![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
120 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
t(9;22) (Philadelphia chromosome)
which cancer association? |
CML
Ber-able hybrid |
|
|
t(8;14)
which cancer association? |
Burkitt lymphoma
c-myc activation |
|
|
t(11;14)
which cancer association? |
Mantle cell lymphoma
Cyclin D1 activation |
|
|
t(14;18)
which cancer association? |
Follicular lymphomas
Bcl-2 activation |
|
|
t(15;17)
which cancer association? |
M3 type of AML
responsive to all-trans retinoic acid |
|
|
key rib in inhalation dysfunction (hard to exhale)
|
bottom rib of group
|
|
|
key rib in exhalation dysfunction (hard to inhale)
|
top rib of group
|
|
|
Fall forward w/wrist pronated - radial head will be pushed =
|
posteriorly
|
|
|
Fall backward w/wrist supinated - radial head will be pushed =
|
anteriorly
|
|
|
chapmans point 1in superior and 1 inch lateral to umbilicus is for?
|
kidney
|
|
|
chapmans point 2inches superior and 1 inch lateral to the umbilicus is for
|
adrenal gland
|
|
|
Chapman's point over the transverse process of T11 is for
|
viserceral dysfunction of the appendix
|
|
|
Chapman's point at the tip of the 12th rib is for
|
classic Chapmans point for the appendix
|
|
|
Chapman's point at the 4th intercostal space is for the
|
lower lung
|
|
|
Chapman's point at the greater tubercle of the humerus is for?
|
retina
conjunctiva |
|
|
Chapman's point at the 2nd rib is for?
|
laryngitis = larynx
|
|
|
monitor pt pulse
extend arm at the elbow shoulder is extended, externally rotated, slightly abducted pt takes a deep breath + turn head toward ipsilateral arm + if decreased /abscent radial pulse tests for thoracic outlet syndrome |
Adson's test
|
|
|
extend & sidebend C-spine to side being tested
push down on pts head + if pain radiates into ipsilateral arm |
Spurling test (compression test)
narrowing of the neural foramina - referred pain into arm upon compression of c-spine |
|
|
test for vertebral artery insufficiency
supine flex neck - hold 10s then extend neck - hold 10s also for rotation + if pt complains of dizziness / visual changes / lightheadedness eye nystagmus |
Wallenberg's test
|
|
|
tests neurovascular bundle as it passes under pectoralis minor muscle at the coracoid process (ant one)
hyperabduct arm above the head some extension + if decreased / absent radial pulse |
Wright's test (arm hyperextension test)
|
|

tests neurovascular bundle compromise btw clavicle and 1st rib
palpate radial pulse depress / extend the shoulder + if decreased / absent radial pulse |
Military posture test (costoclavicular syndrome test)
|
|
|
evaluate ROM of shoulder
1 - pt reaches behind head to opposite shoulder (abduction / external rotation) 2 - reach in front to opposite shoulder (internal rotation / adduction) 3 - reach behind back to opposite inferior angle of scapula (internal rotation / adduction) |
Apley's scratch test
|
|
|
tests rotator cuff tears
pt abducts shoulder to 90 degrees slowly lower arm + if pt cannot lower arm smoothly |
drop arm test
|
|
|
to assess biceps tendon in bicipital groove
pt fully extends elbow flexes shoulder supinates forearm you resist shoulder flexion + if tenderness in bicipital groove |
Speed's test
|
|
|
tests adequacy of blood supply by radial, ulnar arteries
pt opens and closes hand several times pt makes a tight fist you occlude radial & ulnar artery pt opens hand you release 1 + if flushes slowly or not at all |
Allen's test
|
|
|
tests tenosynovitis in abductor pollicis longus
and extensor pollicis brevis tendons at the wrist (De Quervain's disease) pt makes fist w/thumb tucked inside the fingers you ulnar deviate the wrist (adduct) + if the pts feels pain |
Finkelstein test
|
|
|
tests for carpal tunnel (median)
you maximally flex pt's wrist and hold for 60s + if tingling in thumb / index / middle / lateral part of ring fingers = carpel tunnel syndrome |
Phalen's test
|
|
|
tests for carpal tunnel
pt extends wrist for 60s + if tingling |
reverse Phalen's test (Prayer's test)
|
|
|
tests for carpal tunnel syndrome
you tap on the volar aspect (posterior) of pts transverse carpal ligament + if tingling / paresthesia into thumb / index / middle / lateral half of ring finger |
Tinel's test
|
|
|
assesses sidebending ability of lumbar spine at thoracolumbar junction
