![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
480 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Forebrain
|
-largest and most highly developed
-consist of cerebrum and parts underneath it -source of intellectual activities |

|
|
|
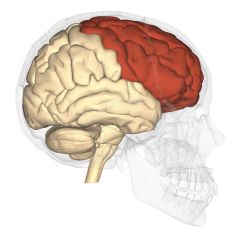
Frontal Lobes
|
-lies directly behind the forehead
--problem solving, motor function, memory, language, initiation, judgement, impulse control and sexual and social behavior |
|
|
|
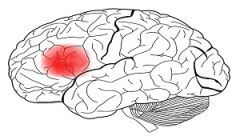
Broca's Area
|
-Located at the rearmost portion of the left frontal lobe
- turns thoughts into words |
|
|
|
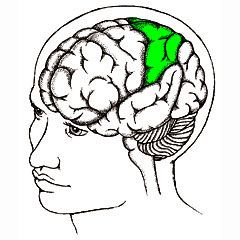
Parietal Lobe
|
-2 sections behing the frontal lobes
-receives information regarding senses -also involved with arithmetic and reading |
|
|
|
Occipital Lobes
|
-2 areas at the back of the brain
- processes information seen with the eyes and links that information with images stored in memory |

|
|
|
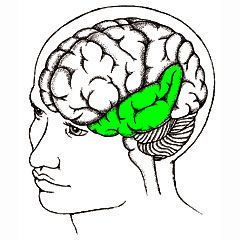
Temporal Lobes
|
-lie in front of the visual areas and nest under the parietal and frontal lobes
- too of the love receives information from the ears -underside of lobe is crucial for forming and retrieving memories -also integrates memories and sensation of taste, sound, sight, and touch |
|
|
|
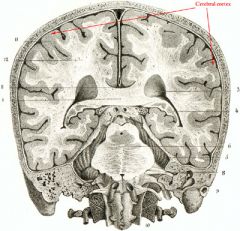
Cerebral Cortex
|
-thin layer of tissue covering the cerebrum and cerebellum
-- most of information processing occurs here - the "Gray Matter" |
|
|
|
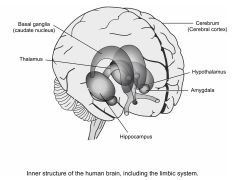
The Inner Brain
|
-Contains the hippocampus, hypothalamus, thalamus, and basal ganglia
- gateway between the cerebral hemispheres and the spinal cord -determine emotional state, and modify our perceptions and responses depending on that state - initiate movement without thinking about it |
|
|
|
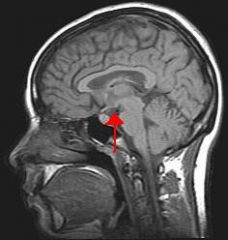
Hypothalamus
|
- Important emotional center controlling molecules that affect state of being
|
|
|
|
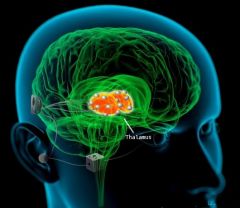
Thalamus
|
-Major clearinghouse for information going to and from the spinal cord and cerebrum
|
|
|
|
Hippocampus
|
-acts as memory index: sending memories out and retrieving them when necessary
|

|
|
|
Basal Ganglia
|
-clusters of nerve cells surrounding the thalamus
-- initiating and integrating movements |

|
|
|
Cell body
|
- Contains nucleus where most of the molecules needed for the neuron to survive and function are produced
|

|
|
|
Dendrite
|
-extend from cell body like roots of a tree
--receive messages from other cells |

|
|
|
Axon
|
-long slender projection of nerve cell
-conducts electrical impulses away from cell body |
|
|
|
Myelin Sheath
|
-provides insulation for the axon
-helps nerve signals travel faster and farther |
|
|
|
Synapse
|
-place where signal passes from neuron to another cell
|
|
|
|
Acetylcholine
|
-Neurotransmitter than carries nerve impulses across a synapse,from one neuron to another
|
|
|
|
Afferent
|
-carrying something, like a nerve impulse, toward the central point
|
|
|
|
Afferent
|
-carrying something, like a nerve impulse, toward the central point
|
|
|
|
Amygdala
|
-part of brain (limbic system) used in emotion
|
|
|
|
Afferent
|
-carrying something, like a nerve impulse, toward the central point
|
|
|
|
Amygdala
|
-part of brain (limbic system) used in emotion
|
|
|
|
Anterior
|
-towards the front
|
|
|
|
Anterior commissure
|
-Small fiber that connects left and right hemispheres
|
|
|
|
Arachnoid
|
-1 of 3 membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Arachnoid
|
-1 of 3 membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Association cortex
|
-Any part of the cortex in which information is processed, analyzed, or stored
|
|
|
|
Arachnoid
|
-1 of 3 membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Association cortex
|
-Any part of the cortex in which information is processed, analyzed, or stored
|
|
|
|
Astroglia/astrocyte
|
-type of glial cell that supports neurons
|
|
|
|
Arachnoid
|
-1 of 3 membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Association cortex
|
-Any part of the cortex in which information is processed, analyzed, or stored
|
|
|
|
Astroglia/astrocyte
|
-type of glial cell that supports neurons
|
|
|
|
Autonomic nervous system
|
-Controls our life support systems we arent consciously aware of
|
|
|
|
Arachnoid
|
-1 of 3 membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Association cortex
|
-Any part of the cortex in which information is processed, analyzed, or stored
|
|
|
|
Astroglia/astrocyte
|
-type of glial cell that supports neurons
|
|
|
|
Autonomic nervous system
|
-Controls our life support systems we arent consciously aware of
|
|
|
|
Axodendritic Synapse
|
-A synapse formed by contact with a presynaptic axon and a postsynaptic dendrite
|
|
|
|
Arachnoid
|
-1 of 3 membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Association cortex
|
