![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
80 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Complement System |
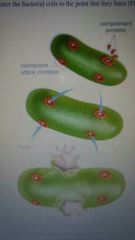
Often simply called complement, is composed of a number of blood plasma protiens designated by the letter C and a number. |
|
|
Cytokines |
They attract white blood cells.and monocytes. If neutrophils are overwhelmed they call them for reinforcements. |
|
|
Macrophages |
Monocytes become these they are even more powerful phagocytes than neutrophils. They can enlist the help of lymphocytes to carry out specific defence mechanisms. |
|
|
Antihistamines |
... |
|
|
Neutrophils |
... |
|
|
Lymph Nodes |
Occur along the lymphatic vessels, and filter lymph. Connective tissue forms a capsule and divides a lymph node in compartments. When the body is fighting infection the nodes can swell from 1/2 an inch to 2 inches in diameter. |
|
|
Lymphatic noduels |
Concentration of lymphoid tissue not surrounded by a capsule. Ex: the tonsils. |
|
|
Peyer patches |
Located in the intestinal wall an tissues within the appendix, a small extension of the large intestine, and encounter pathogens that enter the body by way of the intestinal tract. |
|
|
Lysozyme |
An antibacterial enzyme, contained in perspiration, saliva, and tears. |
|
|
Adaptive Immunity and Innate Immunity |
...pg134 |
|
|
Polypeptide |
...pg139 |
|
|
Antibody |
....pg139 |
|
|
Neutralization |
The process where antibodies react with viruses and toxins by coating them completely. |
|
|
Monoclonal Antibodies |
...pg 139 |
|
|
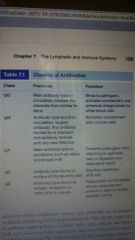
Classes of Antibodies |
|
|
|
Antigen binding sites |
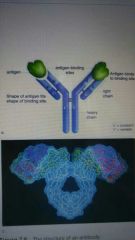
Pg 139 |
|
|
Lymphatic Vessels |
Thye form a one-way system of capillaries to vessels and, finally to ducts. These vessels take lymph to cardiovascular veins in the shoulders. These also take up excess interstital fluid. |
|
|
Lymph |
... |
|
|
Red Bone Marrow |
Produces all types of blood cells. In a child, most bones have red bone marrow; in an adult, it is limited to the sternum, the vertebrae, the ribs, and part of the pelvic girdle, and the upper parts of the humerus and femur. |
|
|
B and T cells |
Types of lymphocytes B matures in bone marrow and T in the thymus. If a B cell reacts with cells of the body it is removed in the bone marrow and does not enter the circulation. This ensuring that the B cells dont harm the body. |
|
|
Spleen |
It filters blood . it is the largest lymphatic organ, it is located in the upper left region of the abdominal cavity posterior to the stomach. |
|
|
Lymphatic organs |

|
|
|
Cell-mediated immunity |
Named for the action of T cells that directly attack diseased cells and cancer cells. |
|
|
Antigen-Presenting Cell (ACP) |
...pg 140 |
|
|
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) |
Pg.140 MHC1- MHC2- |
|
|
Human Leukocyte |
Human MHC protiens pg 140 |
|
|
Cytotoxic T (Tc) |
These have storage vacuoles containing perforins and storage vacoules containing enzymes and granzymes. When they bind to the virus-infected cells or tumor cells it releases preforin molecules. (SEE Cell-mediated immunity) |
|
|
Cell-mediated Immunity |
...pg 141 |
|
|
B Cells |
-antibody-mediated immunity gainst pathogens -Produced and mature in bone marrow - Directly recognize antigen and then undergi clonal selection. -Clonal expansion produces antibody secreting plasma cells as well as memory. |
|
|
T Cells |
T cells mature in the thymus help to fight infections. |
|
|
Passive immunity |
P 143 |
|
|
Interleukins |
Produced by various white blood cells. To help the body fight cancers ...1r3 |
|
|
Antibody Titer |
The amount of antibody present in a sample of plasma. |
|
|
Lymph |
A colorless liquid (creamy after eating because of its fatty content). It is found in the lymphatic vessels. |
|
|
Thymus |
Lymphatic organ located along the trachea behind the sternum , involved in the maturation of T lymphocytes in the thymus gland. Secretes hormones called thymosins which aid in the maturation of T cells and perhaps stimulate immune cells in general |
|
|
Spleen |
. |
|
|
Lobule |
. |
|
|
Lysozyme |
.. |
|
|
Hystimine |
. |
|
|
Cytokines |
. |
|
|
Macrophages |
. |
|
|
Complement system |
. |
|
|
Interferons |
. |
|
|
Antigens |
. |
|
|
Plasma cells |
. |
|
|
Characteristics of B cells |
1. Antibody-mediated immunity against pathogens 2. produced and mature in bone marrow. 3. directly recognize antigen and then undergo conal selection. 4. conal expansion creates antibody -secreting plasma cells as well as memory B cells. |
|
|
Plasma cells |
. |
|
|
Apoptosis |
. |
|
|
Antibody-mediated immunity |
. |
|
|
Structure of an antibody |
. |
|
|
Classes of antibodies |
p. 139 |
|
|
Monoclonal antibodies |
. |
|
|
T-cell receptors (TCR) |
. |
|
|
Antigen-presenting cell |
. |
|
|
Major h.istocompatibility complex |
. |
|
|
Human leukocyte antigens (HLA) |
. |
|
|
Cytotoxic T-cells |
. |
|
|
Cell-mediated immunity |
. |
|
|
Helper T-cells (Th) |
. |
|
|
Memory T-cells |
. |
|
|
Characteristics of T-cells |
1. Cell mediated immunity against virus-infected cells and cancer cells 2. produced in bone marrow, mature in thymus 3. antigen must be present in groove of an HLA (MHC) molecule 4. Cytotoxic T-cells destroy nonself antigen-bearing cells 5. Helper T-cells secrete cytokines that control the immune response |
|
|
Active immunity |
. |
|
|
Passive immunity |
. |
|
|
Immunizations |
. |
|
|
Vaccines |
. |
|
|
Antibody titer |
. |
|
|
Interleukins |
. |
|
|
Allergens |
. |
|
|
Immediate allergic response |
. |
|
|
Allergies |
. |
|
|
anaphylactic shock |
. |
|
|
Delayed allergic response |
. |
|
|
Immunosuppressive |
. |
|
|
Zenotransplantation |
. |
|
|
Severe combined immunodeficiency |
. |
|
|
Autoimmune disease |
. |
|
|
Rheumatoid arthritis |
/ |
|
|
Systemic lupus erythemosis |
. |
|
|
Myasthenia gravis |
. |
|
|
multiple sclerosis |
. |