pt stands you locate lateral iliac crests pt bends 1 knee w/o lifting heel from the floor + if not: - lumbar spine should sidebend toward contralateral side - smooth convesxity on ipsilateral side - ipsilateral iliac crest should drop 20-25 degrees |
hip drop test
|
|
|
tests for sciatic nerve compression
supine lift leg by heel while keeping leg extended by pushing on knee lift until discomfort then lower slightly then dorsiflex the foot (toes superior) no pain = + Braggard's test = tight hamstrings = (-) for sciatic pain down the leg = sciatic problem = + test |
straight leg raising test
|
|
|
assesses iliosacral motion
standing pt bends forward + on side with more superior PSIS |
standing flexion test
= innominate dysfunction |
|
|
assesses sacroiliac motion
seated bends forward + on side with more superior PSIS |
seated flexion test
= sacral dysfunction |
|
|
helps determine side of SI dysfunction
compress each ASIS while pt is supine + on side that resists more |
ASIS compression test
|
|
|
assesses gluteus medius muscle strength
you stand behind pt pt picks up 1 leg gluteus medius should pick up pelvis on that side + if pelvis drops on the side in which the pt picked up their leg/foot |
Trendelenberg's test
|
|
|
assesses if the sacral base is tilted posteriorly
pt prone rapidly spring your heel on the lumbosacral junction + if little or no springing - means the sacral base is posterior |
lumbosacral spring test
|
|
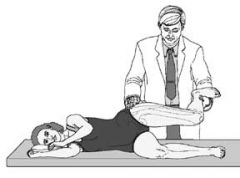
tests for tight tensor fascia lata and iliotibial band
pt lateral recumbent you behind pt flex knee on side to be tested to 90 degrees abduct hip as far as possible slightly extend the hip stabalize pelvis with other hand allow thigh to fall to table + if thigh remains abduct = tight iliotibial band |
Ober's test
|
|
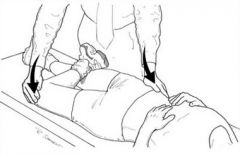
assesses pathology of sacroiliac and hip joint - osteoarthritis of the hip
pts hip is put in: flexion abduction external rotation extension - making a "figure 4" you press down on the knee and contralateral ASIS + if pain anywhere around the hip joint = hip pathology |
FABERE test (Patrick's test)
stands for: flexion abduction external rotation extension |
|

assesses possible flexion contracture of the hip
usually iliopsoas pt supine you flex 1 knee until thigh touches abd + if opposite leg lifts off table |
Thomas test
|
|
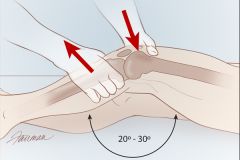
assesses stability of the ACL - slightly more accurate than drawer test
pt supine you grasp distal tibia w/1 hand grasp distal femur with the other flex knee to 30 degrees pull tibia forward compare to other side + if tibia excessively moves out from under the femur |
Lachman's test
|
|
|
to detect tears in the posterior aspect of the menisci
medial meniscus - fully flex pts knee - find joint line externally rotate tibia valgus stress on knee then extend knee maintaining pressure + if audible "click" = posterior tear of the medial meniscus lateral meniscus same procedure w/ internal rotation of the tibia varus stress on the knee |
McMurray's test
|
|
|
assesses meniscus and ligaments of the knee
pt prone knee flexed to 90 degrees 1 - compress straight down on heel 2- internally and externally rotate the tibia while pressing down + if pain = meniscus tear 3 - pull up - distract 4 - internally / externally rotate tibia + if pain = ligamentous injury (usually the medial or lateral collateral ligaments |
Apley's compression / distraction tests
|
|
|
assess posterior articular surfaces
pt supine knees fully extended & relaxed you push patella inferiorly (distally) pt contracts quads + if pain (you might also feel a grind as the patella slides proximally) |
patellar grind test
|
|
|
assess the stability of the collateral ligaments of the knee
pt supine or seated flex knee to unlock from full extension you stabilize ankle other hand pushes on knee - pushing medially with Lateral force is vaLgus stress test + if any gapping on the medial aspect of the joint - pushing laterally with medial force is varus stress test + if any gapping of the lateral joint line |
valgus and varus stress test
|
|
|
monitor pt pulse
extend arm at the elbow shoulder is extended, externally rotated, slightly abducted pt takes a deep breath + turn head toward ipsilateral arm + if decreased /abscent radial pulse tests for thoracic outlet syndrome what does it test for? how is it done? |
