![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
77 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the five neuronal pools responsible for stimulating or depressing parts of the brain or spinal cord? |

Central nervous system (CNS):
Brain and spinal cord ... Contains neural tissue, CT, and blood vessels Peripheral nervous system (PNS): All other nerves and sensors ... All neural tissue outside the CNS |
|
|
|
The peripheral nervous system consists of what two divisions? |
1 Afferent division: Brings info from receptors to CNS
sensory neurons are afferent neurons
unipolar structure
2 Efferent division:
Brings commands from CNS to effectors
motor neurons are efferent neurons |
|
|
|
The afferent division contains what two types of neurons? |
1 visceral sensory neurons: Monitor internal environment
2 somatic sensory neurons: Monitor external environment |
|
|
|
Efferent division breaks up into what two systems? |
1 somatic nervous system (SNS):
Contains somatic motor neurons (multipolar)
control skeletal muscle
voluntary and involuntary control
2 autonomic nervous system (ANS):
Visceral motor neurons
Control all else
Involuntary/subconscious control |
|
|
|
The autonomic nervous system separates into what two divisions? |
1 sympathetic division: Generally stimulating "fight or flight"
2 parasympathetic division: Generally relaxing "rest and digest" |
|
|
|
The CNS neuroglia cells consist of what four types? |
1 ependymal cells (CSF) 2 astrocytes (structure) 3 oligodendrocytes (myelination) 4 microglia (phagocytosis) |
|
|
|
PNS neuroglia contain what two types? |
1 Satellite cells (regulate environment, support)
2 Schwann cells (myelination) |
|
|
|
Neural tissue contains what two kinds of cells? |
1 neurons: cells that send and receive signals
2 Neuroglia (glial cells): Cells that support and protect neurons |
|
|
|
What are the organs of the nervous system? |
1 Brain 2 Spinal cord 3 sensory receptors of sense organs (eyes, ears, etc.) 4 nerves (connection nervous system with other systems) |
|
|
|
What are the three functions of the central nervous system? |
1 sensory data from inside outside body
2 Motor commands that control the activities of peripheral organs (ex: skeletal muscles)
3 higher functions of brain (intelligence, memory, learning and emotion) |
|
|
|
What are the two functions of the peripheral nervous system? |
1 deliver sensory info to the CNS
2 Carry motor commands to peripheral tissues and systems |
|
|
|
What are the two types of nerves? |
1 cranial nerves: connect to brain
2 spinal nerves: attached to spinal cord |
|
|
|
How is information collected and how are commands carried out? |
Receptors: are sensory structures that detect changes or respond to stimuli (example: eyes, neurons, specialized cells)
Effectors: respond by doing something (example: cells and organs) |
|
|
|
What are the four structural classifications of neurons? |
1 Anaxonic neurons: brain and sense organs
2 bipolar neurons: special sensory organs (ex: smell)
3 unipolar neurons: sensory neurons of PNS
4 Multi polar neurons: common in the CNS, includes all skeletal muscle motor neurons |
|
|
|
What are the three functional classifications of neurons? |
1 sensory neurons: afferent neurons of PNS
2 Motor neurons: efferent neurons of PNS
3 Interneurons: association neurons |
|
|
|
What are the three types of sensory receptors? |
1 Interoceptors: Monitor internal systems (digestive, respiratory, cardiovascular, urinary, reproductive) ... Internal senses (taste, deep pressure, pain)
2 Exteroceptors: External senses (Touch, temperature, pressure) ... Distance senses (sight, smell, hearing)
3 Proprioceptors: Monitor position and movement (skeletal muscles and joints) |
|
|
|
True or False: Neuroglia are found in both the CNS and PNS? |
True
All ependymal cells, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, satellite cells and Schwann cells are considered neuroglia |
|
|
|
What is transmembrane potential? |
The potential energy stored across the membrane (Think sodium and potassium) |
|
|
|
What are the five main membrane processes in neural activities? |
1 resting potential: of the membrane potential of resting cell
2 graded potential: temporary, localize change and resting potential caused by stimulus
3 action potential: an electrical impulse triggered by graded potential and propagate along surface of axon to synapse
