the blood and the optic fluid thereby decreasing the fluid in the eye |
|
|
What should you consider before decontamination
|
-risk of ingestion (how much, how toxic, reliability of historian)
-can the substance be removed -risk/benefit of decon (contraindications, does the patient need intubation first) -most appropriate technique |
|
|
What are indications and contraindications for activated charcoal?
|
Indications
-<1 hour since ingestion (consider longer if SR or ER) -10:1 ratio of charcoal to toxin Contraindications caustic aspiration ileus perforation Not useful : alcohols, metals, hydrocarbons |
|
|
What are indications for MDAC?
|
AABCD
Aminophylline Antimalarials (quinine) Barbiturates Carbamazepine Dapsone (+/-dig) 25g q 2hours (drugs with enterohepatic circulation, SR/ER, slowed GI motility) |
|
|
What are indications for WBI?
|
Indications:
-life threatening ingestion that is poorly adsorbed to AC Li Fe Packers Heavy metals 2L/hr until clear effluent |
|
|
What are the indications for gastric lavage?
|
ACCT
-ASA -Colchicine -calcium channel blocker -TCA Life threatening ingestion <1 hour, ineffective antidote, not adsorbed by AC |
|
|
How do you perform gastric lavage?
|
protect the airway
Insert #36 -40 Fr Ewald orogastric tube insert aliquots of 200cc warm saline until clear |
|
|
What is the mechanism and indications for urine alkalinization?
|
Promoted ionization of the excreted drug which prevents tubular reabsorption
CAMP Chlorpropamide ASA Methotrexate Phenobarbital |
|
|
What are indications for HD?
|
I STUMBLE NASA
Isopropanol Salicylate Theophylline Uremia Methanol Barbiturates lithium Ethylene glycol Nadolol atenolol Sotalol Acebutolol Small VD Low protein binding Small size Low endogenous clearance water soluble |
|
|
Which toxins can present with seizures?
|
INH
TCA venlafaxine anticholinergics cholinergics sympathomimetics opioid EtOH withdrawal Carbamazepine Methylxanthines MDMA (hyponatremia) propranolol stimulants bupropion |
|
|
What is the antidote for APAP?
|
NAC
|
|
|
What is the antidote for arsenic/mercury/lead
|
Dimercapral or DMSA
|
|
|
What is the antidote for atropine
|
Physostigmine
|
|
|
What is the antidote for CO
|
HBO
|
|
|
What is the antidote for cyanide
|
amyl nitrite, sodium nitrite, sodium thiosulfate
hydroxycobalamin |
|
|
What is the antidote for ethylene glycol/methanol
|
fomepizole
|
|
|
What is the antidote for iron
|
deferroxamine
|
|
|
What is the antidote for lead
|
EDTA
|
|
|
what is the antidote for opioids
|
naloxone
|
|
|
What is the antidote for phenothiazines
|
diphenhydramine
benztropine |
|
|
What is the antidote for isoniazid
|
pyridoxine
|
|
|
What is the antidote for digoxin
|
digiFAB
|
|
|
What is the antidote for benzodiazepines
|
flumazenil
|
|
|
what is the antidote for organophosphates
|
atropine and pralidoxime
|
|
|
What is the antidote for nitrites
|
methylene blue
|
|
|
Describe the stages of presentation of APAP toxicity
|
0-24 hours - pre injury - N/V/malaise or nothing
24-72 hours - Acute liver injury, RUQ pain, transaminitis, hepatocellular injury 3-4 days - Maximum liver injury - fulminant hepatic failure, DIC, ARDS, hepatorenal syndrome, ASt/ALT >10,000 increased INR, increased Bili 5-7 days - recovery period, heptic regeneration, 1/4 have permanent renal failure |
|
|
What is the dose of NAC and management of common side effects?
|
Load 150mg/kg over 1 hours
then 50g/kg over 4 hours then 100mg/kg over 16 hours Anaphylactoid reaction is the most common SE and should be treated with benadryl, slow down infusion, fluids |
|
|
What is the MOA of NAC?
|
Enhances sulfation
Precursor for glutathione glutathione substitute reduces systemic toxicity |
|
|
What are the indications for liver transplant?
|
Kings college criteria
pH<7.3 Cr >3.3 ( >300umol/L) INR>5 Grade III or IV hepatic encephalopathy |
|
|
What disturbances do salicylates cause?
|
-Stimulate the resp centre (resp alkalosis)
-inhibit the kreb cycle (increase lactate) -uncouple oxidative phosphorylation -increase tissue glycolysis vs hepatic gluconeogenesis results in hypo or hyperglycaemia -direct corrosive toxicity to the gut -increased lipid metabolism |
|
|
What are indications for urine alkalinization in ASA intox?
|
ASA >3.5
Proven ASA + symptoms (tinnitus, fever, delirium, metabolic changes) |
|
|
What are indications for HD in Salicylate intox
|
Worsening clinical status
End organ failure (ARF, NCPE, VS abnormalities, CNS abnormalities) Severe A-B disturbance Volume overload Serum level (acute >7mmol/L, chronic >4mmol/L) |
|
|
What are the mechanisms of action of TCA?
|
-sodium channel blockade
-blocks histamine receptors -antimuscarinic -blocks K+ efflux -alpha blockade -inhibits dopamine, serotonin, NE re-uptake -inhibits GABA |
|
|
What is the normal MOA of digitalis?
|
It inhibits the Na-K ATPase
increases intracellular Na increases extracellular K The increased Na reduces the transmembrane Na gradient thus the Na/Ca exchange drives less CA out resulting in increased intracellular Ca which is then driven into the sarcoplasmic reticulum and increases contractility |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of digitalis in toxic state?
|
-NaKATPase pump is paralyzed resulting in very high extracellular K+
-halted impulses through the SA node and decreased conduction through the AV node with increased sensitivity to catecholamines -increase in PVCs because of Purkinje fibers are affected |
|
|
What are indications for administration of digiFab?
|
Ventricular dysrhythmias
Progressive/refractory hemodynamic instability or bradycardia K+>5mmol/L ingested plant digitoxin and dysrhythmia co-ingestion with another CV drug or TCA Acute ingestion of 10mg (adult) or 0.1mg/kg (child) |
|
|
What is the empiric dosing of digibind?