monitor pt pulse
extend arm at the elbow shoulder is extended, externally rotated, slightly abducted pt takes a deep breath + turn head toward ipsilateral arm + if decreased /abscent radial pulse tests for thoracic outlet syndrome |
|
|
Spurling test (compression test)
what does it test for? how is it done? |
extend & sidebend C-spine to side being tested
push down on pts head + if pain radiates into ipsilateral arm |
|
|
Wallenberg's test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
test for vertebral artery insufficiency
supine flex neck - hold 10s then extend neck - hold 10s also for rotation + if pt complains of dizziness / visual changes / lightheadedness eye nystagmus |
|
|
Wright's test (arm hyperextension test)
what does it test for? how is it done? |
tests neurovascular bundle as it passes under pectoralis minor muscle at the coracoid process (ant one)
hyperabduct arm above the head some extension + if decreased / absent radial pulse |
|
|
Military posture test (costoclavicular syndrome test)
what does it test for? how is it done? |
tests neurovascular bundle compromise btw clavicle and 1st rib
palpate radial pulse depress / extend the shoulder + if decreased / absent radial pulse |
|
|
Apley's scratch test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
evaluate ROM of shoulder
1 - pt reaches behind head to opposite shoulder (abduction / external rotation) 2 - reach in front to opposite shoulder (internal rotation / adduction) 3 - reach behind back to opposite inferior angle of scapula (internal rotation / adduction) |
|
|
drop arm test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
tests rotator cuff tears
pt abducts shoulder to 90 degrees slowly lower arm + if pt cannot lower arm smoothly |
|
|
Speed's test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
to assess biceps tendon in bicipital groove
pt fully extends elbow flexes shoulder supinates forearm you resist shoulder flexion + if tenderness in bicipital groove |
|
|
Allen's test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
tests adequacy of blood supply by radial, ulnar arteries
pt opens and closes hand several times pt makes a tight fist you occlude radial & ulnar artery pt opens hand you release 1 + if flushes slowly or not at all |
|
|
Finkelstein test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
tests tenosynovitis in abductor pollicis longus
and extensor pollicis brevis tendons at the wrist (De Quervain's disease) pt makes fist w/thumb tucked inside the fingers you ulnar deviate the wrist (adduct) + if the pts feels pain |
|
|
Phalen's test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
tests for carpal tunnel (median)
you maximally flex pt's wrist and hold for 60s + if tingling in thumb / index / middle / lateral part of ring fingers = carpel tunnel syndrome |
|
|
reverse Phalen's test (Prayer's test)
what does it test for? how is it done? |
tests for carpal tunnel
pt extends wrist for 60s + if tingling |
|
|
Tinel's test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
tests for carpal tunnel syndrome
you tap on the volar aspect (posterior) of pts transverse carpal ligament + if tingling / paresthesia into thumb / index / middle / lateral half of ring finger |
|
|
hip drop test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
assesses sidebending ability of lumbar spine at thoracolumbar junction
pt stands you locate lateral iliac crests pt bends 1 knee w/o lifting heel from the floor + if not: - lumbar spine should sidebend toward contralateral side - smooth convesxity on ipsilateral side - ipsilateral iliac crest should drop 20-25 degrees |
|
|
straight leg raising test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
tests for sciatic nerve compression
supine lift leg by heel while keeping leg extended by pushing on knee lift until discomfort then lower slightly then dorsiflex the foot (toes superior) no pain = + Braggard's test = tight hamstrings = (-) for sciatic pain down the leg = sciatic problem = + test |
|
|
standing flexion test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
assesses iliosacral motion
standing pt bends forward + on side with more superior PSIS = innominate dysfunction |
|
|
seated flexion test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
assesses sacroiliac motion
seated bends forward + on side with more superior PSIS = sacral dysfunction |
