![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the main role of the kidneys?
|
-Formation of urine through FILTRATION, EXCRETION, and SELECTIVE REABSORPTION.
|
|
|
What are the structures of the renal system?
|
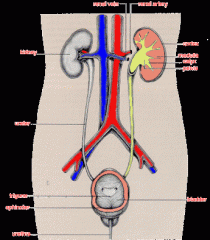
1. Kidneys
2. Ureters 3. Urinary bladder 4. Urethra |
|
|
What are the structures of the kidneys?
|
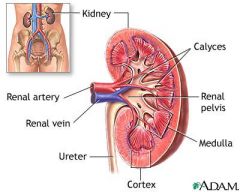
-Renal cortex
-Renal medulla -Renal pelvis |
|
|
What is the function of the nephron?
|
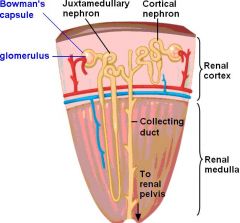
-Urine formation.
|
|
|
Where is the nephron located?
|
-In medulla and cortex of the kidney
|
|
|
What are the structures of the nephron called?
|
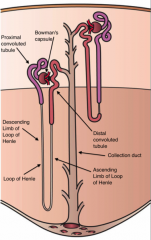
1. Bowman's Capsule
2. Glomerulus 3. Proximal and Distal convoluted tubules 4. loop of Henle 5. Collecting duct |
|
|
What are the functions of the nephron?
|
-Balance sodium and potassium ions
-Removal of drugs -Blood pressure regulation |
|
|
What are symptoms of a urinary tract infection?
|
-Fever
-Back pain -Frequent urination |
|
|
What are symptoms of a stone in the urinary tract?
|
-Blood in the urine
-Pain -Frequent urination -Hesitation |
|
|
What are diagnostics for urinary symptoms?
|
-Palpation of kidney and bladder
-Urine analysis -Ultrasound -CT (computed tomography) -MRI -Kidney biopsy |
|
|
What is a CT scan?
|
-A 3D image rendered by taking a series of 2D Xrays around an axis of rotation.
-Labor intensive -Can give false positives and place burdens on the system |
|
|
What is an MRI?
|
-Magnetic Resonance Imaging
-Uses powerful magnetic field to render images with greater contrast between different soft tissue. -More powerful than CT scan. |
|
|
What is an ultrasound?
|
-Diagnostic tool using cyclic sound pressure.
|
|
|
What is renal/kidney failure?
|
-Abnormal kidney function in which the kidneys fail to adequately excrete toxic substances.
-Can be either acute or chronic. |
|
|
What are the symptoms of renal/kidney failure?
|
-Thirst
-Fatigue -Bad breath -Edema |
|
|
What are the causes of renal/kidney disease?
|
-Nephritis
-Diabetes -Hypertension |
|
|
What are the treatments for renal/kidney failure?
|
-Peritoneal dialysis (fluids pumped into peritoneal space)
-Haemodialysis (blood pumped through artificial filter) -Transplantation -Low-protein diet |
|
|
What causes a urinary tract infection?
|
-Bacteria that causes infection in otherwise sterile urine.
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of a urinary tract infection?
|
-Discharge from urethra
-Frequent urination -Urgent urination -Pain -Cloudy urine -Chills -Fever -Backpain |
|
|
What is the treatment for a urinary tract infection?
|
-Antibiotics
|
|
|
What is a kidney stone?
|
-A solid concretion formed in the kidneys that causes blockage in the urethra.
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of a kidney stone?
|
-Intermittent pain ("renal colic"
-Nausea -Vomiting -Blood in urine |
|
|
How are kidney stones diagnosed?
|
-Intravenous Urography
|
|
|
What is intravenous urography?
|
-Radiological procedure used to visualize abnormalities of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, and bladder.
|
|
|
How are kidney stones treated?
|
-NSAIDs
-Extracorporal shock wave lithotripsy -Surgery |
|
|
How to prevent the formation of kidney stones?
|
-Drugs that interfere with their formation
-Avoid foods rich in oxalate (rhubarb, spinach) |
|
|
What is hydronephrosis?
|
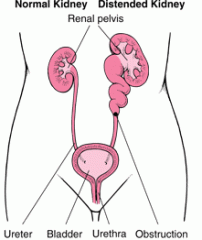
-Distention/dilation of the kidneys caused by backward pressure from obstructed flow.
|
|
|
What are the causes of hydronephrosis?
|
-Structural abnormalities
-Stones -Tumor -Pregnancy |
|
|
What are the symptoms (diagnosis) of hydronephrosis?
|
-Dull aching pain
-Palaptable mass -UTI |
|
|
What is the treatment for hydronephrosis?
|
-Surgery
-Treat underlying cause |
|
|
What is urinary incontinence?
|
-Uncontrollable loss of urine.
|
|
|
Who does urinary incontinence mostly affect?
|
-The elderly
|
|
|
What are the complications of urinary incontinence?
|
-Pressure sores
-Urinary tract infections -Depression |
|
|
What are the treatments for urinary incontinence?
|
-Discontinue certain phamaceuticals
-Estrogen therapy -Pelvic muscle exercises |
|
|
What is urinary tract cancer?
|
-Cancer of the kidney or lower urinary tract.
-2% of all cancers |
|
|
What are some causes of urinary tract cancer?
|
-Smoking
-Chemicals |
|
|
How is urinary tract cancer diagnosed?
|
-Cystoscopy
-CT scan -MRI -Ultrasound |