|
Acute: 10 vials (adults and peds)
Chronic 5 vials (adult) Cardiac arrest 20 vials |
|
|
What are the mechanisms of action of calcium channel blockers?
|
Block slow calcium channels in the myocardium and smooth muscle
decreased contractility decreased SA node activity Slows AV conduction |
|
|
What is the management of CCB OD?
|
IV, O2, monitor, fluid
Atropine (0.5-1mg) up to 3mg Calcium chloride (10-20mL 10% calcium chloride over 10min then 5-10mL/hr) (children 10-30mg/kg) up to 6 g through a central line insulin/Glucose - 1U/kg bolus/1-2amps of D50 then 0,5U/kg/hr infusion insulin, 0.5g/kg/hr) Norepinephrine (Rosen's - isoproterenol or dopamine) |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of BB OD?
|
Competitively inhibits endogenous catecholamines at B1 and B2 receptors
|
|
|
What is the most dangerous B-blocker and why?
|
Propranolol
-penetrates the CNS due to lipophilic change membrane stabilizing effect -may result in seizures -may result in hypoglycemia especially in children |
|
|
What is the management of BB OD?
|
IV,O2, monitor
Atropine 0.5mg Glucagon 5-10mg IV bolus, 2-5mg/hr Fluids Dialysis - Nadolol, Atenolol, Acebutalol, Sotalol Isoproterenol, dopamine, epinephrine Transvenous pacemaker |
|
|
What is the metabolism of ethylene glycol?
|
Ethylene glycol -> (alcohol dehydrogenase) Glycoaldehyde -> (aldehyde dehydrogenase) glycolic acid ->(LDH, Glycolic acid oxydase) glycoxylic acid -> oxalic acid
|
|
|
What are the 4 stages of presentation of ethylene glycol OD?
|
Acute neurologic: inebriated, NV, seizure, osmolar gap
Cardiopulmonary: metabolic acidosis, increased HR, ARF, decreased calcium Renal: calcium oxalate crystaluria, hematuria, proteinuria, flank pain Delayed neuro: CN palsies, deafness, cognitive and motor abnormalities, personality changes |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis of an increased osmolar gap?
|
Methanol
Ethylene glycol Isoprapanol Mannitol Glycerol ARF Ketoacidosis Hyperlipidemia EtOH |
|
|
What is the metabolism of methanol?
|
Methanol -> (alcohol dehydrogenase) formaldehyde -> (aldehyde dehydrogenase) formic acid -> CO2 and H20
|
|
|
What are the 2 stages of methanol toxicity
|
Acute: inebriation, gastritis, decreased LOC, ataxia
Late: visual changes, decreased LOC, metabolic acidosis, seizures |
|
|
What is the management of toxic alcohol exposure?
|
Correct acidosis with bicarb and hyperventilation -> target pH 7.45-7.50
Fomepizole Dialysis Adjunctive treatment thiamine 100mgIV, folic acid 50mg IV, pyridoxine 50mg IV |
|
|
What are indications for dialysis in toxic alcohol ingestion?
|
ethylene glycol >8mmol/L
Methanol >5mmol/L Metabolic acidosis End organ symptoms: renal impairment visual impairment electrolyte abnormalities unstable VS deterioration despite intensive treatment |
|
|
What are the 5 phases of iron toxicity
|
0-6hours - GI corrosive effects, V and diarrhea
6-12 hours - apparent recovery 12-48 horus: lethargy, coma, AG metabolic acidosis, leukocytosis, coagulopathy, renal failure, CV collapse 2-4 days fulminant hepatic failure delayed - pyloric or proximal bowel scarring |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of iron toxicity
|
impaired intracellular metabolism (liver, CNS, CV collapse)
Direct GI toxicity |
|
|
What causes metabolic acidosis in iron toxicity?
|
Fe2+ conversion to Fe3+ releases an H+ ion
vasodilation and hypotension result in lactic acidosis direct negative inotrope disrupts oxidative metabolism |
|
|
What are the toxic doses of ingested elemental Fe?
|
20-40mg/kg - mild
40-60mg/kg - potentially serious >60mg/kg - may be lethal |
|
|
What are toxic levels of Fe (4 hours post ingestion)
|
<55umol/L do not treat
55-90umol/L treat if signs and symptoms >90umol/L treat |
|
|
What is the antidote for iron and what are its main side effects?
|
Deferoxamine
hypotension (slow down infusion) respiratory toxicity if prolonged infusion |
|
|
What 4 characteristics that affect the potential for acute toxicity from hydrocarbons?
|
Viscosity (decreased viscosity increased toxicity)
Volatility (increased volatility increased toxicity) Surface tension (decreased surface tension increased toxicity) side chains (heavy metals, halogens, aromatic) |
|
|
What are the indications for HBO in CO poisoning?
|
-no evidence for decreased mortality but it may limit neuropsychological sequelae
neuro abnormality cardiac instability levels >25% pregnancy end organ damage inability to oxygenate children under 9 months |
|
|
What are toxic time bombs (ingestions that are concerning even if the patient looks good at 6 hours)
|
APAP
anticoagulants antimetabolites body packers ASA Heavy metals Iron lithium methadone MAOi hypoglycemics sotalol SR products thyroid meds toxic alcohols valproic acid TCA |
|
|
List drugs that a single tablet can cause death in a child?
|
Camphor
sulfonylurea essential oils chloroquine CCB BB methadone theophylline methyl salicylate quinine phenothiazine TCA |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis of toxic mushrooms and their effects?
|
Early toxicity (<6hours)
Amanita mushrooms -> anticholinergic Clitocybe -> cholinergic psilocybin -> hallucinogenic coprinus -> disulfiram reaction with alcohol Late (>6 hours) CONCERNING Amanita Phalloides -> GI -> hepatotoxicity Gyromitra -> GI -> seizure orelline -> renal toxicity |
|
|
What are the SIRS criteria?