|
|
ASIS compression test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
helps determine side of SI dysfunction
compress each ASIS while pt is supine + on side that resists more |
|
|
Trendelenberg's test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
assesses gluteus medius muscle strength
you stand behind pt pt picks up 1 leg gluteus medius should pick up pelvis on that side + if pelvis drops on the side in which the pt picked up their leg/foot |
|
|
lumbosacral spring test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
assesses if the sacral base is tilted posteriorly
pt prone rapidly spring your heel on the lumbosacral junction + if little or no springing - means the sacral base is posterior |
|
|
Ober's test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
tests for tight tensor fascia lata and iliotibial band
pt lateral recumbent you behind pt flex knee on side to be tested to 90 degrees abduct hip as far as possible slightly extend the hip stabalize pelvis with other hand allow thigh to fall to table + if thigh remains abduct = tight iliotibial band |
|
|
FABERE test (Patrick's test)
what does it test for? how is it done? |
assesses pathology of sacroiliac and hip joint - osteoarthritis of the hip
pts hip is put in: flexion abduction external rotation extension - making a "figure 4" you press down on the knee and contralateral ASIS + if pain anywhere around the hip joint = hip pathology |
|
|
Thomas test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
assesses possible flexion contracture of the hip
usually iliopsoas pt supine you flex 1 knee until thigh touches abd + if opposite leg lifts off table |
|
|
Lachman's test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
assesses stability of the ACL - slightly more accurate than drawer test
pt supine you grasp distal tibia w/1 hand grasp distal femur with the other flex knee to 30 degrees pull tibia forward compare to other side + if tibia excessively moves out from under the femur |
|
|
McMurray's test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
to detect tears in the posterior aspect of the menisci
medial meniscus - fully flex pts knee - find joint line externally rotate tibia valgus stress on knee then extend knee maintaining pressure + if audible "click" = posterior tear of the medial meniscus lateral meniscus same procedure w/ internal rotation of the tibia varus stress on the knee |
|
|
Apley's compression / distraction tests
what does it test for? how is it done? |
assesses meniscus and ligaments of the knee
pt prone knee flexed to 90 degrees 1 - compress straight down on heel 2- internally and externally rotate the tibia while pressing down + if pain = meniscus tear 3 - pull up - distract 4 - internally / externally rotate tibia + if pain = ligamentous injury (usually the medial or lateral collateral ligaments |
|
|
patellar grind test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
assess posterior articular surfaces
pt supine knees fully extended & relaxed you push patella inferiorly (distally) pt contracts quads + if pain (you might also feel a grind as the patella slides proximally) |
|
|
valgus and varus stress test
what does it test for? how is it done? |
assess the stability of the collateral ligaments of the knee
pt supine or seated flex knee to unlock from full extension you stabilize ankle other hand pushes on knee - pushing medially with Lateral force is vaLgus stress test + if any gapping on the medial aspect of the joint - pushing laterally with medial force is varus stress test + if any gapping of the lateral joint line |
|
|
sympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
head and neck |
T1-5
|
|
|
sympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
heart |
T1-5
|
|
|
sympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
lungs |
T1-4
|
|
|
sympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
asthma (exact level and side) |
T2 left
|
|
|
sympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
esophagus (seg / side) |
T3-6 right
|
|
|
sympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
stomach |
T5-10
|
|
|
sympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
SI |
T8-10
|
|
|
sympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
appendix |
T9-12
|
|
|
sympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