4 synaptic activity: release neurotransmitters at presynaptic membrane and produces graded potential's and postsynaptic membrane
5 information processing: response of postsynaptic cell |
|
|
|
What is equilibrium potential? |
The membrane potential at which there is no net movement of a particular ion across a cell membrane |
|
|
|
Sodium channels are classified as passive or active. What are the differences between passive and active channels? |
1 passive channels (leak channels): are always open
2 Active channels (gated channels): Open and close in response to stimuli ... At resting potential, most gated channels are closed
3 states: 1 closed capable of opening 2 open (activated) 3 incapable of opening (inactivated)
|
|
|
|
What are the three classes of gated channels? |
1 chemically gated channels: Open and close a response to specific chemicals (ACh)
2 voltage gated channels: Open and close in response to changes in transmembrane potential
3 mechanically gated channels: Open and close in response to pressure |
|
|
|
What are the three groups of axons? |
1 Type A fibers: Myelinated, large diameter, high speed ... Carry info like position, balance, touch, and motor impulses to/from the CNS (instant message)
2 Type B fibers: Myelinated, medium diameter, medium speed… Carry intermediate signals like sensory info and commands for a peripheral effectors (e-mail)
3 Type C fibers: Unmyelinated, small diameter, slow speed… Carry slower info like commands for glands (snail mail) |
|
|
|
What are the two types of synapses? |
1 electrical synapses: direct physical contact between cells
2 Chemical synapses: Signal transmitted across a gap by chemical neurotransmitters (most common) |
|
|
|
What are the two classes of neurotransmitters? |
1 excitatory neurotransmitters: Cause depolarization of postsynaptic membrane's and promote action potential's
2 Inhibitory neurotransmitters: Cause hyperpolarization a postsynaptic membranes and suppress action potentials |
|
|
|
True or false: the effect of a Nero transmitter depends on the receptor NOT on the neurotransmitter? |
True |
|
|
|
What are the five most important neurotransmitters? |
1 norepinephrine 2 dopamine 3 serotonin 4 GABA 5 neuromodulators |
|
|
|
What are postsynaptic potentials? |
1 excitatory postsynaptic potential: Grated depolarization of postsynaptic membrane
2 inhibitory postsynaptic potential: Graded hyperpolarization a postsynaptic membrane |
|
|
|
What is the difference between temporal and spatial summation? |
1 temporal summation: multiple times… Rapid, repeated stimuli at one synapse
2 spatial summation: multiple locations… Many stimuli, arrive at multiple synapses |
|
|
|
What are the two axoaxonic synapses? |
1 presynaptic inhibition: decreases neurotransmitter release
2 presynaptic facilitation: Increases neurotransmitter release |
|
|
|
What are the main parts of a neuron? |
Cell body axon - transmit the impulse AWAY from the cell body dendrites - transmit the impulse TOWARD the cell body |
|
|
|
What are the major parts of the brain? |
Cerebrum - associated with movement and sensory input
cerebellum - responsible for muscular coordination
Medulla oblongata - Controls many vital functions such as respiration and heart rate |
|
|
|
The spinal cord is approximately how long? And extends from what to what? |
18 inches long
Extends from the base of the skull (foramen magnum) to the first or second lumbar vertebra |
|
|
|
The spinal cord is approximately how long? And extends from what to what? |
18 inches long
Extends from the base of the skull (foramen magnum) to the first or second lumbar vertebra |
|
|
|
How many pairs of spinal nerves exit the spinal cord? |
31 |
|
|
|
What are the simple (spinal) reflexes? |
Reflexes in which nerve impulses travel to the spinal cord only and do not reach the brain |
|
|
|
What is the difference between afferent and efferent fibers? |
1 Efferent fibers: Motor fibers, carry away
2 Afferent fibers: Sensory fibers, toward |
|
|
|
The cell bodies of neurons farm functional groups called? |
Nuclei
2 types
1 sensory nuclei: connect to preference receptors
2 Motor nuclei: connect to peripheral effectors |
|
|
|
What is the difference between ascending and descending tracts? |
1 ascending tracts: carries sensory information toward the brain
2 descending tracts: Carry motor commands to the spinal cord |