|
Two or more of the following:
T >38 or <36 Heart rate >90 RR >20 or PaCo2 <32 Wbc >12 or <4 or >10% bands |
|
|
Define sepsis
|
SIRS + proven or suspected infectious source
|
|
|
Define severe sepsis
|
sepsis with one or more signs of organ dysfunction: AMS, oliguria, hypoxemia, increased lactate
|
|
|
Define septic shock
|
Severe sepsis with hypotension that is unresponsive to fluid resuscitation
|
|
|
Which patient's were included in Rivers' EGDT trial
|
Presumed source of infection
at least 2/4 SIRS SBP<90 Lactate >4 |
|
|
What are the goals in EGDT
|
CVP 8-12mmHg - fluids
MAP 65>/= but </=90mmHg - vasoactive agents ScVO2 >/=70% - blood +/- inotropic agents HCT >/=30% |
|
|
What are 5 common causes of hyperkalemia?
|
Pseudohyperkalemia (hemolysis, drawn above IV)
Renal failure Drugs (digoxin, NSAIDs, ACE-I, succinylcholine) Acidosis Cell death (rhabdo, burn, crush, tumor lysis, true hemolysis) |
|
|
What are 5 changes of hyperkalemia on EKG
|
Tall peaked T waves
Loss of P waves Wide QRS Loss of PR Sine wave |
|
|
What is the management of hyperkalemia
|
If wide QRS: 10% CaCl over 2 min (membrane stabilization)
Insulin R 10U IV, 2 amps of D50 (gets K into the cell) Salbutamol 5mg Neb x 3 (gets K into cell) NaHCO3 over 10-20 min Kayexelate with sorbitol (not recommeded anymore) dialysis (removes potassium) |
|
|
What are common causes of hypokalemia
|
Diuretics (non-K sparing)
malnutrition alcoholics vomiting (lost in the vomit and from the kidney as they try to retain H+) |
|
|
What are EKG changes associated with hypokalemia
|
Flipped T waves
U wave Prolonged QT |
|
|
What is the management of hypokalemia
|
Hypo K = Hypo Mg (need magnesium to get K into cells or patient will just pee out what you give him
Oral replacement with K elixir for every 0.3mEq below 3.5, need at least 100mEq May also add to IV |
|
|
What is pseudohyponatremia
|
Due to glucose
For every 10mmol/L above 10, sodium decreases by 2 |
|
|
How do you manage hyponatremia
|
Max correction 0.5mmol/L/hr
10-12mmol/L/day Only use hypertonic saline if seizing, coma or focal neuro abnormality (usually Na <110) Complication: Central pontine myelinolysis |
|
|
How do you replace sodium in a 70kg man with a serum Na of 120mmol/L
|
determine total body sodium deficit and replace1/2
140-120 = 20mmol x TBW (wt x 0.6) 840mmol -> 420 0.5mmol/hr (20 hours) 0.9% sodium has 153mmol/L = 0.153/cc 420/0.153/20 = 137cc/hr |
|
|
What are common causes of hypernatremia
|
Water deficit
heat stroke severe diarrhea |
|
|
What is the management of hypernatremia
|
If hypotensive -> give NS
Then replace 0.5mmol/L/hr Complication: cerebral edema |
|
|
What are the most common causes of hypercalcemia
|
Oncology
Hyperparathyroid |
|
|
What is the management of hypercalcemia
|
ABCs
glucose temp NS - bolus to stabilize, then 100-150cc/hr Lasix after rehydration Follow other lytes Consult IM - possibly role of bisphosphonates |
|
|
What are radiologic findings of epiglottitis
|
Thumbprint
Loss of valecula space swollen hypopharynx swollen aryepiglottic folds swollen arytenoids |
|
|
What are risk factors for death in asthma
|
Previous intubation
Previous history of sudden severe excerbation Previous ICU admission >/2 hospitalizations for asthma in the last year >/3 ED visits for asthma in the last year Any ED visit or hospitalization for asthma in the last month >/=2 MDI short acting beta agonist canisters /mo Current use or recent withdrawal of systemic corticosteroids Low socioeconomic status difficulty perceiving symptoms of airflow obstruction serious psychiatric disease Comorbidities such as CV disease or other systemic problems illicit drug use (inhaled cocaine or heroin) |
|
|
Anti - HAV
|
Combo of IgG and IgM defining acute or past HAV infection
|
|
|
Anti-HAV Igm
|
Acute Hep A infection
|
|
|
HBsAg
|
Associated with acute or chornic infection
|
|
|
HBeAg
|
Ag associated with ACTIVE infection (increased infectivity)
|
|
|
HBcAg
|
Core antibody - past or current HBV
|
|
|
HBsAb
|
acute or past infection or IMMUNIZED
|
|
|
HBcAb -IgM
|
Acute infection with HBV
|
|
|
HBeAb
|
possibly represents resolving HBV infection
|
|
|
Antibody HDV
|
Infection with HDC (HBsAg should be present)
|
|
|
Antibody to HCV
|
Infection with HCV acute or past
|
|
|
What are criteria for hospitalization of women with PID
|
Pregnant
Does not clinically respond to PO antibiotics Surgical emergencies such as appendicitis cannot be ruled out Unable to follow or tolerate outpatient oral regimen Patient has severe illness, nausea and vomiting or high fever Patient has a tubo-ovarian abscess (IUD, HIV, youth, compliance issue) |
|
|
What is the treatment for PID?
|
Inpatient
Cefoxitin 2g IV q6h Doxycycline 100mg IV BID Outpatient Ceftriaxone 250mg IM once doxycycline 100mg PO BID x 14 days +/-metronidazole 500g PO BID x 14 days |
|
|
What are reportable STDs in Canada
|
Chlamydia
Gonorrhea Syphillis chancroid HIV/AIDS Hepatitis B |
|
|
Name 5 sites along the ureter where calculi are likely to become impacted
|
Calyx
Ureteropelvic junction Pelvic brim Ureterovesicular junction Vesical orifice |
|
|
What are 4 types of renal calculi
|
Struvite (can see on X-ray)
calcium (can see on x ray Uric acid Cystine |
|
|
What is the impact of size of calculi on passage and treatment of renal calculi
|
<5mm ~90% of those in the lower part of the ureter will pass within 4 weeks
5-8mm ~15% of those in the lower part of the ureter will pass within 4 weeks >8mm ~95% become impacted and require lithotripsy or surgical removal |
|
|
What are indications for hospital admission with a kidney stone
|
Obstructed stone with signs of infection
intractable nausea and vomiting severe pain requiring parenteral analgesics urinary extravasation hypercalcemic crisis pregnant women relative significant comorbidities complicating outpatient management high grade obstruction leukocytosis size of stone solitary kidney/intrinsic renal disease psychosocial disease |
|
|
What are the Major jones criteria
|
Polyarteritis
Carditis Chorea Erythema marginatum subcutaneous nodules (CASES) C-Carditis A- Arthritis S - Sydenham's chorea E - erythema marginatum S - subcutaneous nodules |
|
|
What are the minor jones criteria
|
arthralgia
fever increased ESR increased CRP prolonged PR on EKG |
|
|
How do you diagnose rheumatic fever
|
Evidence of preceding pharyngitis or strep infection + 2major or 1 major and 2 minor
Current evidence of strep infeciton + 1 major or >3minor |
|
|
What is the typical HR and RR in infants <1, children 1-4, 4-12, >12
|
infant: 140, 40
1-4: 120, 30 4-12: 100, 20 >12 80, 15 |
|
|
What is normal blood pressure and lowest tolerable blood pressure in children
|
normal (age x 2) +90
lowest tolerable (age x 2) +70 |
|
|
How do you estimate ETT size?