pancreas |
T5-9 (b/l or right)
|
|
|
sympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
liver and gallbladder (segs/side) |
T5-10 right
|
|
|
sympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
kidney |
T9-L1 ipsilateral
|
|
|
sympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
ureter and bladder |
T11 - L3 ipsilateral
|
|
|
sympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
external genitalia |
T12
|
|
|
sympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
prostate |
T10 - L2
|
|
|
sympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
ovaries / testes |
T10-11
|
|
|
sympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
uterus |
T9 - L2
|
|
|
parasympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
anything respiratory |
C0-2
|
|
|
parasympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
myocardium |
C0-2
|
|
|
parasympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
cardiac rate / rhythm (specific) |
C2 left (vagus)
|
|
|
parasympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
GI - esophagus to ascending colon |
C0-2
|
|
|
parasympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
appendix |
C0-2
|
|
|
parasympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
descending colon / rectum |
S2-4
|
|
|
parasympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
pancreas |
C0-2
|
|
|
parasympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
kidney / proximal ureter |
C0-2
|
|
|
parasympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
bladder / distal ureter |
S2-4
|
|
|
parasympathetic viscerosomatic reflex location for:
prostate / fallopian tubes / uterus |
S2 - 4
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what anterior Chapman's point
upper lungs |
3rd ICS, just lateral to the sternum
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what anterior Chapman's point
lower lung |
4th ICS, just lateral tot he sternum
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what anterior Chapman's point
stomach |
6th ICS, 1" lateral from sternoclavicular jt
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what anterior Chapman's point
gallbladder |
6th intercostal space
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what anterior Chapman's point
pancreas |
7-8th rib on right - lateral to costal cartilage
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what anterior Chapman's point
gallbladder |
6th ICS, midclavicular line
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what anterior Chapman's point
appendix |
tip of the right 12th rib
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what anterior Chapman's point
myocardium |
2nd ICS
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what anterior Chapman's point
liver |
5-6th ICS right
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what anterior Chapman's point
adrenals |
2" superior and 1" lateral to the umbilicus
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what anterior Chapman's point
kidneys |
1" superior and 1" lateral to umbilicus
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what anterior Chapman's point
bladder |
periumbilical region
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what anterior Chapman's point
urethra |
2cm lateral to pubic symphisis
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what anterior Chapman's point
prostate |
iliotibial band
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what anterior Chapman's point
colon |
greater trochanter to just above the knee on the iliotibial band
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what anterior Chapman's point
appendix |
tip of the right 12th rib
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what POSTERIOR Chapman's point
appendix |
transverse process of T11
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what POSTERIOR Chapman's point
adrenals |
btw spinous & transverse processes of T11 - 12
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what POSTERIOR Chapman's point
kidneys |
btw spinous & transverse processes of T12 - L1
|
|
|
the somatic manifestation of a visceral dysfuntion for this organ is what POSTERIOR Chapman's point
stomach |
T6-7
|
|
|
inhalation dysfunction ribs 3-7, which Tx?
|
BOTTOM rib (7)
|
|
|
exhalation dysfunction ribs 3-7 Tx which?
|
TOP rib (3)
|

