![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
1 Joule equals ...... erg |
10^7 |
|
|
|
1 calorie equals |
4.2 Joules |
|
|
|
1 BTU equals ........ calories |
252 calories and 1055 Joules |
|
|
|
Heat current |

|
|
|
|
Thermal resistance |

|
|
|
|
Absorptive power |

|
|
|
|
Relation between spectral absorptive power and absorptive power |

|
|
|
|
Emissive power |

|
Amount of energy radiated by a body per unit surface area per unit time |
|
|
Emissivity of a body |

|
|
|
|
Transmittance or transmittivity |
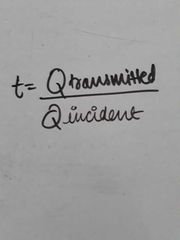
|
|
|
|
Reflectivity |

|
|
|
|
Relation between absorptive power, Transmittance and Reflectivity |
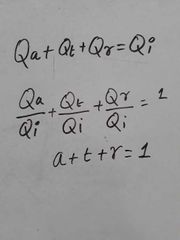
|
|
|

|
C and D |
|
|
|
Kirchoff's radiation law |

|
|
|
|
Acc to Stefan's law or stefan-Boltzmann law; emissive power formula |

|
|
|
|
Rate of cooling of a body by radiation |

|

|
|
|
Rate of cooling acc to Newtons law of cooling (radiation not mentioned) |

|
|
|
|
Newton's law of cooling for problems |

|
|
|
|
Wein's displacement law |

|
|
|
|
Stefan's constant value |

|
|
|
|
Change in time period of pendulum on linear expansion of length of string |

|
|
|
|
Time lost by a clock in one day |

|
|
|
|
V(avg), V(rms) and V(most probable) |

|
|
|
|
Pressure exerted by gas molecules |

|
|
|
|
Pressure exerted by a gas in terms of KE of 1 molecule |

|
|
|
|
Avg KE of per molecule |

|
|
|
|
Total translational KE of molecules of a gas |

|
|
|
|
Define mean free path and write its relation with diameter of molecules |

|
The average distance travelled by a molecule between two successive collision is known as mean free path of the molecule |
|
|
Density of a gas |

|
|
|
|
Boltzman constant |

|
|
|
|
Degree of freedom |

|
|
|
|
Critical volume |

|
|
|
|
Critical pressure |

|
|
|
|
Critical temperature |

|
|
|
|
Critical coefficient of all gases |

|
|
|
|
Work done in isothermal isochoric and isobaric processes |

|
|
|
|
Adiabatic process work done |

|
|
|
|
Work done order: Adiabatic, isochoric, isobaric and isothermal processes |

|
|
|
|
Conditions for adiabatic process |

|
|