|
|
|
What are dermatomes? |
Bilateral regions of the skin monitored by a specific pair of spinal nerves… Shingles produces a rash that corresponds to the dermatome of the affected sensory nerve |
|
|
|
What are the five neuronal pools responsible for stimulating or depressing parts of the brain or spinal cord? |
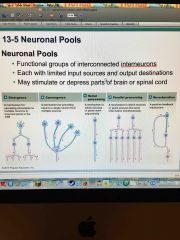
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What are reflexes? |
Rapid, automatic responses coordinated within the spinal cord through neurons |
|
|
|
What are the five steps in a neural reflex? |
1 arrival of stimulus, activation of receptor: physical or chemical changes
2 activation of sensory neuron: graded depolarization
3 information processing by postsynaptic cell: triggered by neurotransmitters
4 activation of motor neuron: action potential
5 responsive peripheral effector: triggered by neurotransmitters |
|
|
|
Reflexes are developed through what two ways? |
1 innate reflexes: Basic neural reflexes, formed before birth
2 acquired reflexes: rapid, automatic… Learned motor patterns (ex: driving a car) |
|
|
|
What are the difference between somatic and visceral reflexes? |
1 somatic reflexes: involuntary control of muscular system
2 visceral reflexes: control systems other than muscular system |
|
|
|
What are the five neuronal pools responsible for stimulating or depressing parts of the brain or spinal cord? |
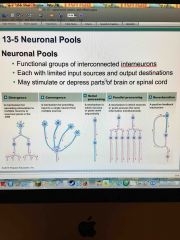
|
|
|
|
What are reflexes? |
Rapid, automatic responses coordinated within the spinal cord through neurons |
|
|
|
What are the five steps in a neural reflex? |
1 arrival of stimulus, activation of receptor: physical or chemical changes
2 activation of sensory neuron: graded depolarization
3 information processing by postsynaptic cell: triggered by neurotransmitters
4 activation of motor neuron: action potential
5 responsive peripheral effector: triggered by neurotransmitters |
|
|
|
Reflexes are developed through what two ways? |
1 innate reflexes: Basic neural reflexes, formed before birth
2 acquired reflexes: rapid, automatic… Learned motor patterns (ex: driving a car) |
|
|
|
What are the difference between somatic and visceral reflexes? |
1 somatic reflexes: involuntary control of muscular system
2 visceral reflexes: control systems other than muscular system |
|
|
|
What is the difference between the monosynaptic reflex and the polysynaptic reflex? |
1 monosynaptic reflex: sensory neuron synapses directly onto motor neuron
2 Polysynaptic reflex: at least one interneuron between sensory neuron and motor neuron |
|
|
|
What are three special types of reflexes? |
1 postural reflexes: maintain normal upright posture
2 tendon reflex: prevents skeletal muscles from developing too much tension
3 with drawl reflexes: move body part away from stimulus (ex: pain or pressure) |
|
|
|
What is the cerebrum responsible for? |
Conscious thought processes
memory storage and processing
conscious and subconscious regulation of skeletal muscle contractions |
|
|
|
What is the cerebrum responsible for? |
Conscious thought processes
memory storage and processing
conscious and subconscious regulation of skeletal muscle contractions |
|
|
|
What is the diencephalon responsible for? |
*** Diencephalon is made up of two parts: the thalamus and hypothalamus |
Thalamus: Relay and processing centers for sensory information
Hypothalamus: Centers controlling emotions, autonomic functions, and hormone production |
|
|
What is the cerebrum responsible for? |
Conscious thought processes
memory storage and processing
conscious and subconscious regulation of skeletal muscle contractions |
|
|
|
What is the diencephalon responsible for? |
*** Diencephalon is made up of two parts: the thalamus and hypothalamus |
Thalamus: Relay and processing centers for sensory information
Hypothalamus: Centers controlling emotions, autonomic functions, and hormone production |
|
|
What is the mid brain responsible for? |
Processing of visual and auditory date
generation of reflexive somatic motor responses
Maintenance of consciousness |
|
|
|
What is the cerebrum responsible for? |
Conscious thought processes
memory storage and processing
conscious and subconscious regulation of skeletal muscle contractions |
|
|
|
What is the diencephalon responsible for? |
