![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define matter |
Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. The various forms of matter are composed of one or more elements. |
|
|
What is the periodic table? |
Table of elements in order of Atomic number |
|
|
List the four most abundant elements in living things |
oxygen carbon hydrogen nitrogen |
|
|
Define compound and give an example. |
Compound is two or more elements in a fixed ratio CO2 is Carbon Dioxide |
|
|
Give an example of how the properties of a compound differ from the properties of the individual elements. |
Water is a liquid at room temperature but hydrogen and oxygen are both gases. |
|
|
Define Atom. |
Smallest piece or particle of an element |
|
|
List and describe the change of the three subatomic particles. |
Protons: Postive Neutrons: Neutral Electrons: negative |
|
|
Discuss the location of the subatomic particles. |
Neutrons and Protons are in the Nucleus and Electrons are found in the electron cloud |
|
|
What is the atomic number? |
The number of protons in each element also electrons Atomic mass is also found on the periodic table. |
|
|
Define isotopes and radioactive isotopes. |
Different forms of different numbers of neutrons |
|
|
List the three subatomic particles that make up an atom. |
Electrons neutrons protons |
|
|
Name the four most abundant elements of the human body. |
Oxygen carbon hydrogen nitrogen |
|
|
What part of an atom is involved in forming bonds? |
Electrons outer or valence electrons Valence electrons are involved in ionic and covelent bonds. |
|
|
Briefly describe ionic bonds. |
Ion -Atom that gives or receives electrons Ionic Bonds - formed when one atom transfers more electrons to another |
|
|
Define Ion. |
Atoms with either a positive or negative charge. |
|
|
Explain how an ionic bond forms. |
An atom that loses elections becomes positive ion and atom that gains electrons become a negative ion |
|
|
When are covalent bonds formed? |
Formed when electrons are shared by the atoms each electron pair forms a covalent bond. |
|
|
How many covalent bonds can an atom form? |
Same as number of electrons needed to all its outer shell |
|
|
Describe van der Waals forces. |
Slight attraction between molecules that can develop between a positively charged regions of nearby molecules |
|
|
Define chemical reaction. |
Molecules become rearranged is exisiting bonds break and new bonds are formed. |
|
|
Briefly discuss the reactants and products of a chemical reaction. |
Reactant are the two things added together products are the answer |
|
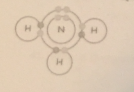
Does the compound pictured here show covalent bonding or ionic bonding? |
covalent |
|
|
What is the importance of valence electrons? |
To bond to other elements |
|
|
Exothermic |
release more energy than absorbed HOT |
|
|
Endothermic |
absorbs more than it releases COLD |
|
|
What is a polar molecule? |
A molecule that has both negative or positive charges. |
|
|
Describe the polarity of water. |
The water molecule has more negative charge around the oxygen atom and has more positive charge around the hydrogen atoms |
|
|
Describe hydrogen bonds. |
The hydrogen atoms attract to the negative oxygen atoms |
|
|
List the four unique properties of water. |
1. Cohesion and adhesion 2.Specific heat capacity. 3. Lower density of ice compared to liquid water 4. Water's ability to dissolve other substances. |
|
|
Compare and contrast cohesion and adhession |
Cohesion - the attraction between molecules of the same substance. Adhesion - the attraction between unlike molecules. |
|
|
Briefly describe why cohesion and adhesion are important in plants. |
Adhesion between water molecules and the walls of plant vessels draw water up out of the roots into stems and leaves. Cohesion between water molecules hold the column of water together as it rises. Capillary reaction |
|
|
Describe surface tension. |
Surface tension pulls water molecules tightly together at the forming an invisible boundary. |
|
|
Where are hydrogen bonds formed? |
Between water molecules. |
|
|
Define specific heat capacity. |
Amount of heat energy required to raise temp. of 1 gram of material b y 1 degree celsius |
|
|
Why is water's high specific heat capacity important? |
Allows bodies of water to absorb large amounts of heat with only small changes in temperature. |
|
|
How is water involved in body temperature regulation in humans? |
Sweating lowers body heat when water evaporates off the surface of the skin |
|
|
Compare the density of ice with that of water. |
Ice has less closely packed molecules than liquid that is how it floats. |
|
|
Why is it important that ice floats |
Living organisms have access to nutrients at the bottom of the body of water. Ice insulates the liquid water. |
|
|
Define solution |
Solution - uniform mixture of two or more substances Solvent - Does the dissolving for substance Solute - Dissolves itself |
|
|
What is an aqueous solution? |
A solution where water is the solvent |
|
|
Name the ions that are formed when water molecules break apart in solution. |
Hydrogen ions (H+) Hydroxide ions (OH-) |
|
|
Draw a pH scale (on the answer card) |

|
|
|
Define acid and list some examples. |
Acids have a pH lower than 7 Acids are compounds that form H+ ions in solution. Ex. Hydrochloric acid Sulfuric acid Cetric acid |
|
|
Define base and list some examples. |
Compounds that produce hydroxide ions Bases have a pH higher than 7 Sodium hydroxide Sodium bicarbonate or baking soda |
|
|
Define buffers and explain why are they important in living things. |
A weak acid or base that can react with strong acids or bases. To prevent sharp, sudden changes in pH Buffers maintain homeostasis Buffers maintain 7.35 - 7.45 in the bloodstream |
|
|
Describe unique property of water caused by its polarity and hydrogen bonding. |
Cohesion and adhesion Specific heat capacity Lower density of ice compared to liquid water Water ability to dissolve other substances. |
|
|
How do pH values differ between acids and bases? |
pH 7- Acids form H+ ions Base pH 7+ form hydroxide ions have pH 7+ |