-Any part of the cortex in which information is processed, analyzed, or stored
|
|
|
|
Astroglia/astrocyte
|
-type of glial cell that supports neurons
|
|
|
|
Autonomic nervous system
|
-Controls our life support systems we arent consciously aware of
|
|
|
|
Axodendritic Synapse
|
-A synapse formed by contact with a presynaptic axon and a postsynaptic dendrite
|
|
|
|
Blood-brain Barrier
|
-Protects brain from chemical intrusion from rest of body
|
|
|
|
Arachnoid
|
-1 of 3 membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Association cortex
|
-Any part of the cortex in which information is processed, analyzed, or stored
|
|
|
|
Astroglia/astrocyte
|
-type of glial cell that supports neurons
|
|
|
|
Autonomic nervous system
|
-Controls our life support systems we arent consciously aware of
|
|
|
|
Axodendritic Synapse
|
-A synapse formed by contact with a presynaptic axon and a postsynaptic dendrite
|
|
|
|
Blood-brain Barrier
|
-Protects brain from chemical intrusion from rest of body
|
|
|
|
Caude equina
|
-Bundle of nerve roots below the end of the spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Arachnoid
|
-1 of 3 membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Association cortex
|
-Any part of the cortex in which information is processed, analyzed, or stored
|
|
|
|
Astroglia/astrocyte
|
-type of glial cell that supports neurons
|
|
|
|
Autonomic nervous system
|
-Controls our life support systems we arent consciously aware of
|
|
|
|
Axodendritic Synapse
|
-A synapse formed by contact with a presynaptic axon and a postsynaptic dendrite
|
|
|
|
Blood-brain Barrier
|
-Protects brain from chemical intrusion from rest of body
|
|
|
|
Caude equina
|
-Bundle of nerve roots below the end of the spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Caudal
|
Towards the tail
|
|
|
|
Central sulcus
|
-a large groove in the brain that separates the frontal and parietal lobe
|
|
|
|
Arachnoid
|
-1 of 3 membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Association cortex
|
-Any part of the cortex in which information is processed, analyzed, or stored
|
|
|
|
Astroglia/astrocyte
|
-type of glial cell that supports neurons
|
|
|
|
Autonomic nervous system
|
-Controls our life support systems we arent consciously aware of
|
|
|
|
Axodendritic Synapse
|
-A synapse formed by contact with a presynaptic axon and a postsynaptic dendrite
|
|
|
|
Blood-brain Barrier
|
-Protects brain from chemical intrusion from rest of body
|
|
|
|
Caude equina
|
-Bundle of nerve roots below the end of the spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Caudal
|
Towards the tail
|
|
|
|
Central sulcus
|
-a large groove in the brain that separates the frontal and parietal lobe
|
|
|
|
Cerebral Aqueduct
|
-part of the ventricular system that connects the 3rd and 4th ventricles
|
|
|
|
Arachnoid
|
-1 of 3 membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Cerebrospinal fluid
|
-Clear watery liquid that surrounds and protects brain and spinal cord
-cushions brain and spine from jolts |
|
|
|
Association cortex
|
-Any part of the cortex in which information is processed, analyzed, or stored
|
|
|
|
Astroglia/astrocyte
|
-type of glial cell that supports neurons
|
|
|
|
Autonomic nervous system
|
-Controls our life support systems we arent consciously aware of
|
|
|
|
Axodendritic Synapse
|
-A synapse formed by contact with a presynaptic axon and a postsynaptic dendrite
|
|
|
|
Blood-brain Barrier
|
-Protects brain from chemical intrusion from rest of body
|
|
|
|
Caude equina
|
-Bundle of nerve roots below the end of the spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Caudal
|
Towards the tail
|
|
|
|
Central sulcus
|
-a large groove in the brain that separates the frontal and parietal lobe
|
|
|
|
Cerebral Aqueduct
|
-part of the ventricular system that connects the 3rd and 4th ventricles
|
|
|
|
Arachnoid
|
-1 of 3 membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Cerebrospinal fluid
|
-Clear watery liquid that surrounds and protects brain and spinal cord
-cushions brain and spine from jolts |
|
|
|
Choroid plexus
|
-Vascular structures within the ventricular system that produce cerebrospinal fluid
|
|
|
|
Association cortex
|
-Any part of the cortex in which information is processed, analyzed, or stored
|
|
|
|
Astroglia/astrocyte
|
-type of glial cell that supports neurons
|
|
|
|
Autonomic nervous system
|
-Controls our life support systems we arent consciously aware of
|
|
|
|
Axodendritic Synapse
|
-A synapse formed by contact with a presynaptic axon and a postsynaptic dendrite
|
|
|
|
Blood-brain Barrier
|
-Protects brain from chemical intrusion from rest of body
|
|
|
|
Caude equina
|
-Bundle of nerve roots below the end of the spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Caudal
|
Towards the tail
|
|
|
|
Central sulcus
|
-a large groove in the brain that separates the frontal and parietal lobe
|
|
|
|
Cerebral Aqueduct
|
