![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the 3 types of well being?
|
Physical, Social and Pyschological
|
|
|
What can under eating result in?
|
weight loss, beter performance in certain activities.
|
|
|
What can overeating result in?
|
weight gain, aid events needing a low centre of gravity, anorexia, bulimia.
|
|
|
What increases with age?
|
Strength and Skill Level
|
|
|
What decreases with age?
|
Flexibility, Recovery rate, O2 capacity
|
|
|
What are the 3 somatotypes and their characteristics?
|
Endomorph- Fat
Ectomorph - thin Mesomorph- muscly |
|
|
What might cause people to not want to do sport?
|
Culture, Religion, Ability
|
|
|
What's the difference between Competitive and Recreational sport?
|
Competitive- highly committed, requires fitness/skill, full time
Recreational- not demanding, no training, played at conveniance. |
|
|
What are the 4 disability categories?
|
Physical, Mental, Permanent, Temporary
|
|
|
Which environmental factors affect training?
|
Weather, Pollution, Altitude, Humidity and Terrain
|
|
|
How does alcohol affect performance levels?
|
coordination, speech, judgement, slows reaction time, muscles get tired easier, increases blood pressure, damages: liver, heart, kidney, brain, immune system.
|
|
|
What are the functions of the skeletons?
|
Protection, Blood cell production, Support, Movement, Shape
|
|
|
Tendons
|
connect muscle to bone
|
|
|
Ligaments
|
Join bone to bone
|
|
|
Cartialage
|
prevents end of bone rubbing together at joints
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of joints?
|
Immovable, Slightly movable, Synovial
|
|
|
What are the health related components of fitness?
|
Muscular Strength, Body Composition, Flexibility, Muscular Endurance, Cardiovascular Endurance.
|
|
|
What are the skill related components of fitness?
|
Power, Speed, Balance, Agility, Reaction Time, Coordination.
|
|
|
Muscular Endurance
|
The amount of force a muscle can apply- Hand grip dynamometer- weight lifting
|
|
|
Power
|
The ability to do strength movements quickly- Sergeant Jump - Diving
|
|
|
Speed
|
The rate at which someone is able to move or cover a distance in a given amount of time - 30m sprint - 100m sprint
|
|
|
Balance
|
The ability to keep your centre of mass over your base of support - Stork stand - balance beam
|
|
|
Agility
|
the ability to control the movement of your entire body and to be able to change your body's position quickly - illinois agility run - tennis
|
|
|
Reaction time
|
The time it takes you to move in response to a stimulus - ruler drop test - tennis
|
|
|
Co - ordination
|
the ability to use 2 or more parts of your body together - alternate hand wall toss test - table tennis
|
|
|
Cardiovascular Endurance
|
the ability to exercise your whole body for a long time - bleep test - long distance running
|
|
|
Muscular Endurance
|
The ability to repetitively use your voluntary muscles over a long time - sit up test - rowing
|
|
|
Flexibility
|
The amount of movement possible at a joint - sit and reach test - splits gymnastics
|
|
|
Body Composition
|
The percentage of your body weight made up by fat, muscle and bone
|
|
|
What are the 3 kinds of stength?
|
Static, Explosive, Dynamic
|
|

example
|
shoulder and hip
|
|

example
|
Skull
|
|
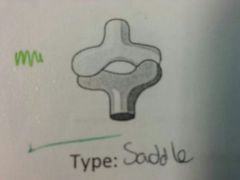
example
|
thumb
|
|
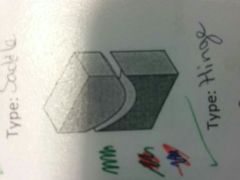
example
|
elbow + knee
|
|
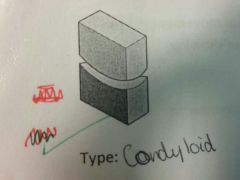
example
|
wrist and ankle
|
|
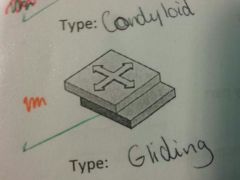
example
|
wrist, vertebrae
|
|
|
What is Extention
|
Straightening limbs at a joint
Elbow |
|
|
Abduction
|
Movement away at the mid-line of the body
Hip |
|
|
Circumduction
|
Movement in which flexion, abduction, extention + adduction are combined in sequence
Shoulder |
|
|
Rotation
|
A circular movement around a fixed point
Neck |
|
|
Adduction
|
Movement towards the mid-line of the body
Hip |
|
|
Flexion
|
Bending the limbs at a joint
Knee |
|
|
what are the principles of training
|
Specificity, Progression, Overload, Reversibility, Tedium
|
|
|
What are the 4 principles of overload?
|
Frequency, Intensity, Time, Type
|
|
|
What does MHR stand for?
|
Maximum Heart Rate
|
|
|
What is a timed circuit?
|
Time is set and you work for that time. Set time for each station.
|
|
|
What is a fixed load circuit?
|
Station is labeled with specific amount of work you have to do.
|
|
|
what is a varied laps circuit
|
different laps in the circuit
|
|
|
what are 3 adv. of circuit training?
|
1. works a lot of muscles
2. easy to organise 3. no special equipment needed |
|
|
what are 2 disadv. of circuit training?
|
1.difficult to exercise only 1 muscle
2. difficult to overload specific muscles. |
|
|
What are 3 training methods?
|
1 . circuit training
2. weight training 3. strength training |
|
|
What are the 2 types of weight training?
|
1. Free-standing weights
2. Specialist weight- training |

