![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Line Postulate |
There is EXACTLY ONE line that passes through / connects any 2 points |
|
|
|
Plane Postulate |
There is EXACTLY ONE plane connecting / containing 3 noncollinear points |
|
|
|
Linear |
Extending along a STRAIGHT line |
|
|
|
Collinear |
2 or MORE points lying in the SAME STRAIGHT line |
|
|
|
Noncollinear |
NOT lying on the SAME STRAIGHT line |
|
|
|
Flat Plane Postulate |
If there are 2 points on a plane, then the line that connects these points are also on that same plane |
|
|
|
Midpoint Theorem |
If a line is divided into 2 at its midpoint, that means the 2 line segments are congruent |
|
|
|
Ruler Postulate |
You can measure any line or line segment given any 2 points from that line |

|
|
|
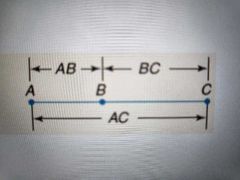
Segment Addition Postulate |
If you have a collinear line with 3 points A, B, C, then line AB + BC = AC
If AB + BC = AC, that means B lies in between A and C |
|
|
|
Reflexive Property |
AB ≅ AB; compare it to itself |
|
|
|
Symmetric Property |
If AB ≅ CD, then CD ≅ AB; comparing 2 congruent items |
|
|
|
Transitive Property |
If AB ≅ CD, and CD ≅ EF, then AB ≅ EF; comparing 3 or more congruent items |
|
|
|
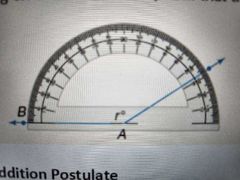
Protractor Postulate |
You can measure any angle given the 2 rays that form that angle |
|
|
|
Adjacent |
They share the same side or they're next to each other |
|
|
|
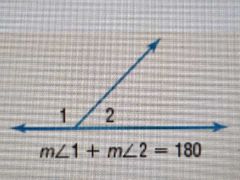
Supplement theorem |
If you merge 2 angles and they form 180°, they are supplementary |
|
|
|
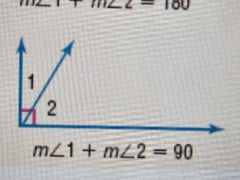
Complement theorem |
If you merge 2 angles and they form 90°, they are complementary |
|
|
|
Vertical Angle Theorem |
Vertical angles are always congruent |
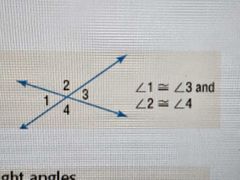
|
|
|
Perpendicular |
When 2 lines connect to form 90° |
|
|
|
Right Angle Theorems |

|
|
|
|
Corresponding Angles Postulate |

Note that the 2 lines have to be PARALLEL |
|
|
|
Alternate Interior Angles Theorem |
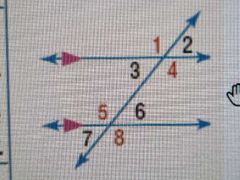
If you have 2 parallel lines cut by a transversal, the alternating angles INSIDE the 2 parallel lines are congruent (4≅5, 3≅6) |
|
|
|
Consecutive Interior Angles Theorem |
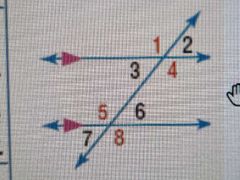
If you have 2 parallel lines cut by a transversal, the angles INSIDE the 2 parallel lines that are also on the same side of the transversal are supplementary (4+6=180°, 3+5=180°) |
|
|
|
Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem |
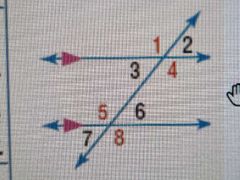
If you have 2 parallel lines cut by a transversal, the alternating angles OUTSIDE the 2 parallel lines are congruent (1≅8, 2≅7) |
|
|
|
Perpendicular Transversal Theorem |
If a transversal line cuts through 2 parallel lines and it is perpendicular to one of them, then it is perpendicular to both lines |
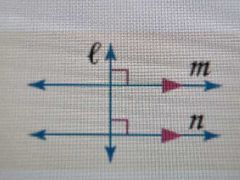
|
|
|
Parallel Postulate |
If you have a line and a random point that's not touching the line, there is EXACTLY ONE line that can go through that point and still be parallel to the first line |
|
|
|
Proving Lines Parallel Theorems |

Just familiarize yourself with these. It'll just help you prove that 2 lines are parallel |
|
|
|
Angle Sum Theorem |
The sum of the angles of a triangle is always 180° |
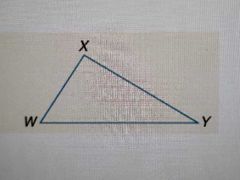
|
|
|
Third Angle Theorem |
If 2 angles of a triangle are congruent to 2 angles of another triangle, then the 3rd angles of both triangles are congruent |
|
|
|
Exterior Angle Theorem |
If you extend one side of a triangle, the angle outside the triangle is equal to the combination of the 2 angles inside the triangle that aren't touching the exterior angle |
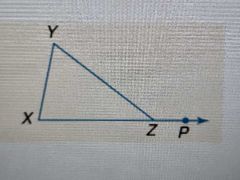
|
|
|
If you have a right triangle, the sum of the 2 acute angles will always be ___. |
90° |
|
|
|
Side-Side-Side Congruence (SSS) Postulate |
Two triangles are congruent if the 3 sides of both triangles are congruent |
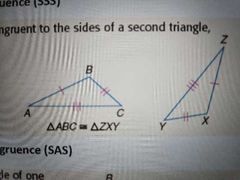
|
|
|
Side-Angle-Side Congruence (SAS) Postulate |
Two triangles are congruent if the 2 sides of both triangles and the angle BETWEEN both sides are congruent |
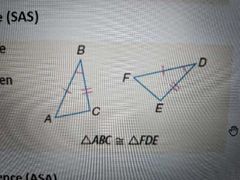
|
|
|
Angle-Side-Angle Congruence (ASA) Postulate |
Two triangles are congruent if the 2 angles of both triangles and the side BETWEEN both sides are congruent |
|
|
|
Right Triangle Congruence |
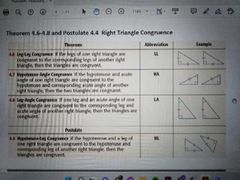
Just remember that the HYPOTENUSE is the longest side (the side that doesn't touch the right angle) and the other sides are LEGS |
|
|
|
Isosceles Triangle Theorem |
If 2 sides of a triangle are congruent, then the 2 angles opposite them are also congruent
FOCUS IS ON THE SIDES BEING CONGRUENT |
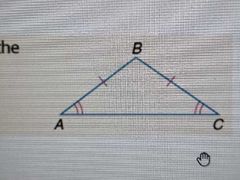
|
|
|
Converse of Isosceles Triangle Theorem |
If 2 angles of a triangle are congruent, then the 2 sides opposite them are also congruent FOCUS IS ON THE ANGLES BEING CONGRUENT |
|

