![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Define Anatomy |
Studies the structure of body parts and their relationship to one another. |
|
|
|
Define Physiology |
The function of the body. How the body works. G |
|
|
|
Gross/ macroscopic anatomy |
The study of large body structures visible to the naked eye. |
|
|
|
Greek meaning of anatomy |
To cut apart |
|
|
|
Subdivisions of gross anatomy. |
1. Regional anatomy 2. Systemic anatomy 3. Surface anatomy |
3 |
|
|
Define regional anatomy |
When all structures in a particular region of the body are examined at the same time. (Abdomen, leg, etc) |
|
|
|
Define systemic anatomy |
Study of the body system by system. ( ex. Cardiovascular system) |
|
|
|
Define surface anatomy |
The study of internal structures as they relate to the overlying skin surface. |
|
|
|
Define microscopic anatomy |
Study of structures too small to be seen by the naked eye. |
|
|
|
Divisions of microscopic anatomy |
1. Cytology 2. Histology |
2 |
|
|
Define cytology |
The study of cells |
|
|
|
Define histology |
The study of tissues. |
|
|
|
Define developmental anatomy |
Tracing structural changes that occur in the body over time. |
|
|
|
Example of developmental anatomy |
Embryology |
|
|
|
Define pathological anatomy |
Study of structural changes caused by disease |
|
|
|
Define radiographic anatomy |
Study of internal structures as visualized by x-rays and specialized scanning procedures. |
|
|
|
Define palpation |
Feeling organs with your hands |
|
|
|
Define auscultation |
Listening to organ sounds with a stethoscope |
|
|
|
Define renal physiology |
Kidney function and urine production. |
|
|
|
Define neurophysiology |
Explains the workings of the nervous system |
|
|
|
What is cardiovascular physiology |
The operation of the heart and blood vessels. |
|
|
|
Levels of Structural organization. |
1. Chemical level 2. Cellular level 3. Tissue level 4. Organ level 5. Organ system level 6. Organismal level |
6 |
|
|
What makes up the chemical level |
Atoms > molecules > organelles |
|
|
|
What makes up the cellular level? |
Cells consisting of organelles |
|
|
|
What are tissues? |
Groups of similar cells that share a common function. |
|
|
|
What are the four basic tissue types? |
1. Epithelium 2. Muscle 3. Connective tissue 4. Nervous tissue |
|
|
|
What is an organ? |
A structure comprised of at least two tissue types (more commonly 4) that performs a specific function for the body. |
|
|
|
What is an organ system? |
Organs that work together to accomplish a common purpose. |
|
|
|
Define catabolism |
Breaking down substances into their simpler building blocks |
|
|
|
Define anabolism |
Synthesizing more complex cellular structures from simpler substances. |
|
|

Name the system. |
Integumentary system |
|
|
|
List the organ systems within our body. |
1. Integumentary 2. Skeletal 3. Muscular 4. Nervous 5. Endocrine 6. Cardiovascular 7. Lymphatic system 8. Respiratory 9. Digestive 10. Urinary 11. Reproductive (m/f) |
|
|
|
What is the integumentary system? |
Forms the external body covering and protects deeper tissues. Synthesizes vitamin D Houses cutaneous (pain, pressure etc) receptors, and sweat and oil glands |
4 |
|
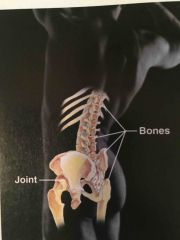
Name the system |
Skeletal |
|
|
|
Function of the skeletal system? |
1. Protects and supports body organs. 2. Provides framework the muscles use to cause movement. 3. Bones store minerals 4. Blood cells formed in the bones.
|
|
|
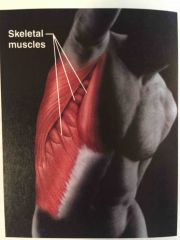
Name the system |
Muscular system |
|
|
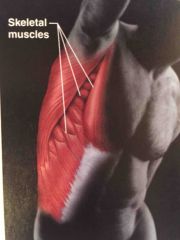
Name the system |
Muscular system. |
|
|
|
Function of the muscular system |
Allows manipulation of the environment, locomotion, and facial expression. Maintains posture Produces heat |
|
|
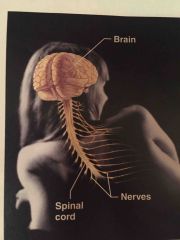
Name the system |
Nervous system |
|
|
|
Name the system |
Digestive system |
|
|
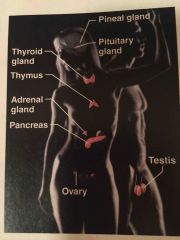
Name the system |
Endocrine system |
|
|
|
Name the system |
Urinary system |
|
|
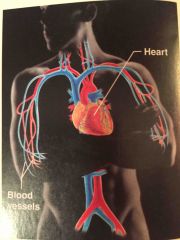
Name the system |
Cardiovascular system |
|
|
|
Name the system |
Nervous system |
|
|
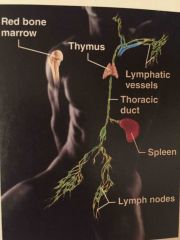
Name the system
|
Lymphatic system |
|
|
|
Name the system |
Endocrine system |
|
|
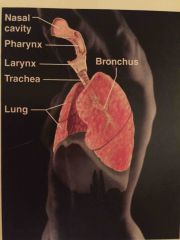
Name the system |
Respiratory system |
|
|
|
Name the system |
Cardiovascular system |
|
|
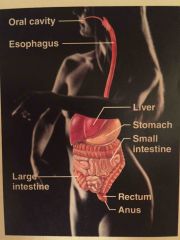
Name the system |
Digestive system |
|
|
|
Name the system
|
Lymphatic system |
|
|
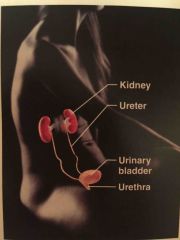
Name the system |
Urinary system |
|
|
|
Name the system |
Respiratory system |
|

