![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
3 things that can happen to Photons from the sun..... |
Reflect , Refract, Absorb |
|
|
Photons : Absorption |
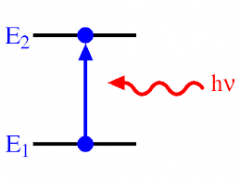
When a Photon absorbs sunlight, the molecules vibrate within the object and then the object becomes hotter and emits thermal energy. |
|
|
Photons: Refraction |

When a photon Refracts sunlight the light goes through the object and changes direction. (The light gets bent). |
|
|
Photons: Reflection |

Sunlight comes in and bounces off of the object Ex. A Mirror |
|
|
Wavelength |
The wavelength = frequency |
|
|
Short wavelength / Long |
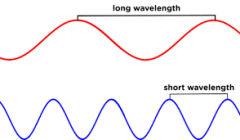
Long Wave lengths are LOW frequency, RED SHORT wavelengths are HIGH Frequency, BLUE |
|
|
Amplitude determines... |
Intensity Great Amp= Bright colors Small Amp= Dull colors |
|
|
Light saturation |
Light intensity beyond light response curve. At this point there are increases n light intensity. |
|
|
Light Purity..... |
the # of wavelengths that it takes to make up light |
|
|
Whytt's Reflex |
Robert Whytt did studies on reflexes and discovered that our bodies have natural reflexes, and often times the body automatically reacts without instruction from the brain |
|
|
What is Accomodation |
The process by which the vertebrate eye changes optical power to maintain a clear image |
|
|
Accommodation: Close |
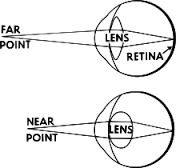
The eye accommodates for close images by tightening the ciliary muscles allowing the lens to become more rounded |
|
|
Accomadation: Far |
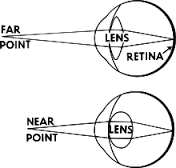
The eye loosens the ciliary muscles allowing the lens to view things further away. |
|
|
More refraction |
When the image is close and the ciliary muscles loosen up |
|
|
Less refraction |
When the image is further away and the muscles loosen up |
|
|
Hyperopia: Far sighted |
Image is focused behind the retina Cause: Eye maybe to short or lens may not refract light. |
|
|
Myopia: Near Sighted |
image is focused on retina Cause: the eye may be to long or the cornea has crystallized lens. |
|
|
Convex Lens |
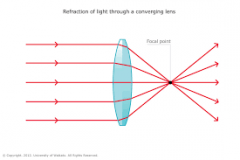
Outwards (more oval like) |
|
|
Concave lens |
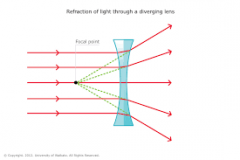
In words (sides are caved in ) |
|
|
The process of Transduction |
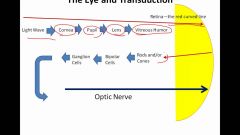
|
|
|
P B Hag |
cornea-> Pupil-> Lens V.Humor- Rods/cones- > Bipolorcells->>Gag. cells-> optic nerve P.B.Hag |
|
|
Cones |
6- 8 Million Phopticvision In the fovea (center) Low sensativity to dim light Hi sensativity to bright light Wavelength= short Low acuity= convergence move mor rapidly |
|
|
Rods |
120- 130mil. scotopic periphery high sensativity to dim light low sensatvity to bright light long wavelengths high acuity = convergence more sensative |
|
|
Blind spot |
Located in the back of the eye, an area that contains not photo receptors. |
|
|
Astigmatism |
lens inside eye is curved differently in one direction |
|
|
Glaucoma |
The nerve connecting the eye to the brain is damaged |
|
|
Macular degeneranration |
loss in the eye center of the field of vsion |
|
|
Retinitis Pigmentosa |
Retina is damaged |
|
|
Floaters |
spots of various shapes/ sizes appear in vitreous humor |
|
|
Achromatic |
Not being able to see colors (only sees in black/ white) |
|
|
Night Blindness |
Not being able to see well at night |
|
|
Duplex vision |
Our visual system consists of two photoreceptors. Photoptic vision and Scotoptic vision. |
|
|
Duplex vision: Photopic Vision |
operates best under dim light. and with the absence of color. like Rods |
|
|
Duplex vision: Scopotopic vision |
operates best in bright light and in color ex. cones |
|
|
Convergence |
Refers to level of detail acuity sensativity depends on level of convergence |
|
|
Off center w/ off surround vs. off center w/ on surround |
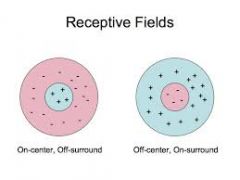
|
|
|
Magnocellular : M- cells |
Rods responds to any wavelength of light large receptive fields process visual motion (poor resolution) fast response |
|
|
Parvocellular : P-cells |
process color info. small receptive field good visual resolution slow responce |
|
|
Simple cells |
small elongated stright lines certin orientatn spacific to edges |

