![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Include the: |
• Carpus (wrist) • metacarpus (Palm) • digits (fingers) composed of phalanges |
|
|
|
Carpus consists of: |
8 carpal bones attached by ligaments |
|
|
|
Metacarpus: |
- consists of 5 long bones, numbered 1-5 (lateral to medial) |
|
|
|
Each metacarpal |
• proximal base • shaft • distal |
|
|
|
Digits (phalanges) |
- 5 digits (fingers), numbered 1 to 5 (lateral to medial) |
|
|
|
-14 phalanges: |
• each fingers has 3 phalanges: proximal, middle, and distal • exception: the thumb (polled), which has 2 phalanges |
|
|
|
Cranial Bones |
• cranial bones • two 2 parietal bones • two 2 temporal bones • one 1 of each: frontal, occipital, sphenoid, and ethmoid bone |
|
|
|
Associated sutures: |
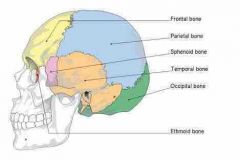
- coronal: b/t parietal / frontal bones - sagittal: b/t the two parietal bones - lambdoid: b/t - occipital / parietal bones - squamous: b/t - temporal/ parietal bones
B/t = between |
|
|
|
Cranium and cranial bone |
Cranium: • encases the brain • divided into a: Vault aka calvaria (skull cap) - top of the skull Base - the floor of the skull |
|
|
|
When the calvaria is removed |
And the brain lifted out of the skull, the cranial base is exposed |
|
|
|
Cranial base has 3 aspects: |
Anterior: contains the frontal bone Middle: part of temporal bone sphenoid bones Posterior: occipital bone |
|
|
|
Frontal bone |
• unpaired • forms the: - anterior part of the cranium - forehead - roofs of the orbits - most of the anterior cranial fossa - coronal suture (articulates w/the 2 parietal bones) |
|
|
|
Occipital Bone |
• unpaired • major landmarks: - foramen magnum - occipital condyles - external occipital protuberance (inion) - superior nuchal line - inferior nuchal line |
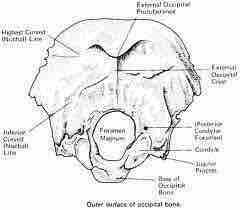
|
|
|
Facial bones |
• unpaired: - mandible - vomer • paired - maxilla - zygomatic - nasal - lacrimal - palatine - inferior nasal conchae |
|
|
|
Facial Bones |
Facial bones form: • the framework for the face • cavities for organs of taste, sight, and smell • openings for air and food • an anchor for the teeth • attachments for muscles |
|
|
|
Mandible |
• unpaired • "lower jaw bone" • largest & strongest facial bone • composed of a body, which forms the chin, & two rami (branches) |
|
|
|
Major landmarks |
• mandibular angle • mandibular notch • mandibular condyle (condylar process) • coronoid process |
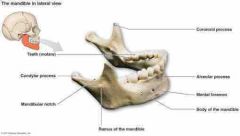
|
|
|
Vomer |
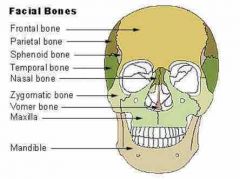
• Located within nasal cavity and form the part of nasal septum |
• located within the nasal cavity and forms part of the nasal septum |
|
|
Maxillary bones |
• paired • form the upper jaw • all facial bones articulate w/ the maxillae, except for the mandible |
|
|
|
• Major landmark |
• palatine processes • frontal processes • maxillary sinuses • zygomatic process • infraorbital foramen |
|
|
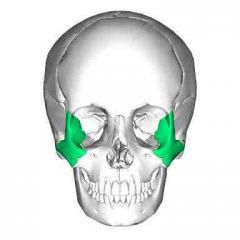
Zygomatic bones |
•form the prominence of the cheeks (a.k.a cheekbones) |
|
|
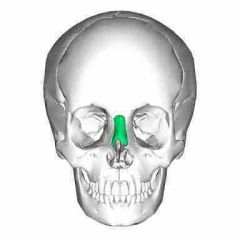
Nasal bones |
• form the bridge of the nose and attach to the nasal cartilage. |
|
|
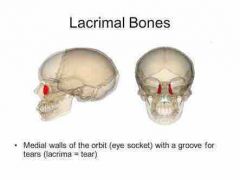