-part of the ventricular system that connects the 3rd and 4th ventricles
|
|
|
|
Arachnoid
|
-1 of 3 membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Cerebrospinal fluid
|
-Clear watery liquid that surrounds and protects brain and spinal cord
-cushions brain and spine from jolts |
|
|
|
Choroid plexus
|
-Vascular structures within the ventricular system that produce cerebrospinal fluid
|
|
|
|
Cranial nerves
|
-12 pairs of nerves that carry information to and from sense organs
|
|
|
|
Association cortex
|
-Any part of the cortex in which information is processed, analyzed, or stored
|
|
|
|
Astroglia/astrocyte
|
-type of glial cell that supports neurons
|
|
|
|
Autonomic nervous system
|
-Controls our life support systems we arent consciously aware of
|
|
|
|
Axodendritic Synapse
|
-A synapse formed by contact with a presynaptic axon and a postsynaptic dendrite
|
|
|
|
Blood-brain Barrier
|
-Protects brain from chemical intrusion from rest of body
|
|
|
|
Caude equina
|
-Bundle of nerve roots below the end of the spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Caudal
|
Towards the tail
|
|
|
|
Central sulcus
|
-a large groove in the brain that separates the frontal and parietal lobe
|
|
|
|
Cerebral Aqueduct
|
-part of the ventricular system that connects the 3rd and 4th ventricles
|
|
|
|
Arachnoid
|
-1 of 3 membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Cerebrospinal fluid
|
-Clear watery liquid that surrounds and protects brain and spinal cord
-cushions brain and spine from jolts |
|
|
|
Choroid plexus
|
-Vascular structures within the ventricular system that produce cerebrospinal fluid
|
|
|
|
Cranial nerves
|
-12 pairs of nerves that carry information to and from sense organs
|
|
|
|
Dorsal
|
-back or upper surface
|
|
|
|
Association cortex
|
-Any part of the cortex in which information is processed, analyzed, or stored
|
|
|
|
Astroglia/astrocyte
|
-type of glial cell that supports neurons
|
|
|
|
Autonomic nervous system
|
-Controls our life support systems we arent consciously aware of
|
|
|
|
Axodendritic Synapse
|
-A synapse formed by contact with a presynaptic axon and a postsynaptic dendrite
|
|
|
|
Blood-brain Barrier
|
-Protects brain from chemical intrusion from rest of body
|
|
|
|
Caude equina
|
-Bundle of nerve roots below the end of the spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Caudal
|
Towards the tail
|
|
|
|
Central sulcus
|
-a large groove in the brain that separates the frontal and parietal lobe
|
|
|
|
Cerebral Aqueduct
|
-part of the ventricular system that connects the 3rd and 4th ventricles
|
|
|
|
Dorsal root
|
-Bundle of nerve fibers that bring information to spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Dorsal root
|
-Bundle of nerve fibers that bring information to spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Dura mater
|
-Tough, translucent membrane that protects brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Dorsal root
|
-Bundle of nerve fibers that bring information to spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Dura mater
|
-Tough, translucent membrane that protects brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Efferent
|
-carries something away from the central part
|
|
|
|
Dorsal root
|
-Bundle of nerve fibers that bring information to spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Dura mater
|
-Tough, translucent membrane that protects brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Efferent
|
-carries something away from the central part
|
|
|
|
Electroencephalogram
|
-EEG
-graphical record of electrical activity of the brain |
|
|
|
Dorsal root
|
-Bundle of nerve fibers that bring information to spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Dura mater
|
-Tough, translucent membrane that protects brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Efferent
|
-carries something away from the central part
|
|
|
|
Electroencephalogram
|
-EEG
-graphical record of electrical activity of the brain |
|
|
|
Eloquent Brain
|
-Part of the brain that controls the senses, speech, and motor function
|
|
|
|
Endocrine gland
|
-Ductless glands that secrete endocrine hormones
-ex:pituitary and thyroid gland |
|
|
|
Endocrine gland
|
-Ductless glands that secrete endocrine hormones
-ex:pituitary and thyroid gland |
|
|
|
Fornix
|
-pathway that connects hippocampus and mammillary bodies
|
|
|
|
Ganglion
|
-a group of neuron bodies that aren't in brain or spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Ganglion
|
-a group of neuron bodies that aren't in brain or spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Glial cells
|
-Nerve cells that form a supporting network for neurons in the brain
|
|
|
|
Ganglion
|
-a group of neuron bodies that aren't in brain or spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Glial cells
|
-Nerve cells that form a supporting network for neurons in the brain
|
|
|
|
Gyrus
|