|
uncuffed: age/4 + 4
cuffed: age/4 + 3 |
|
|
What are differences in the pediatric airway
|
-smaller airway diameter
-larynx higher (C1-C4) -vocal cords have a more anterior angulation -large occiput -floppy epiglottis -large tongue -narrowest portion is subglottic |
|
|
What are the types of sickle cell crises
|
Vaso-occlusive
Chest Aplastic anemia Sepsis Splenic sequestration Hemolytic anemia |
|
|
Sickle cell with fever: organisms of concern, investigations, management
|
Encapsulated organisms: HIB, S pneumoniae, N meningitidis
Investigations: cbc with differential, reticulocytes, renal function, BT, ALT, VBG, blood cultures, urine culture, type and cross Management: bolus NS IV ceftriaxone 100mg/kg (if allergy: clindamycin) +/- vancomycin |
|
|
What is the definition of fever in a child
|
Rectal tmp >38 degrees
|
|
|
What are the most common pathogens in children (prior to penumovax)
|
S pneumoniae
HIB Neisseria Meningitides Salmonella |
|
|
What are the most common pathogens in 0-1mo old infant with fever
|
GBS
Ecoli Enterococcus Listeria Herpes Chlamydia S pneumoniae Enterovirus HIB |
|
|
What is empiric treatment for an infant with fever?
|
Cefotaxime 150mg/kg/24hours divided TID
Ampicillin 100mg/kg/24 hours divided QID |
|
|
What is the management of fever in infants 1-3 months
|
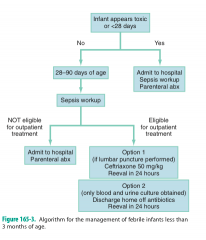
|
|
|
What is the management of fever in 3-36month old
|
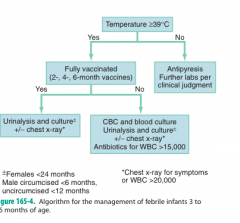
|
|
|
What are the most common organisms for pediatric pneumonia and their treatment in <1month?
|
GBS
Listeria Ecoli Klebsiella No outpatient treatment Ampicillin and cefotaxime |
|
|
What are the most common organisms for pediatric pneumonia and their treatment in 1-3 months
|
S pneumonia
Chlamydia Bordetella S aureus HIB outpatient treatment: not appropriate inpatient treatment: ampicillin + cefotaxime |
|
|
What are the most common organisms for pediatric pneumonia and their treatment in 3mo-5years
|
S pneumo
S aureus HIB Mycoplasma outpatient: amoxicillin inpatient: IV ceftriaxone |
|
|
What are the most common organisms for pediatric pneumonia and their treatment in >5 years?
|
S pneumo
C pneumo S aureus HIB Mycoplasma outpatient: amoxicillin inpatient: ceftriaxone IV |
|
|
What is the definition of pediatric DKA
|
Ketonuria
pH<7.3 HCO3 <18 Glu >11 |
|
|
What is the treatment of DKA in kids?
|
If vascular decompensation - 10cc/kg over 1 hour, then 5cc/kg/hr
If clinical dehydration but normal BP then 7cc/kg over 1 hour then 3.5-5 cc/kg/hr Minimal dehydration - oral rehydration and SC insulin Insulin 0.04U/kg/hr If voided <1hour ago and K+<5.5 then add 40mEq KCl to fluid |
|
|
What is the definition of a simple seizure
|
Duration <15min
1 episode in 24 hours No residual neuro deficits Developmentally normal child |
|
|
What is the definition of an apparent life threatening event
|
An acute event that is frightening to the observer and includes any combination of the following features:
apnea, color change, marked chafe in muscle tone, choking, gaggin |
|
|
What lab tests do you order in a jaundiced newborn?
|
Indirect Bilirubin
Direct bilirubin Coombs test cbc |
|
|
What are red flags in a jaundiced new born
|
jaundice in the 1st 24 hours
gestational age 35-36weeks predischarge serum bili in the high-risk zone ABO incompatibility with + coombs test east asian previously jaundiced sibling cephalohematoma or significant bruiding adequacy of breast feeding |
|
|
What are signs of acute bilirubin encephalopathy
|
Early - lethargy, hypotonia, poor feeding
Intermediate - stupor, irritability, hypertonia, fever, high-pitched cry late - pronounced retrocollis, opisthonos, shrill cry, no feeding, apnea, fever, deep stupor to coma, seizures, death |
|
|
What are the causes of unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia
|
Physiologic jaundice
Breast milk jaundice Hemolysis (ABO incompatibility, breakdown of birth trauma hematoma, intraventricular hemorrhage, sickle cell) Infectious - TORCHs, UTI, sepsis Metabolic - Gilbert, Crigler Najjar |
|
|
What are causes of conjugated hyperbilirubinemia
|
Infectious: TORCHs, UTI, gram negative sepsis, viral
Obstructive - biliary atresia, choledochal cyst Metabolic - Niemann-Pick, Dubin Johnson Drugs/toxins |
|
|
What are indications for workup of a jaundiced infant
|
-Jaundice appearing within the first 24 hours of life
-Elevated conjugated bilirubin level -Rapidly rising total serum bilirubin unexplained by history or physical -Total serum bilirubin approaching exchange level or not responding to phototherapy -Jaundice persisting beyond 3 weeks -Sick appearing infant |
|
|
What are historical indicators of child abuse
|
-Unexplained delay in seeking medical attention
-History does not explain the injury -History changes with time -History is not consistent with the child's developmental abilities -Child has 'magical' injuries |
|
|
What are characteristics of bruises concerning for child abuse?