Lacrimal bones |
• contribute to the medial walls of the orbits. |
|
|
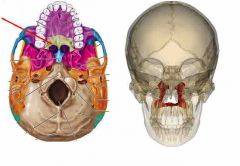
Palatine bones |
• form the posterior portion of the hard palate. |
|
|
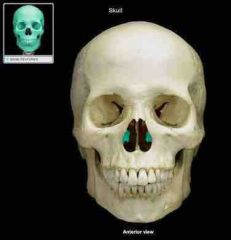
Inferior nasal concha |
• thin, curved bones in the nasal cavity • part of lateral walls of the cavity |
|
|
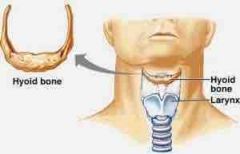
Hyoid bone |
• located in the anterior neck (inferior to the mandible) • shaped like a horn (overall) |
|
|
|
Hyoid bone 5 sub-components |
5 sub-component: - 1 body - 1 pair of lesser horns - 1 pair of greater horns • does not articulate directly with any other bone • attach by ligaments to the styloid processes of the temporal bones |
|
|
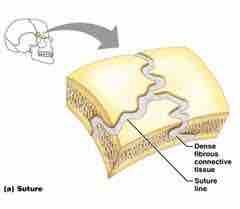
Suture Joints |
- structure: edges of bones overlap/interlock & are connected by short CT fibers - movement: synarthroses (immovable) - found only b/w bones of the skull |
|
|
|
:) |
:) |
|
|
|
Classification of joints |
• STRUCTURAL classification based on type of tissue that holds joint together:
- fibrous - cartilaginous - synovial |
|
|
|
Functional classification |
Based on amount of movement possible at a joint: - synarthroses - amphiarathroses - diarthroses |
|
|
|
6 types of synovial joints |
• glinding joint • condyloid joint • saddle joint • hinge joint • ball and socket joint • pivot joint |
|
|
|
Axial Skeleton |
Consists of:
• skull (cranial bones and facial bones) • hyoid bone • auditory ossicles • vertebral column (spine/backbone) • sternum bone • ribs |
|
|
|
Appendicular skeleton |
Consists of:
• shoulder girdles (shoulder blade/scapulae, clavicle/ collar bone) • upper limb (arms, wrists and hands) • pelvic (hip) girdle, hip bone/ Coxal bone called ilium, ischium and pubis • lower limb - legs, ankles and feet |
|
|
|
Longest and strongest bone in the body |
Femur |
|
|
|
Diarthroses joints |
Freely movable. All diarthroses joints are synovial joint. Eg. Elbows, hips, knees, shoulders |
|
|
|
Movement of spine |
- C/S: flexion/extension, rotation and lateral flexion (occur to some degree together) - T/S: some rotation, limited flexion/extension and lateral flexion - L/S: flexion/extension, limited lateral flexion and rotation |
|
|
|
Ribs ( Typical vs. Atypical ribs) |
• 12 pairs of ribs -> attach posteriorly to thoracic vertebrae
Typical vs. Atypical ribs
- ribs are 3-10 are typical • shape: flat & bow • composed of a head, neck, shaft & tubercle • articulate w/cartilage -> allows for flexibility - ribs 1-2, 11-12 are atypical in size & shape |
|
|
|
Ribs (True vs False ribs) |
True vs False ribs
- ribs 1-7 are true ribs • attach directly to sternum via costal cartilage - ribs 8-12 are false ribs • do not attach directly to sternum
Floating ribs • ribs 11-12 are also floating ribs -> no anterior attachment |
|
|
|
Ribs: Costal Margins |
• composed of cartilage • formed by medial ends of ribs 7-10 • medial ends of the ribs to join form the costal arches |
|
|
|
Radius Landmarks |
• head • neck • radial tuberosity • ulnar notch • styloid process • Lister's tubercle (radial tubercle, dorsal tubercle) |
|
|
|
Type of synovial joint: plane joints |
- flat articular surface - nonaxial - short slipping/glinding |
|