-High areas of the brain, separated by fissures
|
|
|
|
Inferior colliculus
|
-a section in the midbrain used for hearing
|
|
|
|
Ganglion
|
-a group of neuron bodies that aren't in brain or spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Glial cells
|
-Nerve cells that form a supporting network for neurons in the brain
|
|
|
|
Gyrus
|
-High areas of the brain, separated by fissures
|
|
|
|
Inferior colliculus
|
-a section in the midbrain used for hearing
|
|
|
|
Lateral
|
To the side
|
|
|
|
Ganglion
|
-a group of neuron bodies that aren't in brain or spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Glial cells
|
-Nerve cells that form a supporting network for neurons in the brain
|
|
|
|
Gyrus
|
-High areas of the brain, separated by fissures
|
|
|
|
Inferior colliculus
|
-a section in the midbrain used for hearing
|
|
|
|
Lateral
|
To the side
|
|
|
|
Limbic system
|
-interconnected areas of the brain that are used in emotion
|
|
|
|
Ganglion
|
-a group of neuron bodies that aren't in brain or spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Glial cells
|
-Nerve cells that form a supporting network for neurons in the brain
|
|
|
|
Gyrus
|
-High areas of the brain, separated by fissures
|
|
|
|
Inferior colliculus
|
-a section in the midbrain used for hearing
|
|
|
|
Lateral
|
To the side
|
|
|
|
Limbic system
|
-interconnected areas of the brain that are used in emotion
|
|
|
|
Medulla oblongata
|
-lowest section of brain stem
-controls automatic functions |
|
|
|
Ganglion
|
-a group of neuron bodies that aren't in brain or spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Glial cells
|
-Nerve cells that form a supporting network for neurons in the brain
|
|
|
|
Gyrus
|
-High areas of the brain, separated by fissures
|
|
|
|
Inferior colliculus
|
-a section in the midbrain used for hearing
|
|
|
|
Lateral
|
To the side
|
|
|
|
Limbic system
|
-interconnected areas of the brain that are used in emotion
|
|
|
|
Medulla oblongata
|
-lowest section of brain stem
-controls automatic functions |
|
|
|
Meninges
|
-A series of three protective membranes that cover brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Ganglion
|
-a group of neuron bodies that aren't in brain or spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Glial cells
|
-Nerve cells that form a supporting network for neurons in the brain
|
|
|
|
Gyrus
|
-High areas of the brain, separated by fissures
|
|
|
|
Inferior colliculus
|
-a section in the midbrain used for hearing
|
|
|
|
Lateral
|
To the side
|
|
|
|
Limbic system
|
-interconnected areas of the brain that are used in emotion
|
|
|
|
Medulla oblongata
|
-lowest section of brain stem
-controls automatic functions |
|
|
|
Meninges
|
-A series of three protective membranes that cover brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Motor Cortex
|
-Part of both frontal lobes that control voluntary muscle movements
|
|
|
|
Ganglion
|
-a group of neuron bodies that aren't in brain or spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Glial cells
|
-Nerve cells that form a supporting network for neurons in the brain
|
|
|
|
Gyrus
|
-High areas of the brain, separated by fissures
|
|
|
|
Inferior colliculus
|
-a section in the midbrain used for hearing
|
|
|
|
Lateral
|
To the side
|
|
|
|
Limbic system
|
-interconnected areas of the brain that are used in emotion
|
|
|
|
Medulla oblongata
|
-lowest section of brain stem
-controls automatic functions |
|
|
|
Meninges
|
-A series of three protective membranes that cover brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Motor Cortex
|
-Part of both frontal lobes that control voluntary muscle movements
|
|
|
|
Motoneurons
|
-Neurons responsible for movement
-cell body in brain or spinal cord and axons are located in muscle fibers |
|
|
|
Ganglion
|
-a group of neuron bodies that aren't in brain or spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Neuroglia
|
-Connecting or supportive tissue of nervous system
|
|
|
|
Glial cells
|
-Nerve cells that form a supporting network for neurons in the brain
|
|
|
|
Gyrus
|
-High areas of the brain, separated by fissures
|
|
|
|
Inferior colliculus
|
-a section in the midbrain used for hearing
|
|
|
|
Lateral
|
To the side
|
|
|
|
Limbic system
|
-interconnected areas of the brain that are used in emotion
|
|
|
|
Medulla oblongata
|
-lowest section of brain stem
-controls automatic functions |
|
|
|
Meninges
|
-A series of three protective membranes that cover brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Motor Cortex
|
-Part of both frontal lobes that control voluntary muscle movements
|
|
|
|
Motoneurons
|
-Neurons responsible for movement
-cell body in brain or spinal cord and axons are located in muscle fibers |
|
|
|
Ganglion
|
-a group of neuron bodies that aren't in brain or spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Neuroglia
|
-Connecting or supportive tissue of nervous system
|
|
|
|
