![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
93 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
how long do symptoms of depression have to last to be considered major depressive disorder?
|
2 weeks or longer
|
|
|
when a patient presents with anxiety and/or somatic complaints (pain, nausia, etc.) what type of depression might they be suffering from?
|
masked depression
|
|
|
when is suicide most likely in a depressed patient?
|
in severe cases where the patient begins to lose touch with reality, experiences delusions, and can have hallucinations
|
|
|
who is more likely to become depressed? Men or women?
|
women are 2x more likely to become depressed (20-25%) as compared to men (8-12%)
|
|
|
what age group is most likely to get depression?
|
40's
|
|
|
what is the time frame of the untreated major depressive episode?
|
6-13 months
|
|
|
when is risk of reccurrence greatest for depression?
|
within 1 year of the episode
|
|
|
what are the chances a patient with one depressive episode will have another?
|
50%
|
|
|
what percentage of depressed patients think about attempting suicide?
|
66%
|
|
|
what percentage of depressed patients actually complete suicide?
|
10-15%
|
|
|
when dealing with a depressed patient what is the single most important question to ask?
|
are you thinking about suicide
|
|
|
who is most likely to commit suicide?
|
elderly males
|
|
|
when in a depressed patient most likely to commit suicide?
|
when they first start getting better, they have more energy and drive, but still the depressed feelings which allows them to actually follow through with ideation
|
|
|
what percentage of patients that complain of 9 or more physical symptoms have depression?
|
60%
|
|
|
an elderly person in a nursing home who appears cognitively impaired may not be suffering from dementia, but actually this type of depression?
|
pseudodementia
|
|
|
Name the type of depression?
-anhedonia and/or loss of -decreased reactivity to pleasurable stimuli -distinct quality of depressed mood -depression worse in a.m. -early morning awakening -psychomotor agitation or retardation -significant weight loss -excessive guilt |
Depression with melancholic features
|
|
|
Name the type of depression?
-Preserved mood reactivity -Reversed neurovegetative signs -Leaden paralysis -Rejection sensitivity |
Depression with atypical features specifier
|
|
|
Name the type of depression?
-When severe, patient can experience psychosis -Medical emergency if experiencing command hallucinations, or if not attending to basic human needs |
Depression with psychotic features specifier
|
|
|
Name the type of depression?
-Stupor -Mute/Very Negative -Lays around hardly moving |
Depression with catatonic features specifier
|
|
|
Name the type of depression?
-Onset of episode within four weeks parturition -Medical emergency in severe cases, especially if psychotic -Examine with the baby, and other family members |
Depression with postpartum onset specifier
|
|
|
Name the type of depression?
-Recurrent episodes of depression with a pattern on onset at same time of year -Full remissions occur at a characteristic time of year |
Depression with seasonal pattern specifier
|
|
|
Name the type of depression?
-Symptoms persist for at least 2 years |
Depression with chronic specifier
|
|
|
what percentage of women experience post-partum depression?
|
10%
|
|
|
what is a big difference between the typical "baby blues" that a lot of pregnant women experience and the true post-partum depression?
|
women experiencing the baby blues do not contimplate suicide
|
|
|
whats the "big picture" difference between hypermanic and hypomanic states?
|
both present with similar symptoms, but hypomanic is simply a lesser degree than hypermanic meaning hospitalization or interference with work is unlikely
|
|
|
what are the 4 types of bipolar disorders?
|
1. Type I
2. Type II 3. Mixed 4. Rapid Cycle |
|
|
which type of bipolar disorder is this?
Manic episode with or without a history of depressive episodes |
type I
|
|
|
which type of bipolar disorder is this?
Hypomanic episodes with history of major depressive episodes |
type II
|
|
|
which type of bipolar disorder is this?
Features of both depression and mania or hypomania present at the same time |
mixed
|
|
|
which type of bipolar disorder is this?
Four or more mood episodes are present within a year More common in females |
rapid cycling
|
|
|
What psychiatric disorder does this describe?
