![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
4 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What does the vascular system transport?
|
Transports water, minerals and sugars (does not use diffusion alone.
|
|
|
|
Xylem
|
Hollow narrow tube that transports water and minerals from the roots to the leaves of the plant. • Xylem made of vessel called xylem vessel elements, stacked end to end • Xylem cells are dead, with no cytoplasm or organelles and no end plates between the cells • Walls of the xylem contain lignin which adds strength to the xylem and keeps water inside • Water can pass to nearby xylem through pits in the xylem |
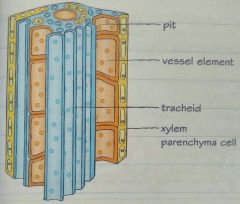
|
|
|
Phloem |
Transports sugars(usually sucrose) and other assimilates up and down the plant. • Made of cells called sieve tube elements, stacked end to end to make a narrow tube, with a sieve plate between them • Sieve plates contain many pores that allow sugars through • Phloem cells are living, but contain a thin layer of cytoplasm around the edge of the cell and few organelles • Each phloem cell is supported by a companion cell that loads sugars (mostly sucrose) into the phloem. Companion and phloem cells are linked by pores in the phloem wall called plasmodesmata
|

|
|
|
The role of companion cells in the phloem tissue
|
• To provide support for the phloem sieve tube elements • Lacks organelles, the companion cell with its nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, enzymes etc controls the movement of solutes and provides ATP for active transport in the sieve tube element |
|