Node of Ranvier
|
-One of many gaps in myelin sheath
-where the action potential occurs during saltatory conduction along the axon |
|
|
|
Glial cells
|
-Nerve cells that form a supporting network for neurons in the brain
|
|
|
|
Gyrus
|
-High areas of the brain, separated by fissures
|
|
|
|
Inferior colliculus
|
-a section in the midbrain used for hearing
|
|
|
|
Lateral
|
To the side
|
|
|
|
Limbic system
|
-interconnected areas of the brain that are used in emotion
|
|
|
|
Medulla oblongata
|
-lowest section of brain stem
-controls automatic functions |
|
|
|
Meninges
|
-A series of three protective membranes that cover brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Motor Cortex
|
-Part of both frontal lobes that control voluntary muscle movements
|
|
|
|
Motoneurons
|
-Neurons responsible for movement
-cell body in brain or spinal cord and axons are located in muscle fibers |
|
|
|
Ganglion
|
-a group of neuron bodies that aren't in brain or spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Neuroglia
|
-Connecting or supportive tissue of nervous system
|
|
|
|
Node of Ranvier
|
-One of many gaps in myelin sheath
-where the action potential occurs during saltatory conduction along the axon |
|
|
|
Optic chiasm
|
-controls vision and the optic nerve
--area in front of brain where optic nerves cross one another |
|
|
|
Glial cells
|
-Nerve cells that form a supporting network for neurons in the brain
|
|
|
|
Gyrus
|
-High areas of the brain, separated by fissures
|
|
|
|
Inferior colliculus
|
-a section in the midbrain used for hearing
|
|
|
|
Lateral
|
To the side
|
|
|
|
Limbic system
|
-interconnected areas of the brain that are used in emotion
|
|
|
|
Medulla oblongata
|
-lowest section of brain stem
-controls automatic functions |
|
|
|
Meninges
|
-A series of three protective membranes that cover brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Motor Cortex
|
-Part of both frontal lobes that control voluntary muscle movements
|
|
|
|
Motoneurons
|
-Neurons responsible for movement
-cell body in brain or spinal cord and axons are located in muscle fibers |
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Pons
|
-part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum
-where the 5-8 cranial nerves originate |
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Pons
|
-part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum
-where the 5-8 cranial nerves originate |
|
|
|
Posterior
|
Towards the back
|
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Pons
|
-part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum
-where the 5-8 cranial nerves originate |
|
|
|
Posterior
|
Towards the back
|
|
|
|
Posterior fossa
|
-part of skull that contains brain stem and cerebellum
|
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Pons
|
-part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum
-where the 5-8 cranial nerves originate |
|
|
|
Posterior
|
Towards the back
|
|
|
|
Posterior fossa
|
-part of skull that contains brain stem and cerebellum
|
|
|
|
Proprioception
|
-response to internal stimuli
|
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Pons
|
-part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum
-where the 5-8 cranial nerves originate |
|
|
|
Posterior
|
Towards the back
|
|
|
|
Posterior fossa
|
-part of skull that contains brain stem and cerebellum
|
|
|
|
Proprioception
|
-response to internal stimuli
|
|
|
|
Pseudounipolar cells
|
-type of neuron that has 2 axons, one is towards spinal cord the other towards Skokie muscle
|
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Pons
|
-part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum
-where the 5-8 cranial nerves originate |
|
|
|
Posterior
|
Towards the back
|
|
|
|
Posterior fossa
|
-part of skull that contains brain stem and cerebellum
|
|
|
|
Proprioception
|
-response to internal stimuli
|
|
|
|
Pseudounipolar cells
|
-type of neuron that has 2 axons, one is towards spinal cord the other towards Skokie muscle
|
|
|
|
Reticular Formation
|
-Network of nerve cells in the brain stem that are involved in maintains sleep or wakefulness
|
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Pons
|
-part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum
-where the 5-8 cranial nerves originate |
|
|
|
Posterior
|
Towards the back
|
|
|
|
Posterior fossa
|
-part of skull that contains brain stem and cerebellum
|
|
|
|
Proprioception
|
-response to internal stimuli
|
|
|
|
Pseudounipolar cells
|
-type of neuron that has 2 axons, one is towards spinal cord the other towards Skokie muscle
|
|
|
|
Reticular Formation
|
-Network of nerve cells in the brain stem that are involved in maintains sleep or wakefulness
|
|
|
|
Schwanns Cells
|
-Cells that produce myelin
|
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Sensory cortex
|
-Any brain part that receives messages from a sense organ
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Pons
