![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where is the heart located?
|
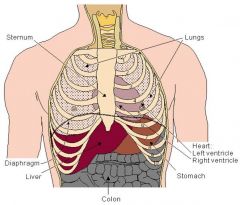
In the thorax, between the lungs. It is bounded by the diaphragm, lungs, esophagus, descending aorta and sternum.
|
|
|
What is the size of the heart?
|
About that of a fist, weight = 250-300g
|
|
|
What are the great vessels located above the heart?
|
The superior vena cava, the inferior vena cava, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein & aorta.
|
|
|
Name of the sac enclosed by the heart
|
Pericardium
|
|
|
Three layers of tissue that form the heart wall
|

1. outer layer = epicardium
2. middle layer = myocardium 3. inner layer = endocardium |
|
|
Internal cavity of the heart is divided into 4 chambers
|
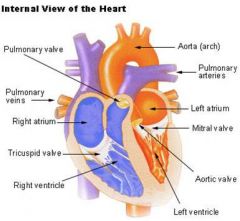
1. Right atria
2. Left atria 3. Right ventricle 4. Left ventricle |
|
|
systemic veins receive what from the right atrium?
|
deoxygenated blood
|
|
|
pulmonary veins receive what from the left atrium?
|
oxygenated blood
|
|
|
The right atrium contains...
|
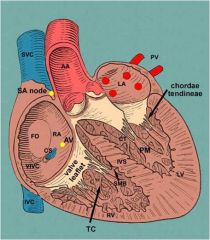
1. Fossa ovalis
2. Openings of CVC, IVC and the coronary sinus opening 3. SA 4. AV |
|
|
What is fossa ovalis?
|

An oval depression on the lower part of the septum of the right atrium; it is a vestige of the foramen ovale, the communication between the 2 atria of the foetal heart. If it remains open, then blood will shunt from left atrium to right because of pressure.
|
|
|
The Anterior surface shows parts of each of the four chambers of the heart.
|
1. Right Atrium
2. Left Atrium 3. Right Ventricle 4. Left Ventricle |
|
|
The three borders of the heart
|
1. Right border made up of the right atrium
2. Inferior border made up of the right atrium, right ventricle and left ventricle |
|
|
What makes the diaphragmatic surface of the heart?
|
The left and right ventricles.
|
|
|
What chamber makes up the base of the heart?
|
The left Atrium. When the body is in the supine position, the heart rests on its base and the apex of the heart (the tip of the left ventricle) projects up and to the left.
|
|
|
What are the two categories of Valves of the heart?
|

1. Atrioventricular valves
2. Semilunar valves |
|
|
What are the valves part of the Atrioventricular valves?
|
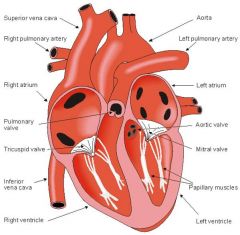
1. Tricuspid valve: between the right atrium and ventricle
2. Mitral valve: between the left atrium and ventricle |
|
|
What the valves part of the Semilunar valves?
|

1. Pulmonary valve: between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery
2. Aortic valve: in the outflow tract of the left ventricle (controlling flow to the aorta) |
|
|
What do the two categories of valve do?
|
When the ventricles contract, atrioventricular valves close to prevent blood from flowing back into the atria. When the ventricles relax, semilunar valves close to prevent blood from flowing back into the ventricles.
|
|
|
Normal path of blood flow?
|

1. Blood from systemic circuit
2. Venae cavae 3. Right atrium throw the tricuspid valve 4. Right ventricle throw the pulmonary valve 5. Pulmonary trunk 6. Pulmonary arteries 7. Alveolar capillaries (lungs) 8. Pulmonary veins 9. Left atrium throw mitral valve 10. Left ventricle throw the aortic valve 11. Aorta 12. Blood to systemic circuit |
|
|
Major vessels?
|
1. Superior & Inferior Vena Cava
2. Pulmonary trunk 3. Left & Right pulmonary arteries 4. Left Right Pulmonary veins 5. Aorta |
|
|
Why does the cardiac muscle has an extension network of blood vessels to bring oxygen to the contracting cells and to remove waste products?
|
The myocardium of the heart wall is a working muscle that needs a continuous supply of oxygen & nutrients to function with effficiency.
Source: The right and left coronary arteries, branches of the ascending aorta, supply blood to the walls of the myocardium, capillaries, coronary veins, coronary sinus, which opens into the right atrium. |
|
|
What are the different coronary arteries?
|

1. Aorta
2. Right coronary artery 3. Right marginal branch 4. Left main coronary artery 5. Left circumflex branch 6. Left anterior descending branch |
|
|
Where does the left coronary artery (LCA) supply blood to?
|
To the left ventricle and left atrium.
|
|
|
Where does the left anterior descending artery supply blood to?
|
To the front of the left side of the heart
It supplies a major portion of the ventricular septum, including the right and left bundle branches of the myocardial conduction system, and the anterior and apical portions of the left ventricle. |
|
|
Where does the circumflex branch supply blood?
|
To the lateral side and back of the heart
It supplies blood to the left ventricle and left atrium |
|
|
The right coronary artery (RCA) divides into:
|
1. The right posterior descending
2. The right marginal arteries |
|
|
Where does the right coronary artery supply to?
|
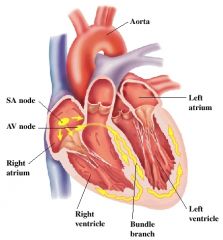
1. Right atrium
2. Right ventricle 3. SA Node 4. Bottom portion of both ventricles and back o the septum |
|
|
Innervations of the heart
|
COP (cardiac output)= SV (amount of blood pumped by each ventricle/min) X HR
|
|
|
What is controlled by the Autonomic Nervous system ( parasympathetic & sympathetic)?
|
The strength and frequency of the heart beat
|
|
|
The effect of the sympathetic nerves
|
1. At the SA node is an increase in Heart rate
2. The effect on the muscle is a progressive rise of pressure within the ventricle, thus increasing stroke volume |
|
|
What provides the parasympathetic control to the heart?
|
The Vagus
|
|
|
Why is the effect of the vagus at the SA node is the opposite of the sympathetic nerves?
|

1. It decreases the heart rate
2. It also decreases the excitability of the tissue around the AV node and this results in slower transmission Strong Vagal stimulation here may produce AV block |

