![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
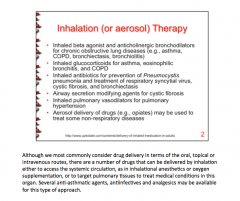
Diseases for therapy: 1. Inhaled beta agonist and anticholinergic bronchodilators 2. Inhaled glucocorticoids 3. Inhaled antibiotics 4. Airway secretion modifying agents 5. Inhaled pulmonary vasodilators 6. Aerosol delivery of drugs Choices: ASTHMA, COPD, BRONCHIECTASIS, BRONCHIOLITIS, EOSINOPHILIC BRONCHITIS, PNEUMOCYSTIC PNEUMONIA, SYNCYTIAL VIRUS, CYSTIC FIBROSIS, PULMONARY HYPERTENSION, NON-RESPIRATORY DISEASE |
|
|
|
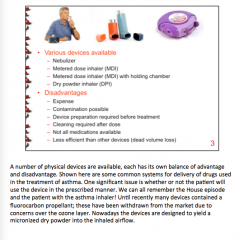
What are some physical devices used for treatment of asthma? Disadvantages? |
|
|
|
The lung is far more ___________ to macromolecules than any other portal, even more so than the GI tract. The lung has a low capacity for __________________ and ____________ activity. Small molecules are delivered cleanly without the production of a complex array of _____________. No noninvasive route of delivery provides the speed of action that an __________ drug can provide. |

|
|
|
What two things are critical for inhaled drugs? Problems that can result if too much drug deposited in mouth. What is the device efficiency normally? What represents the barrier? |

How patient inhales and size of aerosol. |
|
|
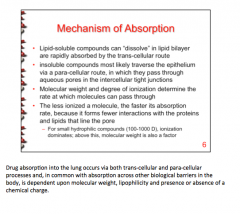
Drug absorption occurs via what two processes? What does it depend on? Which compounds are absorbed via trans cellular route? Which traverse epithelium via para cellular route? What determines rate they can pass through? What determines rate for small hydrophilic compounds (100-1000D)? |
|
|
|
What are the three main conditions that require drug treatment of the lung? |
Inflammation Infection Transformation
|
|
|
Name some inflammatory conditions of the lung: |
Asthma COPD Allergic rhinitis Restrictive lung disease PAH |
|
|
Name some infections of the lung: |
Tuberculosis Pneumonia (bacterial, fungal, viral) |
|
|
Name some "transformation" conditions of the lung: |
NSCLC (adenocarcinoma, squamous cell) SCLC |
|
|
What are the two major divisions of the pulmonary system? |
1. Upper respiratory tract 2. Lungs |
|
|
What agents are used to treat the upper respiratory tract (4)? |
1. Mucolytics (never enter body) 2. Vasoconstrictors (alpha-1 agonists) 3. Drugs acting in the CNS cough center 4. Antihistamines (1st and 2nd gen)
|
|
|
What are three major divisions of lung diseases? |
1. Obstructive --> Asthma and COPD 2. Restrictive Lung Disease 3. PAH |
|
|
What two major types of drugs (and examples) can be used to treat restrictive and obstructive lung diseases? |
1. Anti-inflammatory (corticosteroids, LTAs, andenosine ant) 2. Bronchial tone (anticholinergic, adrenergics, adenosine ant) |
|
|
What major type of drug can by used to treat PAH ? |
1. Vascular tension --> Prostanoids, Endothelin antagonists, PDE-5 inhibitors |
|
|
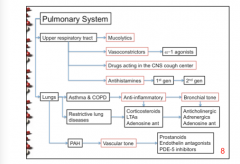
Summarize the past few slides! |
|
|
|
What are the two major types of pulmonary infections? What can pneumonia be broken down into? |
1. Pneumonia (fungal, viral, bacterial) 2. Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
|
|
What can be used to treat pneumonia? |
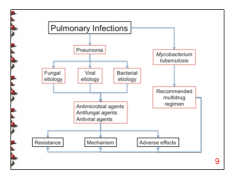
Antimicrobial Antifungal Antiviral |
|
|
Which lung cancer type (NSCLC or SCLC) does not currently have targeted therapy? |
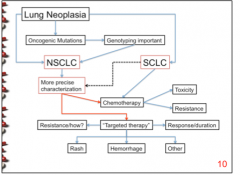
SCLC |