|
Multiple bruises of different ages
Pattern injury - hand prints, belt marks, cord loops, linear marks, bite marks Unusual distribution - neck, groin, inner aspect of the thigh Restraint marks on the wrists or ankles |
|
|
What are the x and y axis on the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve?
|
x - PO2
y - % saturation |
|
|
What factors shift the oxyhemoglobin curve to the left?
|
Left (holds onto oxygen more)
-increased pH -decreased DPG -decreased temp -CO -Methemoglobinemia -Fetal hemoglobin |
|
|
What factors shift the oxyhemoglobin curve to the right?
|
-decreased pH
-increased DPG -increased temp -altitude |
|
|
What are Ransons criteria on admission?
|
LEGAL
LDH >350 Elevated AST >250 Glucose >11 Age >55 Leukocytes >16 |
|
|
What are Ransons criteria after 48hr of admission
|
Fall in hematocrit >10%
Increased BUN to >2 Calcium <2 PO2<60mmHg Base deficit >4 Fluid sequestration >6L |
|
|
What is the management of rhabdomyolysis
|
-NS aim for 200-300cc/hr of urine output
-urine alkalinization (1-2 amps NaHcO3 in 1L of D5W at 200cc/hr, decreases myoglobin protein binding wiht goal of urine pH >6.5 -treat hyperkalemia (insulin/gluc, NaHCO3, ventolin, kayexelate) -consider mannitol (increased urine flow, increased renal vasodilation, potential decreased muscle swelling) |
|
|
What is the definition of thyroid storm
|
Thyrotoxicosis + fever + altered mental status
|
|
|
What is the treatment of thyroid storm
|
1. Block thyroid hormone synthesis - PTU 600mg PO/NG q 6hours then 200-250mg q 4hours
2. Block thyroid hormone release - saturated solution of potassium iodide (SSKI) 5 drops PO/NG q 6 hours (also sodium iodide or lithium) 3. Block peripheral effects of thyroid hormone: propranolol 0.5-1mg IV q 15 minutes to effect 4. treat relative adrenal insufficiency, block conversion of T4 to T3 hydrocortisone 300mg IV (may also give dexamethasone) volume resuscitation Cooling (probably don't use tylenol) Lorazepam for anxiety Carnitine to block thyroid hormone going into cells cholestyramine blocks enterohepatic circulation |
|
|
What do you in thyrotoxicosis and thyroid storm with congestive heart failure
|
If rate-related, high-output failure -> beta blockade is first line therapy
If depressed EF -> 1/4 dose of BB or avoid If pulmonary hypertension oxygen and sildenifil |
|
|
What do you do in thyrotoxicosis and thyroid storm with atrial fibrillation?
|
BB is the preferred rate control medication
CCB are prone to hypotension therefore try a test dose of diltiazem 10mg Digoxin is less effective but may be tried Amiodarone should be avoided because of the iodine load They will be refractory to conversion until euthyroid |
|
|
What is the treatment of subacute thyroiditis
|
NSAIDs for inflammation and pain control
Prednisone 40mg/day if refractory to NSAIDs BB to control thyrotoxic symptoms No PTU, methimazole or iodides |
|
|
What is the treatment of myxedema coma
|
Protect the airway, monitor for alkalosis
Fluid resuscitation Thyroid hormone replacement (see below) Hydrocortisone 50-100mg q6-8 Avoid hypotonic fluids, use only 0.9NS or D50.9NS, if less than 120mEq/L consider 3% saline 50-100cc boluses Passive rewarming Treat precipitating illness T4 alone (elderly and/or cardiac comorbidity) -300-500ug IV bolus then 50-100ug IV daily T3 alone (young, no cardiac comorbidity, rapid correction desired) 10-20ug IV the 10ug q4hrs (there is also an intermediate approach combining T4 and T3 therapy) |
|
|
What is the difference between primary and secondary adrenal insufficiency?
|
Primary adrenal failure leads to a deficiency of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids
Secondary adrenal failure is related to decreased production of ACTH by the pituitary therefore there is only cortisol deficiency and no aldosterone deficiency |
|
|
What are causes of primary adrenal crisis?
|
Congenital adrenal hypoplasia
Adrenal hemorrhage Autoimmune (Addison's disease) Infection: TB, histoplasmosis, meningococcemia |
|
|
What are causes of secondary adrenal crisis?
|
Suppression of ACTH in patients on regular glucocorticoids
|
|
|
What is the presentation of adrenal crisis? in infancy?
|
-Gradual onset of weakness, fatigue, malaise, anorexia, weight loss, salt craving
-acute adrenal hemorrhage may present as abdominal pain -failure to thrive, vomiting, dehydration, hyperpigmentation of genitalia, fusion of labia in girls, normal or small phallus in boys, ambiguous genitalia -> most common congenital adrenal hyperplasia |
|
|
What are the electrolytes in adrenal crisis
|
Low sodium
High potassium low chloride +/-low glucose Metabolic acidosis may accompany |
|
|
What is the treatment of adrenal crisis
|
If shock: NS 20cc/kg then D10W0.9NS for infnat, D5W0.9NS for child
hydrocortisone 50-100mgq6 |
|
|
What do you do for patients on maintenance steroids who present with other illness?
|
Minor illness - double steroids
Severe illness - triple steroids |
|
|
What do the following letters in describing pregnant patients stand for : GPTAL
|
G - gestations
P - parity (carried >20weeks) T - term births (>37weeks) A - aborted (at any time) L - live births |
|
|
The pregnant patients BP is low, what maneuver can be attempted to increase it?
|
-tilt to the left or manually push uterus to the left
IVC becomes occluded (decrease cardiac preload) |
|
|
What are the live vaccines that are contraindicated in pregnancy
|
MMR
Mumps Polio Rotavirus Varicella Small pox |
|
|
When is BHCG detectable?
|
7 days after implantation
14 days post conception Often coincides with 1st missed period |
|
|
When can intrauterine pregnancy be deteceted on TA or TV US?
