![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name 5 types of bone... |
Long Bone (Humerous/ Femur) Flat Bone (Sternum / Scapula) Short Bone (Trapezoid) Irregular Bone (vertebra) Sesamoid Bone (patella) |
|
|
What does Osteogenesis mean? |
Formation of bone |
|
|
What are the four phases of regeneration? |
Fracture Hematoma: Inflammtoryresponse initiated. Phagocytes(neutrophils and macrophagesremove dead cells
Fibrocartiliaginous CallusFormation: Collagen fibers &cartilage bridge the gap Bony Callus Formation:Oesteoblast cells start to calcifycartilage Bone Remodelling: Reabsorptionof the callus. |
|
|
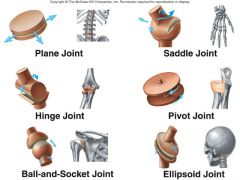
What are the 6 types of joint? |
|
|
|
Examples of joints |
pivot = axis/atlas in neck ball and socket = shoulder / hip saddle = thumbs Ellipsoid = wrist Hinge = finger / knee Gliding plate = vertebrae |
|
|
Three types of Muscle |
Cardiac muscle: has it own built in autoryhmicity Skeletal Muscle: Attached to, and responsible for movement ofbone. Microscopic striated bands. Electrically excitable Smooth Muscle: Nonstriated making upwalls of organs ie Bloodvessels |
|
|
Glenoidhumeral joint |
The shoulder joint. |
|
|
Bones |
206 Axial - trunk Appendicular - limbs and pelvis |
|
|
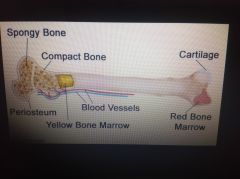
Bone structure |
|
|
|
Bone structure further |
In long bones red marrow concentrated at the ends (epiphyses) (diaphysis is central portion of the long bone). Yellow marrow inside the medullary cavity. Spongy bone - trabeculae |
|
|
Osteons |
Cylindrical units of bone made up of many lamellae. Resists torsion. Inside each Osteons are nerves and blood vessels. Osteocytes sit between lamellae. Osteocytes monitor the bone matrix and control osteoblasts and osteoclasts. |
|
|
Osteoblasts |
Bone makers Forms bone by secreting collagen and minerals making calcium phosphate on cartilage matrix to make bone. |
|
|
Osteoclasts |
Bone breakers Allows for bone regeneration / remodelling. Dissolve the calcium phosphate then they apoptose to allow for osteoblasts to come in and rebuild the bone. Stress from exercise will cause this process yo increase, strengthening bone over time. |
|
|
Ossification |
Building bone from cartilage / membranous tissue. The process starts from an ossification centre. Osteoblasts then start to build the bone by calcification. Then woven with blood vessels |
|
|
Osteogenesis |
Making bone |
|
|
synovial joint |
articulating capsule is the surrounding membrane Filled with synovial fluid Accessory ligaments hold this together/ |
|
|
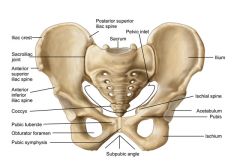
Pelvis |
|
|
|
Burns |
Local response - inflammatory response, infection, tissue, nerve and cell damage Systemic response - CV changes, Resp changes, metabolic changes, immunological changes |
|
|
time critical burns |
more than 15% in adults More than 10 % in kids |
|
|
Estimating burn size |
Rule of 9s, Lund and Browder chart, mersy burns Parkland fluid formula - to estimate fluid replacement. |

