![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Elements of Economic Systems
|
Ownership of Factors of Production
Methods used to Motivate, Coordinate, and Direct Economic Activity; |
|
|
The Market System
|
Capitalism
Pure Capitalism - Laissez-Faire: limits government's role to protecting private property and establishing an environment appropriate to the operation of market system |
|
|
SIMILARITIES
-Specialization & Division of Labor; -Importance of technological advancement & capital goods; -Use money; -Strive for progress + higher living standards; -Have issues with environment; |
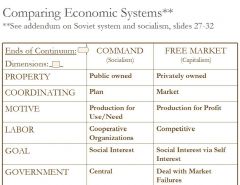
Free Market vs. Command System
|
|
|
Five Fundamental Questions
1. What goods will be produced? 2. How will goods be produced? 3. Who will get the output? 4. How will the system accommodate change? 5. How will the system promote progress? |
1. Consumer sovereignty; Dollar votes;
2. Available technology; Prices of needed resources; 3. Consumers; 4. Guiding function of prices; 5. Technological advancement; Creative destruction; Capital accumulation. |
|
|
The Invisible Hand
|
FIRMS and RESOURCE SUPPLIERS further own self interest = further the interests of SOCIETY
-Efficiency: promotes efficient use of resources; -Freedom: emphasis on personal freedom; -Incentives: encourages skill acquisition, hard work and innovation; |
|
|
Circular Flow
Businesses --> Resource Market --> Households --> Product Market --> Businesses |
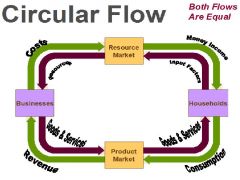
Circular Flow
|
|
|
GDP: Gross Domestic Product
|
All goods and services produced within the borders of a country in a given year.
|
|
|
GDY = Gross Domestic Income
|
All the money income earned by resource providers in a country per given year.
|
|
|
Positives of The Soviet Socialist System
|
-Turned agricultural society into industrialized economy;
-Continued to grow after the soviet union; -No unemployment of inflation; -Provided universal education, healthcare, and pensions; -Access to science and the arts; -More equitable distribution of income; |
|
|
Problems of Soviet Socialist System
|
-Lack of democracy;
-Purges of opponents; -Establishment of political prisons; -Forced collectivization of agriculture; -Production motivations; |
|
|
Characteristics of Market System
|
-Private Property;
-Freedom (Enterprise and Choice); -Self Interest; -Competition; -Specialization (Geographic and Division of Labor); -Use of Money; -Active but limited government role; -Technology and capital goods; |
|
|
Freedom of Enterprise
|
Ensures entrepreneurs and private businesses are free to obtain and use economic resources to produce their choice of goods and services and sell them on chosen markets.
|
|
|
Freedom of Choice
|
Enables owners to employ or dispose of their property and money as they see fit.
|
|
|
Specialization
|
Division of Labor
- Makes use of difference in ability; -Fosters learning by doing; -Saves time; Geographic Specialization -use of land and climate resources more effeciently |
|
|
Creative Destruction
|
The creation of new productions and production methods completely destroys the market positions of firms that are wedded to existing products and production methods.
|