|
Transabdominal - 6 weeks (BHCG 3000)
Transvaginal - 5 weeks (BHCG 1500) |
|
|
What is the order of appearance of IU gestation on ultrasound?
|
Decidual reaction - 4.5 weeks
Gestational sac - 5 weeks yolk sac 6 weeks Fetal pole 7 weeks Fetal heart beta 8 weeks |
|
|
What is the Kleinhauer-Betke test and when is it used?
|
Blood test used in pregnant trauma patients to ascertain if fetal blood has been transferred to the mother's blood -> this is concerning if the mother is Rh-ve and the fetus in Rh+ve
This will help determine if more rhogam is necessary (every Rh- patient gets 300ug) |
|
|
What is a threatened abortion
|
Bleeding but closed os
|
|
|
What is an incomplete abortion
|
Open cervical os
products of conception coming out but not expelled |
|
|
What is a complete abortion
|
Complete expulsion of products of conception - cervical os closed
|
|
|
What is a missed abortion
|
US or other sign of fetal death prior to expulsion of products of conception
|
|
|
What are RF for ectopic pregnancy?
|
Tubal surgery
PID Smoking Advanced age Prior spontaneous abortion Medically induced abortion History of infertility IUD |
|
|
What is the management of the pre-eclamptic patient
|
MgS04 6gIV over 10 minutes then 2g/hr
Maintain UO at <25cc/hr (don't diurese, but don't over fluid resuscitate) cbc, uric acid, LFTs, INR, PTT, fibrinogen Seizure precautions Stat OB consult If HTN persists post MgS04 -labetalol 20mg IV over 2 min |
|
|
What is HELLP syndrome
|
Hemolysis
Elevated liver enzymes Low platelets |
|
|
What is the treatment for HELLP syndrome
|
Supportive
Seizure prophylaxis BP control Deliver if at term Transfuse platelets <50 Steroids for fetus <34 weeks |
|
|
What should you remember about the management of vaginal bleeding in the 3rd trimester
|
Major differential: abruptio vs placenta previa
NEVER do a pelvic exam until after the US (it can precipitate severe hemorrhage in placenta previa) |
|
|
What is the management of a prolapsed umbilical cord
|
STAT c-section
Mother in knee to chest position Bed in Trendelenburg Instruct mother not to push Digital elevation of the presenting part until the baby is removed in the c-section |
|
|
What are maneuvers for shoulder dystocia
|
Help - obs, neonatology, anesthesia
Episiotomy - generous medio-lateral (at 4 or 7 o'clock) Legs flexed - McRoberts maneuver Pressure - suprapubic pressure Enter vagina - Rubin's maneuver - push the shoulders towards the chest to decrease the diameter Remove the posterior arm |
|
|
What is incidence
|
# of new cases occurring in a population during a specific interval /# of persons at risk during that time
|
|
|
What is prevalence
|
# of new cases present in a population during a specific interval/# of persons in the population at that time
|
|
|
What is the mortality
|
total # of deaths from all causes in one year/ # of persons in the population at midyear or that year
|
|
|
What is the case fatality rate
|
# of individuals dying during a specific period of time after disease onset or diagnosis/ # of individuals with the specific disease
|
|
|
Define sensitivity, specificiy, PPV, NPV, OR, LR+, LR-
|
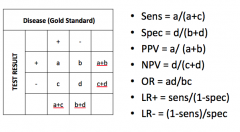
|
|
|
What is a type I error
|
concluding there is a difference when none exists
|
|
|
What is a type II error
|
concluding there is no difference when one does exist
|
|
|
What is power
|
The power of a study to detect a true difference 1-B
|
|
|
What are pros and cons of descriptive studies
|
Observational
-no apriori hypothesis -hypothesis generating -describes what it sees -describes a disease or a RF with respect to population, geographic distribution, frequencies types: case report or series correlational cross-sectional pro -quick, inexpensive, efficient cons - always retrospective, conclusions can be misleading due to bias or confounding, no help with causality |
|
|
What is a case control study
|
-Cases have the disease
-they are matched to controls -then compare the exposure history of the two pro -quick, often only method for rare diagnosis cons -very susceptible to recall bias -potential for confounding -only one outcome -can't calculate incidence rates |
|
|
What is a cohort study
|
-individuals are classified as to whether they have the exposure or not and then outcomes are compared
pros -allows measure of incidence -can look at multiple outcomes -subjects can be matched for possible confounders cons -expensive, time consuming -loss to fu can be a serious threat to validity -inefficient for uncommon outcomes |
|
|
What is a P-value?
|
Probability that an outcome as large or larger than the outcome was due entirely to chance variability of individuals or measurements alone
(P<0.05 - 5% chance that this difference was found by chance alone) |
|
|
What are T-tests
|
Sample T-test: assesses whether the means of two groups are statistically difference from each other (no assumptions of distribution)
Student T-test: same as Sample T-test but assumes a Gaussian distribution Paired Student T-test: assesses whether means of same group tested in different points in time are different from one another |
|
|
Which nerve injury accompanies elbow injury
|
Median or ulnar
|
|
|
Which nerve injury accompanies shoulder dislocation
|
axillary
|
|
|
Which nerve injury accompanies radial styloid fracture
|
Radial
|
|
|
Which nerve injury accompanies colles fracture
|
median
|
|
|
Which nerve injury accompanies sacral #
|
Cauda equina
|
|
|
Which nerve injury accompanies acetabular #
|
sciatic
|
|
|
Which nerve injury accompanies hip dislocation
|
sciatic
|
|
|
Which nerve injury accompanies femoral shaft fracture
|
peroneal
|
|
|
Which nerve injury accompanies lateral knee dislocation
|
peroneal
|
|
|
Which nerve injury accompanies lateral tibial plateau fracture
|
peroneal
|
|
|
Name 4 fractures prone to undergo AVN post-fracture
|
Femoral head
scaphoid capitate talus |
|
|
What is the onset of peripheral vs central vertigo
|
peripheral: sudden
central: gradual |
|
|
What is the intensity of peripheral vs central vertigo
|
peripheral: severe
central: mild |
|
|
What is the duration of peripheral vs central vertigo
|
peripheral: usually seconds or minutes. Occasionally hours or days
central: usually weeks or months |
|
|
What is the direction of nystagmus in peripheral vs central vertigo
|
peripheral: one direction
central: horizontal, rotary or vertical (different directions in different positions) |
|
|
What is the effect of head position in peripheral vs central vertigo
|
peripheral: worsened by position, often there is a single critical position
central: little change with head position, associated with more than one position |
|
|
What are the associated neuro findings in peripheral vs central vertigo
|
peripheral: none
central: usually present |
|
|
What are the associated auditory findings in peripheral vs central vertigo
|
peripheral: may be present, including tinnitus
central: none |
|
|
What is the laterality of peripheral vs central vertigo
|
peripheral: bilateral
central : unilateral or bilateral |
|
|
What are the position testing effects on peripheral vs central vertigo
|
peripheral: long latency, transient in duration, mild to severe in intensity, fatiguable
central: short latency, sustained duration, mild intensity, non-fatiguable |
|
|
What are the effects of visual fixation in peripheral vs central vertigo
|
peripheral: suppressed
central: not suppressed |
|
|
What physical signs help localize upper motor neuron lesions?