-Little sleep -Grandiosity -Pressured speech -Physical restlessness -Half present with psychotic symptoms |
Bipolar disorder
|
|
|
how much time must elapse for a diagnosis of a manic episode?
|
1 week
|
|
|
how much time must elapse for a diagnosis of a hypomanic episode?
|
4 days
|
|
|
how much time must elapse with both major depressive and manic episodes occuring everyday for mixed bipolar disorder to be diagnosed?
|
1 week
|
|
|
what is the median age of onset for bipolar disorder?
|
18-21
|
|
|
how long will an untreated bipolar episode last?
|
3 months
|
|
|
what is the recurrence percentage with bipolar disorder?
|
90%
|
|
|
why can bipolar disorder be very hard to diagnose?
|
long lag time between symptoms onset and treatment/hospitalization (5-10)
|
|
|
what systemic factor can lead to bipolar disorder?
|
hyperthyroidism
|
|
|
what specific drug class is associated with bipolar disorder?
|
corticosteroids
|
|
|
how long does it take to make a diagnosis of dysthymic disorder?
|
2 years of depressed mood
|
|
|
who is affected more by bipolar disorder, men or women?
|
both are equally represented
|
|
|
who is more likely to be affected by dysthymic disorder, men or women?
|
women
|
|
|
what is the term used to describe the 40% of MDD patients who also could be classified at dysthymic?
|
double depressed
|
|
|
what psychiatric disorder does this describe?
A chronic mood disorder of at least two years duration with periods of hypomania and depression (that does not meet criteria for major depression) - with no symptom free period of more than two months. |
Cyclothymic Disorder (mild form of bipolar type II)
|
|
|
30% of patients with Cyclothymic Disorder have a family history of what other psychiatric disorder?
|
bipolar type I
|
|
|
what drug type is most effective in patients with Cyclothymic Disorder?
|
antimanic
|
|
|
what psychiatric disorder does this describe?
A reaction (depression) to an identifiable psychosocial stressor within 3 previous months, resulting in impairment of occupational or social functioning |
Adjustment Disorder with Depressed Mood
|
|
|
How long do symptoms of Adjustment Disorder with Depressed Mood persist?
|
Symptoms do not persist beyond 6 months
|
|
|
while bereavement can present very similarly to a major depressive episode, what two key features of major depression are lacking in bereavement?
|
1. guilt or feelings of worthlessness
2. Suicidal thoughts |
|
|
normal bereavement with severe symptoms should not last longer than what time frame?
|
2 months
|
|
|
These symptoms describe which psychiatric disorder?
-Depressed mood -Anxiety or tension -Affective lability -Decreased interest in usual activities -Difficulty concentrating -Lethargy -Appetite changes -Hypersomnia or insomnia -Feeling of being overwhelmed -Physical symptoms |
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder
|
|
|
describe when the symptoms of Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder develope?
|
the begin before menses, wane during menses, and are absent post-menses
|
|
|
how long does it take to confirm Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder diagnosis?
|
1 year of consistent episodes
|
|
|
how can PMDD be differentiated from PMS symptoms?
|
PMDD symptoms are much more severe and often can interfere with baseline functioning and relationships
|
|
|
what type of drugs are most effective in treating PMDD resulting in a reduction of symptoms in 60% of cases?
|
SSRI's
|
|
|
give the percentage likelyhood for developing major depressive disorder for
1. Monozygotic twins 2. Dizygotic twins 3. First-degree relatives |
1. 50%
2. 15-25% 3. 10-20% |
|
|
loosing a parent when below the age of ___ is a predisposing factor for depression?
|
11
|
|
|
what are the three NT systems implicated in the cause of major depressive disorder?
|
1. Norepinephrine
2. Serotonin 3. Dopamine |
|
|
Alertness, Concentration, and Energy are all regulated by what NT?
|
Norepinephrine
|
|
|
Obsessions, compulsions, and memory are all regulated by what NT?
|
Serotonin
|
|
|
Pleasure, Reward, Motivation/Drive are all regulated by what NT?
|
Dopamine
|
|
|
Appetite, Sex, and Agression are all regulated by what NT?
|
Serotonin and Dopamine
|
|
|
Anxiety, Impulse, and irritability are all regulated by what NT?
|
Serotonin and Norepinephrine
|
|
|
Attention is regulated by what NT?
|
Norepinephrine and Dopamine
|
|
|
is problems with the serotonin system more likely a dysregulation of receptors in post-synaptic membrane or a depletion of the serotonin NT (unknown cause)?
|
dysregulation of receptors
|
|
|
where might grey matter be lacking in the depressed brain?
|
subgenual prefrontal cortex
|
|
|
to what brain area is there 50% increased blood flow in the depressed brain?
|
the amygdala
|
|
|
describe how the use of cellular mechanisms is currently being researched to improve depression?
|
-Increased intersynaptic levels of NT's
-Increased CREB expression -Increased BDNF -Regulate neurogenesis, thus structural brain changes |
|
|
describe the likelyhood of this person developing bipolar if...
