![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In what 3 different types of molecules can the -OH group occur?
|
1. Alcohols
2. Phenols 3. Carboxylic acids |
|
|
Alcohol
|

|
|
|
Carboxylic Acid
|
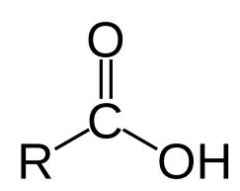
|
|
|
Phenol
|
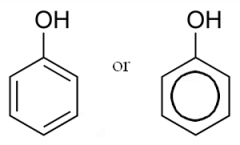
|
|
|
What is the test for a phenol?
|
When neutral iron (III) chloride solution is added to a phenol or its derivatives, a purple complex is formed.
|
|
|
Why are alcohols, phenols and carboxylic acids classed as weak acids?
|
In aqueous solution, they produce oxonium ions. (H3O+)
|
|
|
What is the order of acidic strength of water, alcohols, phenols and carboxylic acids?
|
Alcohol → Water → Phenol → Carboxylic acid
|
|
|
What determines the acidic strength of alcohols, phenols and carboxylic acids?
|
The strength of these compounds as acids can be explained by comparing the stability of the anion (R-O-).
|
|
|
Explain the relative acidic strengths of alcohols, phenols and carboxylic acids
|
The phenoxide ion C6H5OH(-) and carboxylate ion RCOO(-) are more stable than the hydroxide OH(-) and the ethoxide CH3CH2O(-) ions because the negative charge on the ion can be delocalised across several atoms. The equilibrium lies further to tthe right, so there is a higher concentration of H+ ions.
|
|
|
Reactions of alcohols, phenols and carboxylic acids with sodium hydroxide.
|
•Alcohol-No reaction
•Phenol- Reacts to form a salt & water •Carboxylic acid- Reacts to form a salt & water |
|
|
Reactions of alcohols, phenols and carboxylic acids with sodium carbonate & other carbonates
|
•Alcohol-No reaction
•Phenol- No reaction •Carboxylic acid- Reacts to form a salt, water & CO2. Fizzes as CO2 is given off |