|
Upgoing plantar reflexes
Increased deep tendon reflexes normal to increased muscle tone or spasticity |
|
|
What physical signs help localize lower motor neuron lesions?
|
Normal or absent plantar relaxes
Deep tendon reflexes decreased or absent Decreased to flaccid muscle tone |
|
|
What physical signs help localize neuromuscular junction or muscle lesions
|
Normal or absent plantar reflexes
Deep tendon reflexes usually preserved but may be decreased Decreased to flaccid muscle tone |
|
|
What are upper motor neuron lesions?
|
Transverse myelitis
Poliomyelitis Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (mixed) MS |
|
|
What are lower motor neuron lesions?
|
Guillain Barre syndrome
Toxic neuropathies Impingement syndromes Diphtheria Porphyria Ciguatera, shllfish or puffer fish toxin |
|
|
What are myoneuronal or muscle fiber lesions?
|
Myasthenia gravis
Lambert Eaton syndrome botulism Periodic paralysis Electrolyte imbalances Tick paralysis |
|
|
How do you differentiate between an UMN lesion and a facial nerve palsy?
|
CNVII -unable to wrinkle forehead in facial nerve palsy
|
|
|
What are indications for neuro-imaging in patients with a headache
|
New onset HA
HA with progressive course or change in pattern HA that never alternates sides HA with any neuro finding or seizures Immunocompromised (HIV must use contrast) |
|
|
Which EKG changes are seen in a patient with SAH
|
ST/T wave changes
U waves QT prolongation |
|
|
What are the 4 criteria for idiopathic intracranial hypertension
|
CT - no mass or large ventricles
CT - no signs of sinus venous thrombosis LP - normal protein LP pressure >20cm H20 |
|
|
What are signs and symptoms of idiopathic intracranial hypertension
|
CN 6 - can't look laterally
HA - worse in the AM |
|
|
What are the typical patients for idiopathic intracranial hypertension
|
OCP
Tetracycline vit A Obese Young females |
|
|
What are the most common primary cancers that metastasize to the brain?
|
Lung
breast followed by Malignant melanoma Kidney GI |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis for delirium
|
I WATCH DEATH
infectious withdrawal acute metabolic toxic hypoxia deficiencies endocrinopathies acute vascular trauma heavy metals |
|
|
Differentiate organic and functional causes of psychosis with regards to memory impairment
|
organic: recent impairment
functional: remote impairment |
|
|
Differentiate organic and functional causes of psychosis with regards to activity
|
organic: psychomotor retardation, tremor, ataxia
functional: repetitive activity, posturing, rocking |
|
|
Differentiate organic and functional causes of psychosis with regards to distortions
|
organic: visual hallucinations
functional: auditory hallucinations |
|
|
Differentiate organic and functional causes of psychosis with regards to orientation
|
organic: disoriented
functional: oriented |
|
|
Differentiate organic and functional causes of psychosis with regards to cognition
|
organic: islands of lucidity, perceives occasionally, attends occasionally, focuses
functional: continuous scattered thourghts, unfiltered perceptions, unable to attend |
|
|
Describe a transverse cord syndrome
|
Sensory impaired below the lesion
motor impaired below the lesion Loss of sphincter control |
|
|
Describe a Brown-sequard syndrome
|
Sensory: impaired ipsilateral position and vibration sense and contralateral pain and temperature sensation
motor: ipsilateral motor loss sphincter involvement is variable |
|
|
Describe central cord syndrome
|
MOI: hyperextension of the c-spine
Sensory: variable Motor: UE>LE, Distal>Proximal sphincter involvement is variable (MUD) |
|
|
Describe anterior cord syndrome
|
Sensory: loss of pain and temperature sensation, position and vibration preserved
Motor: loss or weakness below level sphincter varible |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis of flaccid paralysis?
|
Ascending:
Guillaine Barre Tick Paralysis Descending Myasthenia Gravis Botulism MS |
|
|
Differentiate between myasthenia gravis and botulism
|
Myasthenia gravis: too few receptors for ACh on the muscle, ACh is broken down before it can fully stimulate the receptors. edrophonium (the tensilon test) blocks Acetylcholinesterase and improves mg symptoms
Botulism: irreversibly binds to the presynaptic membrane on peripheral and cranial nerves inhibiting the release of ACh Peripheral effects: descending, symmetrical flaccid paralysis CN effects: bulbar - diplopia, dysarthria, dysphagia |
|
|
What is the blood loss in the 4 classes of shock
|
I - 750cc
II-750-1500 III - 1500-2000 IV- >2000 |
|
|
What is the % blood loss in the 4 classes of shock
|
I - up to 15%
II - 15-30% III -30-40% IV - >40% |
|
|
What is the pulse rate in the 4 classes of shock
|
I - <100
II 100-120 III 120-140 IV >140 |
|
|
What is the BP in the 4 classes of shock?
|
I - normal
II - normal III- decreased IV - decreased |
|
|
What is the pulse pressure in the 4 classes of shock?
|
I - normal to increased
II - decreased III - decreased IV - decreased |
|
|
What is a massive transfusion?
|
10U prbc in 24 hours
|
|
|
What are the complications of massive transfusion
|
consumptive coagulopathy
excessive fibrinolysis dilutional coagulopathy hypothermia acidosis, citrate, hypocalcemia/magnesemia hyperkalemia TRALI |
|
|
What are the immune mediated complications of massive transfusion
|
Hemolytic transfusion reactions
Non-hemolytic febrile reaction Allergic reaction (simple or severe) |
|
|
What is Cushing's Reflex?