1. Monozygotic twin has it 2. Dizygotic twin has it 3. First degree relative has it |
1. 80%
2. 10-14% 3. 4-18 times normal population |
|
|
what is the single most effective treatment for major depression?
|
electroconvulsive therapy
|
|
|
what patients will most likely require electroconvulsive therapy?
|
extremely psychotic or suicidal patients
|
|
|
what are the 5 main antidepressent medications?
|
1. Selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors
2. Dual serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors 3. Tricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants 4. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors 5. Sympathomimetics |
|
|
how long does medication need to be at therapeutic levels for its effects to become evident?
|
4 weeks
|
|
|
after remission of symptoms how long should patients continue on there antidepressent medication?
|
1 year
|
|
|
why is it important to perscribe minimum quantities of an antidepressent medication?
|
suicidal patients may use medication to OD (esp. tricyclics)
|
|
|
what are the 5 SRI's we have to know?
|
1. flouxetine
2. sertraline 3. paroxetine 4. fluvoxamine 5. citalopram |
|
|
what drug does this describe?
is a mildly stimulating antidepressant and is particularly useful in patients who have had sexual impairment from other drugs. It is unique in having effects on dopamine neurotransmission. There is a very low incidence of sexual dysfunction, and is weight neutral. |
Bupropion
|
|
|
what drug does this describe?
is a selective inhibitor of serotonin in higher doses and affects norepinephrine reuptake. Insomnia, nervousness and nausea are common side effects. Diastolic blood pressure can be elevated, thus requiring the monitoring of blood pressure |
Venlafaxine
|
|
|
what drug does this describe?
is an alpha-2adrenegic antagonist that enhances noradrenergic neurotransmission. Additionally, increases transmission of serotonin and is a 5HT2A and 5HT3 blocker. Marked sedation and weight gain (antihistamine effects) are common, usually decreasing after the first weeks of treatment and at higher doses, which may provide more activation due to greater noradrenergic enhancement. There is a low incidence of sexual dysfunction. |
Mirtazapine
|
|
|
phenelzine and tranylcypromine are examples of what type of drug?
|
MAO inhibitors
|
|
|
what are three special considerations to make when using MAOI's?
|
1. Tyramine free diet
2. Orthostatic hypotension is common 3. Coadministration of epinephrine, ephedrine, meperidine, and SSRIs can be life threatening |
|
|
what psychotherapy does this describe?
The main goal is to link the patient’s past experience of loss or guilt to current life conflicts that recreate earlier feelings of abandonment or unworthiness. The therapist examines the patient’s personality and life-long habits of thought, feelings or behaviors. |
Psychodynamic Psychotherapy
|
|
|
what psychotherapy does this describe?
Based on the theory that negative perceptions of oneself and the environment causes depression. The therapist teaches the patient how to systematically monitor the thoughts that accompany depressed feelings, examining automatic thoughts. The goal is to develop new cognitive strategies to alter the negative perception of self. |
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
|
|
|
what psychotherapy does this describe?
The premise is that those patients’ painful social experiences and troubled interpersonal relationships contribute to depression. The goal is to develop better strategies for coping effectively with interpersonal problems. |
Interpersonal Psychotherapy
|
|
|
which antidepressent drug should not be used in women of child-bearing age?
|
valproic acid
|
|
|
which drug has the best efficacy in treating fast cycling bipolar disorder?
|
valproic acid
|
|
|
what is the safest treatment for a pregnant woman for major depression?
|
electroconvulsant therapy
|
|
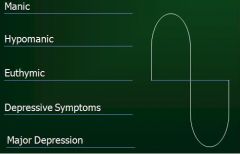
What disorder does this represent?
|
Bipolar Disorder Type I
|
|

what psychiatric disorder does this represent?
|
bipolar type II
|
|

what psychiatric disorder does this represent?
|
Cyclothymic Disorder
|
|

What psychiatric disorder does this represent?
|
Dysthymic Disorder
|
|
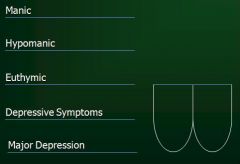
What psychiatric disorder does this represent?
|
Major Depression Disorder
|