|
-part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum
-where the 5-8 cranial nerves originate |
|
|
|
Posterior
|
Towards the back
|
|
|
|
Posterior fossa
|
-part of skull that contains brain stem and cerebellum
|
|
|
|
Proprioception
|
-response to internal stimuli
|
|
|
|
Pseudounipolar cells
|
-type of neuron that has 2 axons, one is towards spinal cord the other towards Skokie muscle
|
|
|
|
Reticular Formation
|
-Network of nerve cells in the brain stem that are involved in maintains sleep or wakefulness
|
|
|
|
Schwanns Cells
|
-Cells that produce myelin
|
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Sensory cortex
|
-Any brain part that receives messages from a sense organ
|
|
|
|
Sensory neuron
|
-Afferent nerve cell that carries sensory information to the CNS
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Pons
|
-part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum
-where the 5-8 cranial nerves originate |
|
|
|
Posterior
|
Towards the back
|
|
|
|
Posterior fossa
|
-part of skull that contains brain stem and cerebellum
|
|
|
|
Proprioception
|
-response to internal stimuli
|
|
|
|
Pseudounipolar cells
|
-type of neuron that has 2 axons, one is towards spinal cord the other towards Skokie muscle
|
|
|
|
Reticular Formation
|
-Network of nerve cells in the brain stem that are involved in maintains sleep or wakefulness
|
|
|
|
Schwanns Cells
|
-Cells that produce myelin
|
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Sensory cortex
|
-Any brain part that receives messages from a sense organ
|
|
|
|
Sensory neuron
|
-Afferent nerve cell that carries sensory information to the CNS
|
|
|
|
Somatosensory cprtex
|
-Area of the sensory cortex in the parietal lobes that receive messages of touch, temp, and certain other bodily sensations
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Pons
|
-part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum
-where the 5-8 cranial nerves originate |
|
|
|
Posterior
|
Towards the back
|
|
|
|
Posterior fossa
|
-part of skull that contains brain stem and cerebellum
|
|
|
|
Proprioception
|
-response to internal stimuli
|
|
|
|
Pseudounipolar cells
|
-type of neuron that has 2 axons, one is towards spinal cord the other towards Skokie muscle
|
|
|
|
Reticular Formation
|
-Network of nerve cells in the brain stem that are involved in maintains sleep or wakefulness
|
|
|
|
Schwanns Cells
|
-Cells that produce myelin
|
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Sensory cortex
|
-Any brain part that receives messages from a sense organ
|
|
|
|
Sensory neuron
|
-Afferent nerve cell that carries sensory information to the CNS
|
|
|
|
Somatosensory cprtex
|
-Area of the sensory cortex in the parietal lobes that receive messages of touch, temp, and certain other bodily sensations
|
|
|
|
Stereognosis
|
-the appreciation of form through touch
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Pons
|
-part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum
-where the 5-8 cranial nerves originate |
|
|
|
Posterior
|
Towards the back
|
|
|
|
Posterior fossa
|
-part of skull that contains brain stem and cerebellum
|
|
|
|
Proprioception
|
-response to internal stimuli
|
|
|
|
Pseudounipolar cells
|
-type of neuron that has 2 axons, one is towards spinal cord the other towards Skokie muscle
|
|
|
|
Reticular Formation
|
-Network of nerve cells in the brain stem that are involved in maintains sleep or wakefulness
|
|
|
|
Schwanns Cells
|
-Cells that produce myelin
|
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Sensory cortex
|
-Any brain part that receives messages from a sense organ
|
|
|
|
Sensory neuron
|
-Afferent nerve cell that carries sensory information to the CNS
|
|
|
|
Somatosensory cprtex
|
-Area of the sensory cortex in the parietal lobes that receive messages of touch, temp, and certain other bodily sensations
|
|
|
|
Stereognosis
|
-the appreciation of form through touch
|
|
|
|
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
|
-Area of hypothalamus that controls circadian rhythms and reproductive cycles
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Pons
|
-part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum
-where the 5-8 cranial nerves originate |
|
|
|
Posterior
|
Towards the back
|
|
|
|
Posterior fossa
|
-part of skull that contains brain stem and cerebellum
|
|
|
|
Proprioception
|
-response to internal stimuli
|
|
|
|
Pseudounipolar cells
|
-type of neuron that has 2 axons, one is towards spinal cord the other towards Skokie muscle
|
|
|
|
Reticular Formation
|
-Network of nerve cells in the brain stem that are involved in maintains sleep or wakefulness
|
|
|
|
Schwanns Cells
|
-Cells that produce myelin
|
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Sensory cortex
|
-Any brain part that receives messages from a sense organ
|
|
|
|
Sensory neuron
|
-Afferent nerve cell that carries sensory information to the CNS