|
Progressive HTN
Bradycardia Decreased Respiratory effort |
|
|
How does hyperventilation help in head injuries? What is your goal and why? What is reperfusion injury?
|
Hyperventilation avoids hypercarbia which promotes cerebral edema
Keep the PCO2 between 30-35 mmHg, because you don't want the vasoconstriction to be so pronounced as to promote tissue schema Reperfusion injury -over time, injured vessels may lose their responsiveness to hyperventilation and become vasodilated, blood may then be shunted to the injured area, resulting in brain swelling |
|
|
What are indications for acute seizure prophylaxis in head injuries? What is the goal?
|
-depressed skull fracture
-paralyzed/intubated patient -seizure at the time of injury -seizure in the ED -penetrating brain injury -severe TBI GCS<8 -Acute subdural hematoma -Acute epidural hematoma -Acute ICH -Prior history of seizures goal: to reduce the risk of early seizures (decreases by 66%), prevents additional insult to the brain |
|
|
What are the landmarks for the zones of the neck?
|
Zone I - clavicle to cricoid cartilage
Zone II - cricoid to angle of the mandible Zone III - above angle of the mandible |
|
|
What are indications for a chest tube?
|
Traumatic causes of pneumothorax
Moderate to large PTX Respiratory symptoms regardless of PTX size increasing size of PTX after initial conservative therapy Recurrence of PTX after removal of initial chest tube Patient requires ventilator support Patient requires general anesthesia Associated hemothorax Bilateral PTX regardless of size Tension PTX |
|
|
What are radiologic findings on xray of traumatic aortic disruption
|
Wide mediastinum
Obliteration of the aortic knob Deviation of the trachea to the right Obliteration of the space between the pulmonary artery and the aorta (obscuration of the AP window) Depression of the left mainstem bronchus Deviation of the esophagus (NG) to the right Widened paratracheal stripe Widened paraspinal stripe Presence of a pleural or apical cap Left hemothorax Fractures of the first or second rib or scapula |
|
|
What is the Tile classification of pelvic #?
|
A - avulsion, stable ring
B - rotationally unstable C - Rotationally and Vertically unstable |
|
|
What are the most common sources of bleeding in pelvic#?
|
Venous plexus
Arterial Internal iliac artery-> anterior branch (inferior gluteal artery, obturator artery posterior brach (superior gluteal artery) |
|
|
What are the physiologic mechanisms of heat loss?
|
Evaporation
Radiation Conduction Convection |
|
|
What are the ACLS guidelines for rewarming a hypothermic patient?
|
Passive rewarming Mild for T>34degrees
Active external rewarming for Moderate T30-34 Internal rewarming for Severe T<30 |
|
|
What do you do with cardiac arrest in hypothermia
|
-Best rewarming is cardiopulmonary bypass
-Alternative effective techniques include warm-water lavage of the thoracic cavity and extracorporeal blood warming with partial bypass -Adjuncts - warmed IV, warm humidified oxygen -Attempt defib once, then possibly defer further defies -give meds according to ACLS algorithm |
|
|
Define heat exhaustion
|
Volume depletion under conditions of heat stress
Malaise, fatigue, HA Temp usually <40 Normal neuro function Salt or water deficiency |
|
|
Define heat stroke
|
Exogenous hyperthermia
Loss of thermoregulatory function Signs of severe CNS dysfunction (coma, seizure, neuro) Temp usually >40 often see dry, hot skin Rapid cooling - ice water immersion Evaporative cooling Aim Temp 39 If shivering, then BZD, if still so severe that cannot cool consider chlorpromazine (though anticholinergic so counterproductive) |
|
|
Differentiate between classic and exertional heat stroke with regards to age
|
classic: elderly
exertional young |
|
|
Differentiate between classic and exertional heat stroke with regards to health
|
elderly: impaired
exertional: good |
|
|
Differentiate between classic and exertional heat stroke with regards to activity
|
elderly: sedentary
exertional : strenuous |
|
|
Differentiate between classic and exertional heat stroke with regards to drug use
|
elderly: diuretics, anticholinergics, antipsychotics, antiHTN
exertional: usually none |
|
|
Differentiate between classic and exertional heat stroke with regards to Sweating
|
elderly: no
Exertional: profuse |
|
|
Differentiate between classic and exertional heat stroke with regards to lactic acidosis
|
elderly: usually no, but poor prognosis if present
exertional: yes, is not prognostic |
|
|
Differentiate between classic and exertional heat stroke with regards to rhabdo
|
elderly: unusual
exertional: often |
|
|
Differentiate between classic and exertional heat stroke with regards to hyperuricemia
|
elderly: modest
exertional: severe |
|
|
Differentiate between classic and exertional heat stroke with regards to ARF?
|
elderly <5%
exertional ~30% |
|
|
Differentiate between classic and exertional heat stroke with regards to hypocalcemia
|
elderly: uncommon
exertional: common |
|
|
Differentiate between classic and exertional heat stroke with regards to DIC
|
elderly: mild
exertional marked |
|
|
Differentiate between classic and exertional heat stroke with regards to CK
|
elderly: mild
exertional: severe elevations |
|
|
Differentiate between classic and exertional heat stroke with regards to hypoglycemia
|
elderly - unusual
exertional : common |
|
|
Differentiate between classic and exertional heat stroke with regards to cause
|
elderly poor heat dissipation
exertional excess heat production |
|
|
What are BLS/ACLS issues in Electric shock and lightening injuries?
|
-Highest priority should be given to cardiac and respiratory arrest - as the outcome with ROSC are good
-BLS rescuers must ensure their own safety prior to helping the victim -Spinal immobilization due to potential for traumatic injuries -there are no modifications in ACLS protocols -extensive soft tissue swelling may complicate airway control therefore early intubation should be performed in patients with extensive burns |
|
|
What are the indications for ECG monitoring in electrical injury?
|
Cardiac arrest
Documented LOC abnormal ECG dysrhythmia observed by EMS or in ED Hx of cardiac disease presence of significant RF for cardiac disease concomitant injury severe enough to warrant admission suspicion of conductive injury hypoxia chest pain |