*** Diencephalon is made up of two parts: the thalamus and hypothalamus |
Thalamus: Relay and processing centers for sensory information
Hypothalamus: Centers controlling emotions, autonomic functions, and hormone production |
|
|
What is the mid brain responsible for? |
Processing of visual and auditory date
generation of reflexive somatic motor responses
Maintenance of consciousness |
|
|
|
What is the pons responsible for? |
Relays sensory information to cerebellum and thalamus
Subconscious somatic and visceral motor centers |
|
|
|
What is the cerebrum responsible for? |
Conscious thought processes
memory storage and processing
conscious and subconscious regulation of skeletal muscle contractions |
|
|
|
What is the diencephalon responsible for? |
*** Diencephalon is made up of two parts: the thalamus and hypothalamus |
Thalamus: Relay and processing centers for sensory information
Hypothalamus: Centers controlling emotions, autonomic functions, and hormone production |
|
|
What is the mid brain responsible for? |
Processing of visual and auditory date
generation of reflexive somatic motor responses
Maintenance of consciousness |
|
|
|
What is the pons responsible for? |
Relays sensory information to cerebellum and thalamus
Subconscious somatic and visceral motor centers |
|
|
|
What is the Medela oblongata responsible for? |
Relays sensory information to thalamus and to other portions of the brain stem
Autonomic centers regulation of visceral function (cardiovascular, respiratory, and digestive system activities) |
|
|
|
What is the cerebellum responsible for? |
Coordinates complex somatic motor patterns
Adjusts output of other somatic motor centers in brain and spinal cord |
|
|
|
The hypothalamus contains what structures? |
Mammillary bodies: processes all factory and other sensory information, control reflex eating movements (ex: chewing)
infundibulum |
|
|
|
What is the limbic system? |
A functional grouping that...
establishes emotional states
Links conscious, intellectual functions of cerebral cortex with unconscious and autonomic functions of brain stem
Facilitates memory storage and retrieval |
|
|
|
What are the four lobes of the brain and what are their responsibilities? |
1 frontal lobe: primary motor cortex and somatic motor association area
2 parietal lobe: primary sensory cortex and somatic sensory association area
3 occipital lobe: visual association area and visual cortex
4 temporal lobe: auditory association area, auditory cortex and olfactory cortex |
|
|
|
What do the left and right hemispheres of the brain control? |
Left hemisphere: Reading, writing, math, decision making, speech and language
Right hemisphere: senses (Touch, smell, sight, taste, feel) and recognition (faces, voice inflections) |
|
|
|
The somatic nervous system versus the autonomic nervous system? |
Somatic nervous system: operates under conscious control, seldom affects long-term survival, SNS controls Skelton muscles
Autonomic nervous system: operates without conscious construction, Annas controls visceral effectors, coordinate system functions = "life support" |
|
|
|
The autonomic nervous system has two divisions: sympathetic division and parasympathetic division. What are the differences? |
Sympathetic division: increases alertness, metabolic rate, and muscular abilities… Fight or flight during exertion, stress or emergency
Parasympathetic division: reduces metabolic rate and promotes digestion… Rest and digest during resting conditions |
|
|
|
What are seven responses to increased sympathetic activity? |
1 heightened mental alertness 2 increased metabolic rate 3 reduced digestive and urinary functions 4 Energy reserves activated 5 increased respiratory rate and respiratory passageways dilate 6 increased heart rate and blood pressure 7 sweat glands activated |
|
|
|
What are five responses to increased parasympathetic activity? |
1 decreased metabolic rate 2 decreased heart rate and blood pressure 3 increased secretion by salivary and digestive glands 4 increase motility and blood flow in digestive tract 5 urination and defecation stimulation |
|
|
|
Pre-ganglionic neurons versus ganglionic neurons? |
Preganglionic: stimulation leads to ACh release at synapses with ganglionic neurons… Excitatory effect on ganglionic neurons
Ganglionic neurons: release various neurotransmitters that target specific target organs... Release NE |
|