|
|
|
|
Somatosensory cprtex
|
-Area of the sensory cortex in the parietal lobes that receive messages of touch, temp, and certain other bodily sensations
|
|
|
|
Stereognosis
|
-the appreciation of form through touch
|
|
|
|
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
|
-Area of hypothalamus that controls circadian rhythms and reproductive cycles
|
|
|
|
Tactile sensation
|
-sense of touch
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Pons
|
-part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum
-where the 5-8 cranial nerves originate |
|
|
|
Posterior
|
Towards the back
|
|
|
|
Posterior fossa
|
-part of skull that contains brain stem and cerebellum
|
|
|
|
Proprioception
|
-response to internal stimuli
|
|
|
|
Pseudounipolar cells
|
-type of neuron that has 2 axons, one is towards spinal cord the other towards Skokie muscle
|
|
|
|
Reticular Formation
|
-Network of nerve cells in the brain stem that are involved in maintains sleep or wakefulness
|
|
|
|
Schwanns Cells
|
-Cells that produce myelin
|
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Sensory cortex
|
-Any brain part that receives messages from a sense organ
|
|
|
|
Sensory neuron
|
-Afferent nerve cell that carries sensory information to the CNS
|
|
|
|
Somatosensory cprtex
|
-Area of the sensory cortex in the parietal lobes that receive messages of touch, temp, and certain other bodily sensations
|
|
|
|
Stereognosis
|
-the appreciation of form through touch
|
|
|
|
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
|
-Area of hypothalamus that controls circadian rhythms and reproductive cycles
|
|
|
|
Tactile sensation
|
-sense of touch
|
|
|
|
Tectum
|
-dorsal section of midbrain
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Pons
|
-part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum
-where the 5-8 cranial nerves originate |
|
|
|
Posterior
|
Towards the back
|
|
|
|
Posterior fossa
|
-part of skull that contains brain stem and cerebellum
|
|
|
|
Proprioception
|
-response to internal stimuli
|
|
|
|
Pseudounipolar cells
|
-type of neuron that has 2 axons, one is towards spinal cord the other towards Skokie muscle
|
|
|
|
Reticular Formation
|
-Network of nerve cells in the brain stem that are involved in maintains sleep or wakefulness
|
|
|
|
Schwanns Cells
|
-Cells that produce myelin
|
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Sensory cortex
|
-Any brain part that receives messages from a sense organ
|
|
|
|
Sensory neuron
|
-Afferent nerve cell that carries sensory information to the CNS
|
|
|
|
Somatosensory cprtex
|
-Area of the sensory cortex in the parietal lobes that receive messages of touch, temp, and certain other bodily sensations
|
|
|
|
Stereognosis
|
-the appreciation of form through touch
|
|
|
|
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
|
-Area of hypothalamus that controls circadian rhythms and reproductive cycles
|
|
|
|
Tactile sensation
|
-sense of touch
|
|
|
|
Tectum
|
-dorsal section of midbrain
|
|
|
|
Tegmentun
|
-ventral(bottom) part of midbrain
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Pons
|
-part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum
-where the 5-8 cranial nerves originate |
|
|
|
Posterior
|
Towards the back
|
|
|
|
Posterior fossa
|
-part of skull that contains brain stem and cerebellum
|
|
|
|
Proprioception
|
-response to internal stimuli
|
|
|
|
Pseudounipolar cells
|
-type of neuron that has 2 axons, one is towards spinal cord the other towards Skokie muscle
|
|
|
|
Reticular Formation
|
-Network of nerve cells in the brain stem that are involved in maintains sleep or wakefulness
|
|
|
|
Schwanns Cells
|
-Cells that produce myelin
|
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Sensory cortex
|
-Any brain part that receives messages from a sense organ
|
|
|
|
Sensory neuron
|
-Afferent nerve cell that carries sensory information to the CNS
|
|
|
|
Somatosensory cprtex
|
-Area of the sensory cortex in the parietal lobes that receive messages of touch, temp, and certain other bodily sensations
|
|
|
|
Stereognosis
|
-the appreciation of form through touch
|
|
|
|
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
|
-Area of hypothalamus that controls circadian rhythms and reproductive cycles
|
|
|
|
Tactile sensation
|
-sense of touch
|
|
|
|
Tectum
|
-dorsal section of midbrain
|
|
|
|
Tegmentun
|
-ventral(bottom) part of midbrain
|
|
|
|
Ventral
|
-lower or underneath
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Pons
|
-part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum
-where the 5-8 cranial nerves originate |
|
|
|
Posterior
|
Towards the back
|
|
|
|
Posterior fossa
|
-part of skull that contains brain stem and cerebellum
|
|
|
|
Proprioception
|
-response to internal stimuli
|
|
|
|
Pseudounipolar cells
|
-type of neuron that has 2 axons, one is towards spinal cord the other towards Skokie muscle
|
|
|
