![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
the eye
|
● two eyes necessary for depth perception
● photoreceptor cells (rods and cones) are stimulated by light. ● stimulant translated into a nerve impulse that travels along the optic nerve to the cerebrum. where an image is formed. |
|
|
|
yellow spot/fovea
|
clearest vision. consists of cones.
● cones are for colour ● rods are for black and white |
|
|
|
refraction of light by the cornea and lens
|
light rays enter the eye passing through the cornea , aqueous humour, pupil,lens,vitreous humour and fall on the retina .
cornea refracts light rays and the lens focuses light sharply onto the retina |
|
|
|
accommodation
|
near vision (less than 6m)
● ciliary muscles contract which pulls ciliary process and choroid towards the lens. ● tension on suspensory ligaments is released ● elastic lens becomes more convex. increasing its refracting power ● clear image formed on retina |
distant vision ( greater than 6m)
● ciliary muscles relax and ciliary process and choroid return to normal position. ● tension on suspensory ligaments increases. ● elastic lens becomes less convex. decreasing refracting power ● clear image formed on retina |
|
|
pupillary mechanism
|
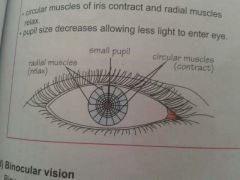
bright light
● circular muscles of iris contract and radial muslces relax ● pupil size decreases allowing less light to enter eye |
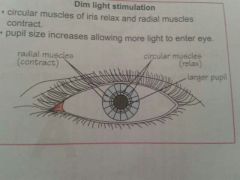
dim light
● circular muscles relax. radial contract. ● pupil size increases to allow more light to enter eye |
|
|
binocular vision/stereoscopic vision
|
each eye forms a different image of an object. both images from each eye are sent to the cerebrum, where a 3D image is formed. this enlarges the visual field and helps the person to estimate size distance and depth
|
|
|
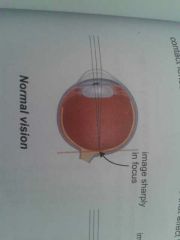
normal vision
|
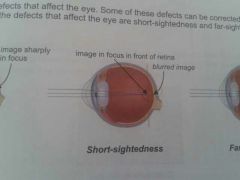
short sightedness / myopia
glasses with concave lens |
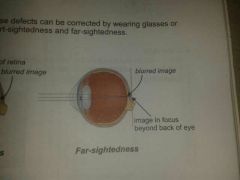
far-sightedness/ hyperopia
glasses with convex lens |
|
|
astigmatism
|
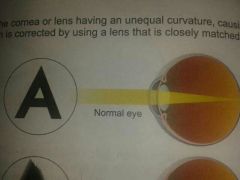
normal eye
|
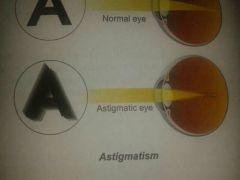
caused by unequal curvature og lens or cornea. only part of image is focused
|
|
|
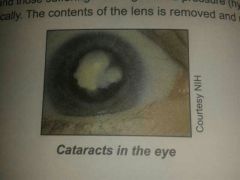
cataracts
|
results when the lens becomes cloudy and vision is impaired. mainly affects older people. diabetics and hypertension people
|
|

