![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
pathogen
|
an organism that invades body tissue, causing tissue damage and disease
|
|
|
virulence
|
ability to overcome host defenses
|
|
|
5 types of microorganism that can cause infectious diseases
|
bacteria, virus, fungi, protozoa, and helminths
|
|
|
5 places exogenous pathogens exist
|
air, food, water, body fluids
objects contaminated with from substances |
|
|
5 place endogenous normal flora exist
|
skin, nose, mouth, gastrointestinal tract, and urogenital tract
|
|
|
A normal flora skin bacteria
|
Staphylococcus epidermitis
|
|
|
A normal flora intestinal bacteria
|
Escherichia coli
|
|
|
6 variables in chain of infection
|
-agent (organism),
-reservoir (route by which agent exists and multiplies), -portal of exit (route by which agent leaves the host), -mode of transmission -portal of entry (route by which agent enters new host) -host susceptibility (internal and external enviromental factors that increase or decrease the likelihood that host will develop disease) |
|
|
bats can carry...
|
rabies virus
|
|
|
mosquitoes can carry...
|
malaria protozoa
|
|
|
Soil/dirt can carry...
|
tetanus bacteria spores
|
|
|
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) attaches to what kind of cells?
|
T cells
|
|
|
What is a trigger for herpes simplex virus?
|
stress
|
|
|
exanthem
|
eruption or rash on skin
|
|
|
7 characteristics of rash
|
color
elevation pattern/shape size in cm location distribution drainage |
|
|
Rubeola (Measles) agent
|
RNA virus
|
|
|
Rubeola (Measles) incubation period
|
8-12 days from exposure to onset of symptoms
|
|
|
Rubeola (Measles) infectious period
|
ranges from 3-5 before the appearance of rash to 4 days after rash disappears
|
|
|
Rubeola (Measles) immunity
|
natural disease or live attenuated vaccine
|
|
|
Rubeola (Measles) season
|
late winter and spring
|
|
|
Rubeola (Measles) respiratory symptoms appear after average of how many days?
|
10 days
|
|
|
Rubeola (Measles) three C's
|
coryza (profuse runny nose)
cough conjunctivitis |
|
|
Rubeola (Measles) prodrome period symptoms
|
fever and three C's: coryza (profuse runny nose), cough, and conjunctivitis
|
|
|
Rubeola (Measles) prodrome period symptoms last how many days?
|
between 1-4 days
|
|
|
When do Koplik Spots appear in Rubeola (Measles)?
|
approximately 2 days before the appearance of rash
|
|
|
What do Koplik Spots look like?
|
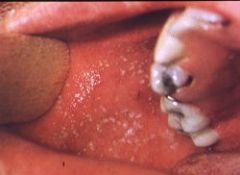
small, blue-white spots with a red base that cluster near the molars on the buccal mucosa
|
|
|
How long to Koplik Spots last?
|
3 days, after which they slough off
|
|
|
Rubeola (Measles) transmission
|
direct contact with droplets or less frequently airbone
|