|
Reticular Formation
|
-Network of nerve cells in the brain stem that are involved in maintains sleep or wakefulness
|
|
|
|
Schwanns Cells
|
-Cells that produce myelin
|
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Sensory cortex
|
-Any brain part that receives messages from a sense organ
|
|
|
|
Sensory neuron
|
-Afferent nerve cell that carries sensory information to the CNS
|
|
|
|
Somatosensory cprtex
|
-Area of the sensory cortex in the parietal lobes that receive messages of touch, temp, and certain other bodily sensations
|
|
|
|
Stereognosis
|
-the appreciation of form through touch
|
|
|
|
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
|
-Area of hypothalamus that controls circadian rhythms and reproductive cycles
|
|
|
|
Tactile sensation
|
-sense of touch
|
|
|
|
Tectum
|
-dorsal section of midbrain
|
|
|
|
Tegmentun
|
-ventral(bottom) part of midbrain
|
|
|
|
Ventral
|
-lower or underneath
|
|
|
|
Ventricle
|
-4 snall hollow spaces in the brain filled with cerebrospinal gluid
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Pons
|
-part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum
-where the 5-8 cranial nerves originate |
|
|
|
Posterior
|
Towards the back
|
|
|
|
Posterior fossa
|
-part of skull that contains brain stem and cerebellum
|
|
|
|
Proprioception
|
-response to internal stimuli
|
|
|
|
Pseudounipolar cells
|
-type of neuron that has 2 axons, one is towards spinal cord the other towards Skokie muscle
|
|
|
|
Reticular Formation
|
-Network of nerve cells in the brain stem that are involved in maintains sleep or wakefulness
|
|
|
|
Schwanns Cells
|
-Cells that produce myelin
|
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Sensory cortex
|
-Any brain part that receives messages from a sense organ
|
|
|
|
Sensory neuron
|
-Afferent nerve cell that carries sensory information to the CNS
|
|
|
|
Somatosensory cprtex
|
-Area of the sensory cortex in the parietal lobes that receive messages of touch, temp, and certain other bodily sensations
|
|
|
|
Stereognosis
|
-the appreciation of form through touch
|
|
|
|
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
|
-Area of hypothalamus that controls circadian rhythms and reproductive cycles
|
|
|
|
Tactile sensation
|
-sense of touch
|
|
|
|
Tectum
|
-dorsal section of midbrain
|
|
|
|
Tegmentun
|
-ventral(bottom) part of midbrain
|
|
|
|
Ventral
|
-lower or underneath
|
|
|
|
Ventricle
|
-4 snall hollow spaces in the brain filled with cerebrospinal gluid
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Viscera
|
Organs of the body
|
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Pons
|
-part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum
-where the 5-8 cranial nerves originate |
|
|
|
Posterior
|
Towards the back
|
|
|
|
Posterior fossa
|
-part of skull that contains brain stem and cerebellum
|
|
|
|
Proprioception
|
-response to internal stimuli
|
|
|
|
Pseudounipolar cells
|
-type of neuron that has 2 axons, one is towards spinal cord the other towards Skokie muscle
|
|
|
|
Reticular Formation
|
-Network of nerve cells in the brain stem that are involved in maintains sleep or wakefulness
|
|
|
|
Schwanns Cells
|
-Cells that produce myelin
|
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
-part if nervous system that includes cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
Sensory cortex
|
-Any brain part that receives messages from a sense organ
|
|
|
|
Sensory neuron
|
-Afferent nerve cell that carries sensory information to the CNS
|
|
|
|
Somatosensory cprtex
|
-Area of the sensory cortex in the parietal lobes that receive messages of touch, temp, and certain other bodily sensations
|
|
|
|
Stereognosis
|
-the appreciation of form through touch
|
|
|
|
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
|
-Area of hypothalamus that controls circadian rhythms and reproductive cycles
|
|
|
|
Tactile sensation
|
-sense of touch
|
|
|
|
Tectum
|
-dorsal section of midbrain
|
|
|
|
Tegmentun
|
-ventral(bottom) part of midbrain
|
|
|
|
Ventral
|
-lower or underneath
|
|
|
|
Ventricle
|
-4 snall hollow spaces in the brain filled with cerebrospinal gluid
|
|
|
|
Pia
|
-innermost layer of the meninges
- |
|
|
|
Viscera
|
Organs of the body
|
|
|
|
Plexus
|
-network of nerves or veins
|
|
|
|
Pons
|
-part of the brainstem that joins the hemispheres of the cerebellum and connects the cerebrum with the cerebellum
-where the 5-8 cranial nerves originate |
|
|
|
Posterior
|
Towards the back
|
|
|
|
Posterior fossa
|
-part of skull that contains brain stem and cerebellum
|
|
|
|
Proprioception
|
-response to internal stimuli
|
|
|
|
Pseudounipolar cells
|
-type of neuron that has 2 axons, one is towards spinal cord the other towards Skokie muscle
|
|
|
|
Reticular Formation
|
-Network of nerve cells in the brain stem that are involved in maintains sleep or wakefulness
|
|
|
|
Schwanns Cells
|
-Cells that produce myelin
|
|

